Windows lets you create multiple user accounts to let multiple users use a single computer. But what if you suspect someone to have accessed your PC or user account without your knowledge?
While physically monitoring your computer all the time is not feasible for most people, the built-in Windows log utility, Event Viewer, can reveal the recent activities on your computer, including login attempts. Here we show you how to audit failed and successful login attempts in Windows using Event Viewer and other methods.
How to Enable Logon Auditing via Group Policy Editor
You need to enable logon auditing in Group Policy Editor to be able to view login audit in Event Viewer. While this feature may be enabled by default on some computers, you can also enable logon auditing manually by following these steps.
Note that Group Policy Editor is only available on the Pro, Edu, and Enterprise edition of the Windows OS. If you are on the Home edition, follow our guide to enable gpedit in the Windows home edition.
Note that if you don't configure your Group Policy for Logon Auditing, you can only view the successful login attempts in Event Viewer.
Once you have the Group Policy Editor enabled, follow these steps to enable logon auditing:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type gpedit.msc and click OK to open the Group Policy Editor.
-
Next, navigate to the following location:
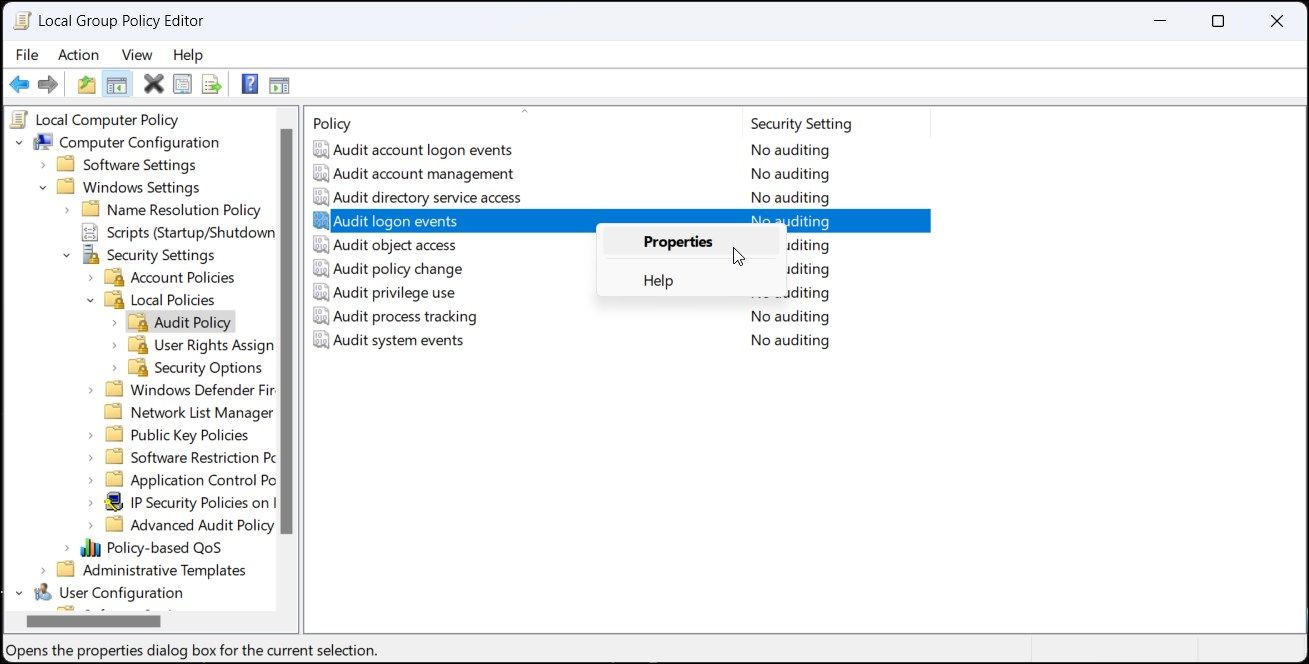
Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Audit Policy -
In the right pane, right-click on Audit logon events and select Properties.
-
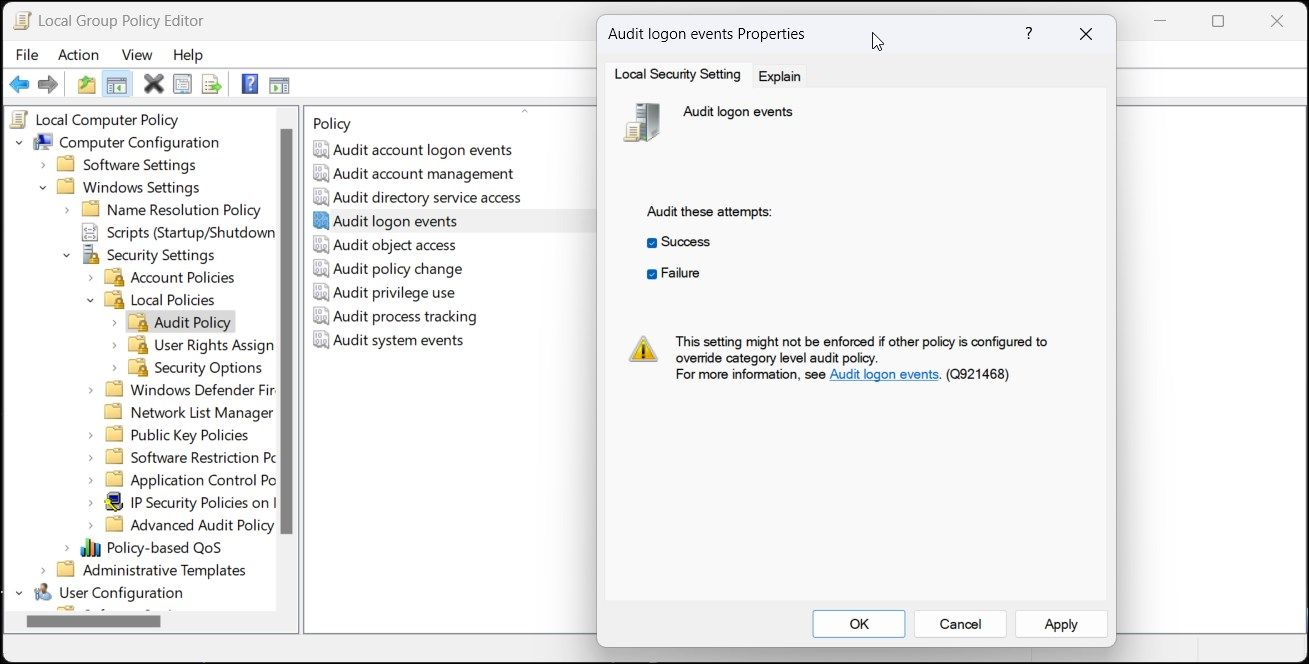
In the Properties dialog, select Success and Failure options under the Audit these attempts section.
- Click Apply and OK to save the changes.
Close Group Policy Editor and move to the next set of steps to view login attempts in Event Viewer.
How to View Failed and Successful Login Attempts in Event Viewer
The Event Viewer lets you view Windows logs for the application, security, system, and other events. While a useful application to troubleshoot system issues, you can use it to audit login events on your Windows PC.
Follow these steps to view failed and successful login attempts in Windows:
- Press the Win key and type event viewer. Alternatively, click on Search in the taskbar and type event viewer.
- Click on Event Viewer from the search result to open it.
-
In the left pane, expand the Windows Logs section.
- Next, select Security.
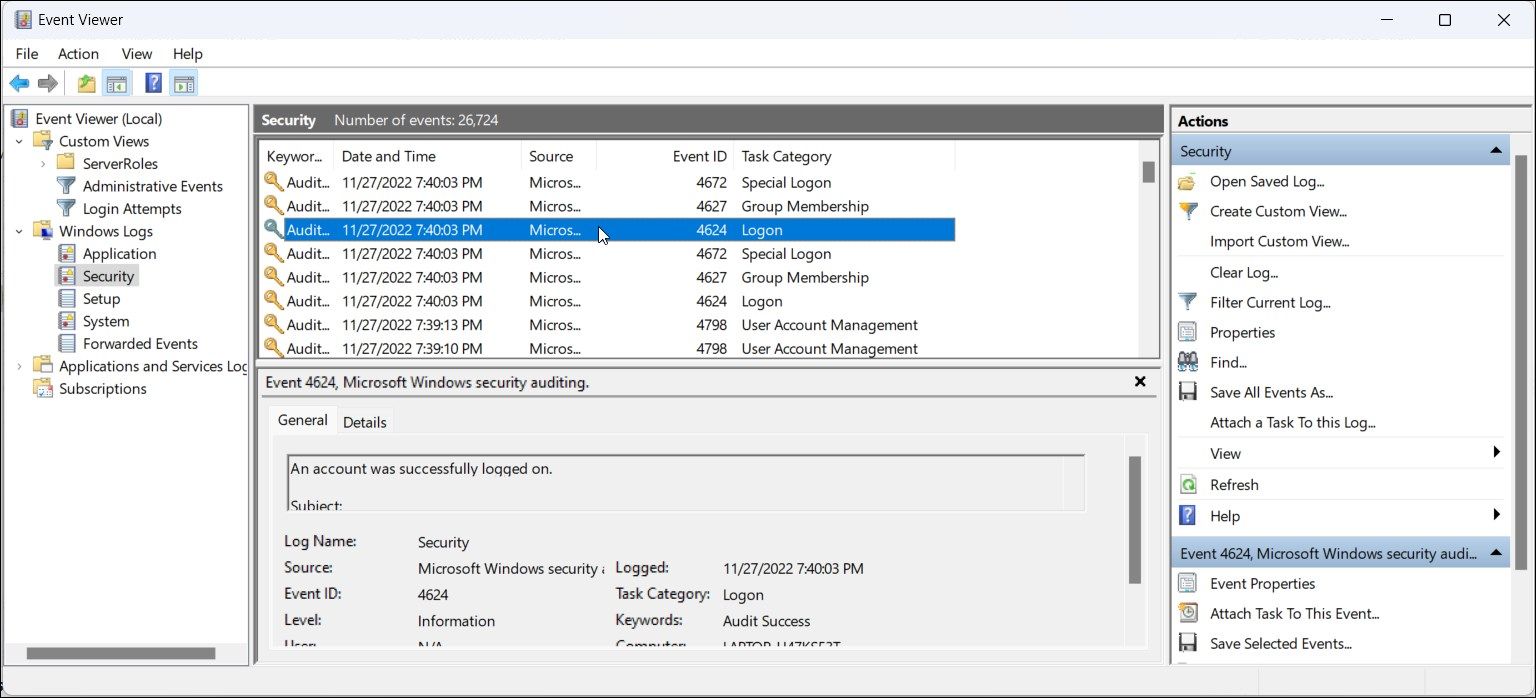
- In the right pane, locate the Event 4624 entry. It is a user logon event ID, and you may find multiple instances of this ID in the event log.
- To find failed login attempts, locate Event ID 2625 entries instead.
- Next, select the Event 4624 entry you want to view, and Event Viewer will display all the related information in the bottom section. Alternatively, right-click on the event entry and select Properties to view detailed information in a new window.
How to Decipher the Logon Entries in Event Viewer
While Event ID 4624 is associated with logon events, you will likely find multiple instances of this entry occurring every few minutes in the log. This is due to Event Viewer recording every logon event (whether from the local user account or system services such as Windows Security) with the same event ID (Event 4624).
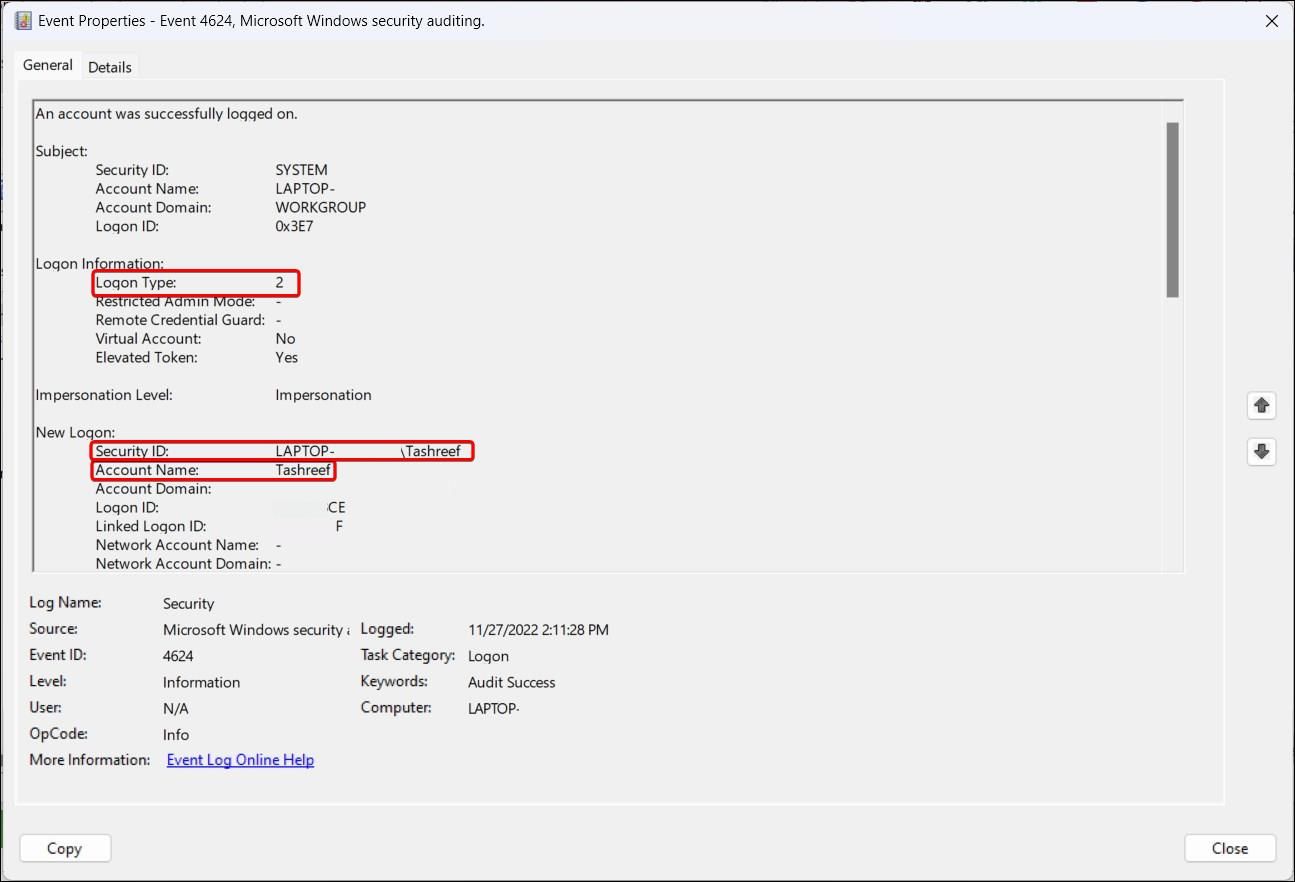
To identify the source of login, right-click on the event record and select Properties. In the General tab, scroll down and locate the Logon information section. Here, the Logon Type field indicates the kind of logon that occurred.
For example, Logon Type 5 indicates a service-based login, while Logon Type 2 indicates user-based login. Know more about the different logon types in the table below.
Next, scroll down to the New Logon section and locate the Security ID. This will show the user account that was affected by the logon.
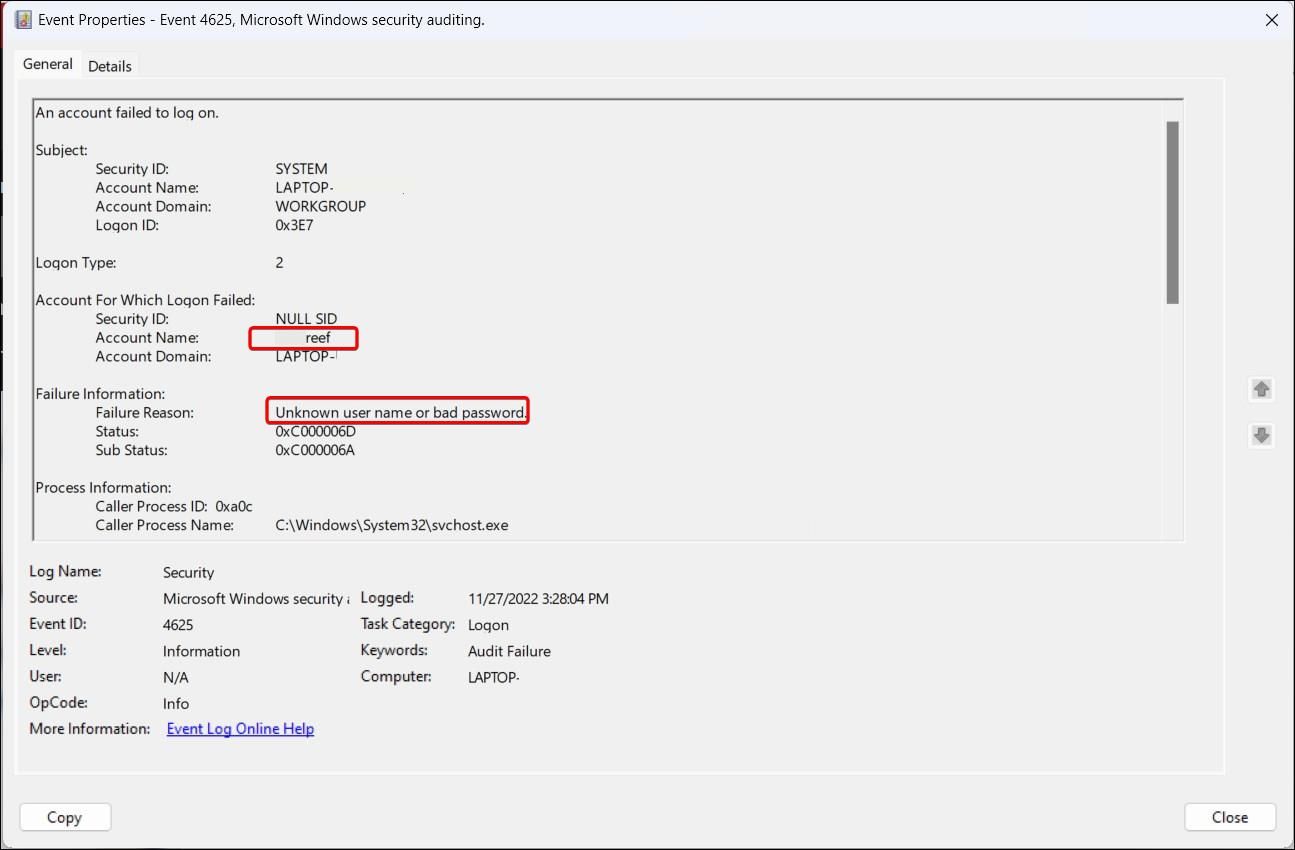
Similarly, for failed login attempts, review Event ID 4625. In the Properties dialog, you can find reasons for the failed login attempt and the affected user account. If you find multiple instances of unsuccessful attempts, consider learning how to limit the number of failed login attempts to protect your Windows PC.
Below is the list of all nine Logon Types for logon events that you may encounter reviewing login events in Event Viewer:
|
Logon Type |
Description |
|
Logon Type 2 |
A local user logged on to this computer. |
|
Logon Type 3 |
A user logged on to this computer from the network. |
|
Logon Type 4 |
Batch logon type without user intervention – Scheduled Tasks, etc. |
|
Logon Type 5 |
Logon by system service started by Service Control Manager – Most common type |
|
Logon Type 7 |
System unlocked by a local account user |
|
Logon Type 8 |
NetworkClearText - Logon attempted over the network where the password was sent as clear text. |
|
Logon Type 9 |
NewCredentials – triggered when a user uses the RunAs command with the /netonly option to start a program. |
|
Logon Type 10 |
RemoteInteractive – Generated when a computer is accessed via a remote access tool such as Remote Desktop Connection. |
|
Logon Type 11 |
CachedInteractive – When the user logged on to the computer via console using the cached credentials when the domain controller is not available. |
How to View the Last Logon History Using Command Prompt
You can use the Command Prompt to view the last login attempt. It is a handy way to find user-based login attempts without having to go through all the logon events in Event Viewer.
To view the login history of a specific user using Command Prompt:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type cmd. While holding the Ctrl + Shift key, click OK. This will open the Command Prompt as administrator.
-
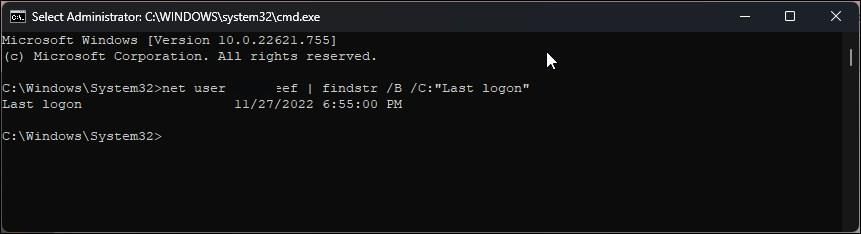
In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
net user administrator | findstr /B /C:"Last logon" - In the above command, replace "administrator" with the username to view their login history.
- The output will show the last login time and date for the specified user.
Viewing Failed and Successful Login Attempts in Windows
If you suspect someone to have logged in to your PC, the Event Viewer will likely catch and record the attempt. For this to work, you must enable the Logon Auditing policy in Group Policy Editor. You can also use Command Prompt to view a specific user's login history.
That said, anyone who knows their way around Event Viewer can easily clear the logs. So, if anything, beefing up your Windows computer security is the best way to prevent unauthorized access. You can begin by limiting the number of failed login attempts on your Windows PC.