Struggling to resolve memory problems on your Windows device? Then it's time to use the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool and resolve those issues. This tool will help you test the RAM (Random Access Memory) and troubleshoot all memory problems.
To begin, let's explore what RAM is for a bit. From there, we’ll check out how you can resolve Windows memory problems with the Memory Diagnostic tool.
What Is the RAM (Random Access Memory), and How Does It Work?
The RAM (Random Access Memory) is your PC’s working memory. The operating system and PC programs continually write data to the RAM and then read it back. For example, when you load a web page, the browser stores that page in the RAM while you read it.
However, if the RAM has issues, you might encounter several problems while trying to run software programs. This could lead to application crashes, data corruption, and other system issues.
If your PC’s RAM is faulty, the Memory Diagnostic tool could help you fix it.
What Is the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool, and How Do You Use It?
The Windows Memory Diagnostic tool is a reliable feature that helps you troubleshoot memory problems. You can use it to test the RAM and check if everything is working properly.
If Windows suspects that your device has memory problems, it will suggest that you run the Memory Diagnostic tool. However, there are instances where you might have to run this tool manually.
For example, if your PC keeps rebooting while you’re playing games, that could be a sign of hardware problems. In this instance, your device might not suggest that you should run the Memory Diagnostic tool.
In this case, you’d need to run the tool manually to check and troubleshoot memory issues.
Now, here’s how you can run the Memory Diagnostic tool:
- Press Win + S to open the Start Menu search bar.
- Type Windows Memory Diagnostic and select the Best match.
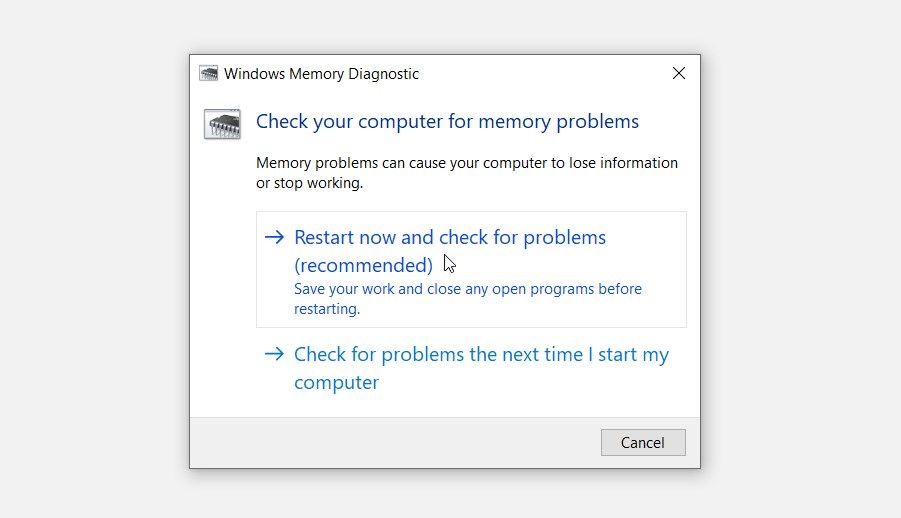
From there, you should see the Restart now and check for problems and the Check for problems the next time I start my computer options.
To proceed and troubleshoot memory problems right away, select the Restart now and check for problems on the Windows Memory Diagnostic screen.
You might be wondering why you have to restart your device when running this tool. It’s mainly because your RAM is used by lots of apps, and that might disrupt the entire troubleshooting process. So, restarting your device frees up your RAM so that the Memory Diagnostic tool will work effectively.
How to Run Windows Memory Tests
At this point, your device will restart so that the Memory Diagnostic tool could run some tests. By default, the tool will run a test called the Standard test, which might take around 10 minutes to complete.
From there, your device will restart normally. Now, you can check if your device still shows signs of memory problems.
If the issues persist, then you could consider running an Extended test on the tool. This could take too long, but it'll help get to the root of the issues that are causing memory problems.
Here’s how you can run the Extended test:
- Open the Memory Diagnostic tool as per the previous steps.
- Select the Restart now and check for problems option.
- Press F1 immediately when your device restarts. This should take you to the Advanced options screen.
You should see a Test Mix option on the Advanced options screen. Below this option, you’ll see the Basic, Standard, and Extended scan options. Now, use the arrow keys to select the Extended test option and then press F10 to apply these changes.
The Memory Diagnostic tool will run the Extended test for about 30 minutes. From there, your device should restart automatically.
How to Analyze the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool Results
Now, immediately after booting up your device, the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool should send a notification. The message will indicate whether the memory errors were detected or not.
Now, you should take a step further to understand the results from the Memory Diagnostic tool. In this case, we’ll show you how you can use the Event Viewer to analyze those results.
The Event Viewer is a built-in Windows tool that helps you check and analyze the processes that take place on your PC. In this case, this tool will help you understand the log results from the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool.
So, here’s how you can analyze Windows Memory Diagnostic tool results with the Event Viewer:
- Press Win + X to open the Quick Access Menu.
- Select Event Viewer from the menu items.
- Click the Windows Logs drop-down menu in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Select System from the options.
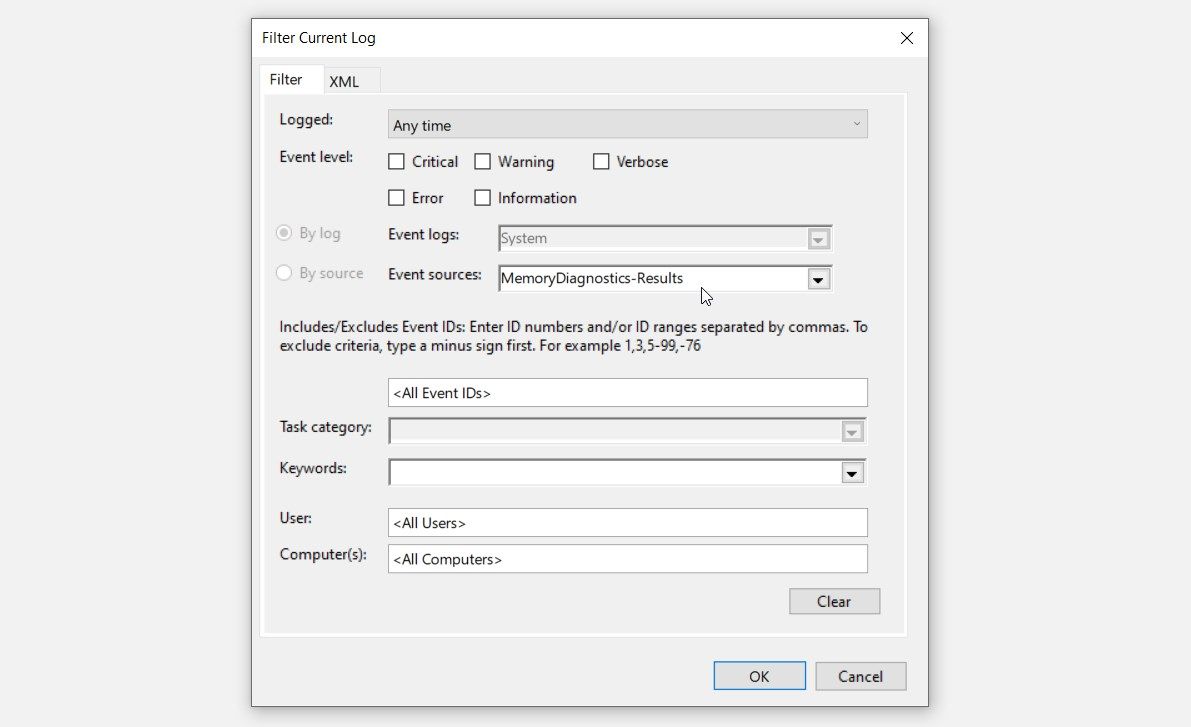
- Click the Filter Current Log option on the right-hand side pane.
- Next, click the Event sources drop-down menu and check the MemoryDiagnostics-Results box. Click OK to continue (this should filter your results based on Memory Diagnostics results.)
Now, check the log results in the middle pane of the Event Viewer. Each log result will give you information on what issue has been resolved, and what still needs your attention.
The results that have the Information tag will highlight the issues that the Memory Diagnostic tool has resolved. In this case, no further action is required.
Next, check the results with Warning and Error tags. These are the log results that show some of the issues that couldn’t be resolved.
To understand these results better, click on each log event data in the top part of the middle pane. From there, check the log details in the bottom part of the middle pane.
Once you understand the log results, you can then troubleshoot those issues using other relevant Windows diagnostic tools.
Tackle Windows Memory Problems Without a Hassle
If your Windows device crashes or freezes regularly, that could be a sign of memory problems. Fortunately, the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool can help you get rid of these issues.
Using this tool is fairly simple if you follow the tips we’ve covered. But if you find it hard to resolve Windows memory problems, then maybe it’s time to get a new, advanced RAM.