The network adapter is a critical piece of hardware that connects your Windows computer to the internet via a wired or wireless connection. In order to achieve the maximum speeds offered by your Internet Service Provider, it is important to know what network speed your card is capable of.
Whether you want to upgrade your internet plan or diagnose your network for performance issues, there are several ways to determine the network adapter speed on Windows. Let’s go over all of them one by one.
1. How to Check the Network Adapter Connection Speed Using the Settings App
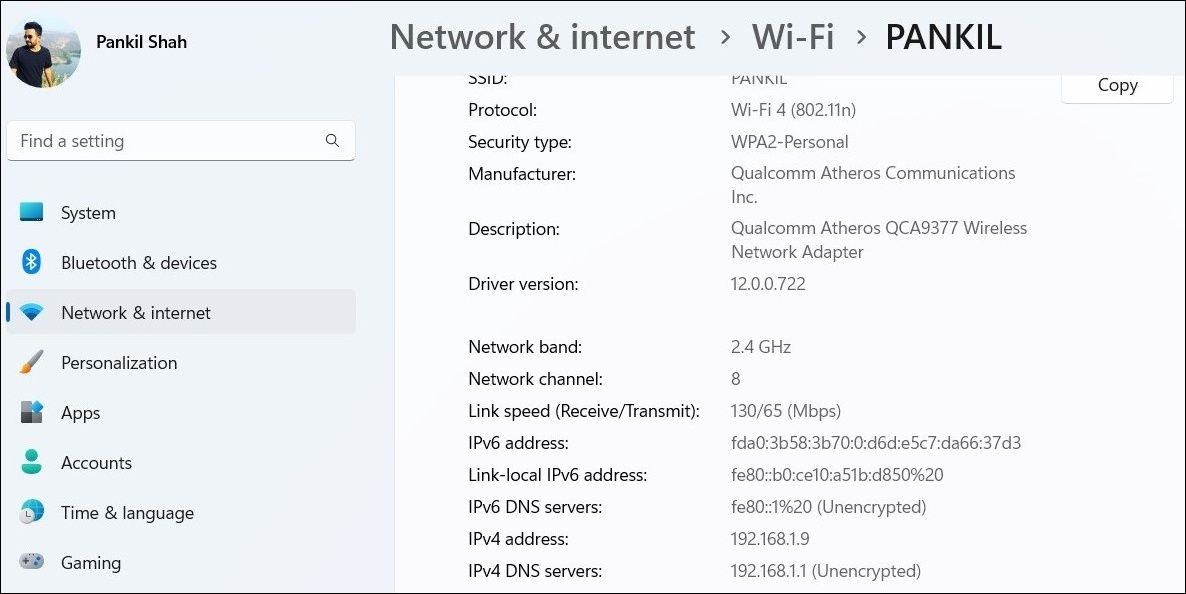
The quickest way to check the connection speed for a Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter is through the Windows Settings app. Aside from network speed, the Settings app also provides important information like network band, local IP address, MAC address, and more.
To check the network adapter speed via the Settings app:
- Press Win + I to open the Settings app.
- Select Network & internet from the left sidebar.
- Click on Properties at the top.
-
Scroll down to the Link speed (Receive/Transmit) field to check the connection speed.
2. How to Check the Network Adapter Connection Speed Using Control Panel
Although Microsoft is gradually moving a large number of features to the Settings app, many people still prefer to use the Control Panel to modify settings and troubleshoot issues. If you are one of them, here's how you can check the network adapter connection speed via Control Panel.
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog (see how to open Run for more ways).
- Type control in the box and press Enter.
- In the Control Panel window that opens, use the drop-down menu in the top right corner to change the view type to Small icons or Large icons.
- Go to Network and Sharing Center.
- Click the Change adapter settings link from the left pane.
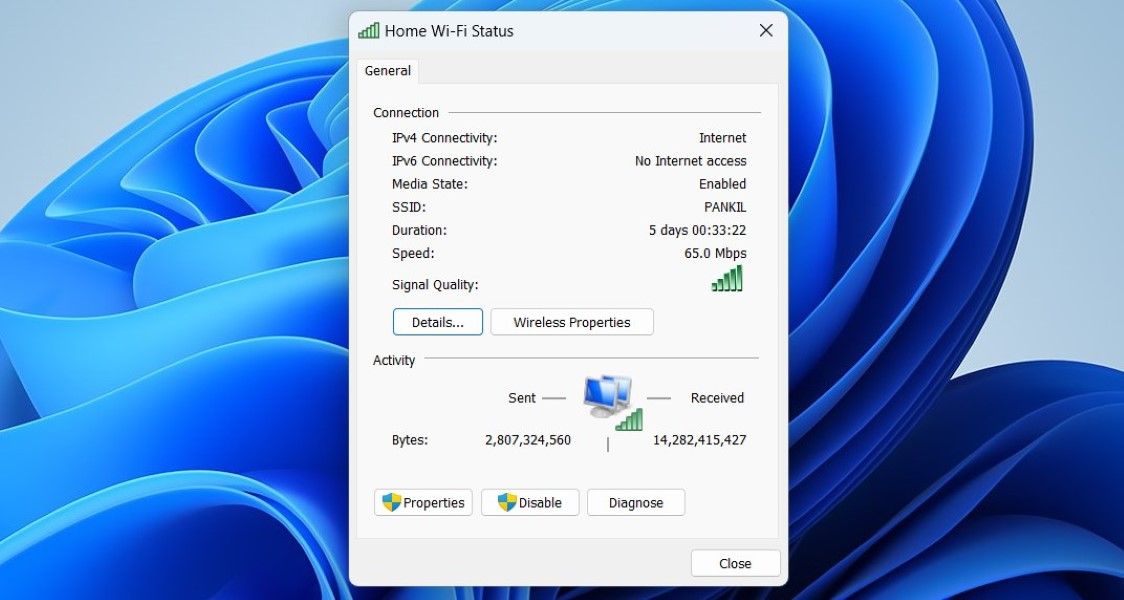
- Double-click on your Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter to open its properties.
-
Check the connection speed of your network adapter in the Speed field.
Seeing too many network adapter entries on your Windows computer? Learn how to get rid of old or inactive network adapters from Windows in a few easy steps.
3. How to Check Network Adapter Connection Speed via Command Prompt
Not a fan of GUI? No problem. You can also use a command-line utility like Command Prompt to check the network adapter connection speed on Windows. Here are the steps for the same.
- Right-click on the Start icon or use the Win + X shortcut to open the Power User menu.
- Select Terminal from the list.
-
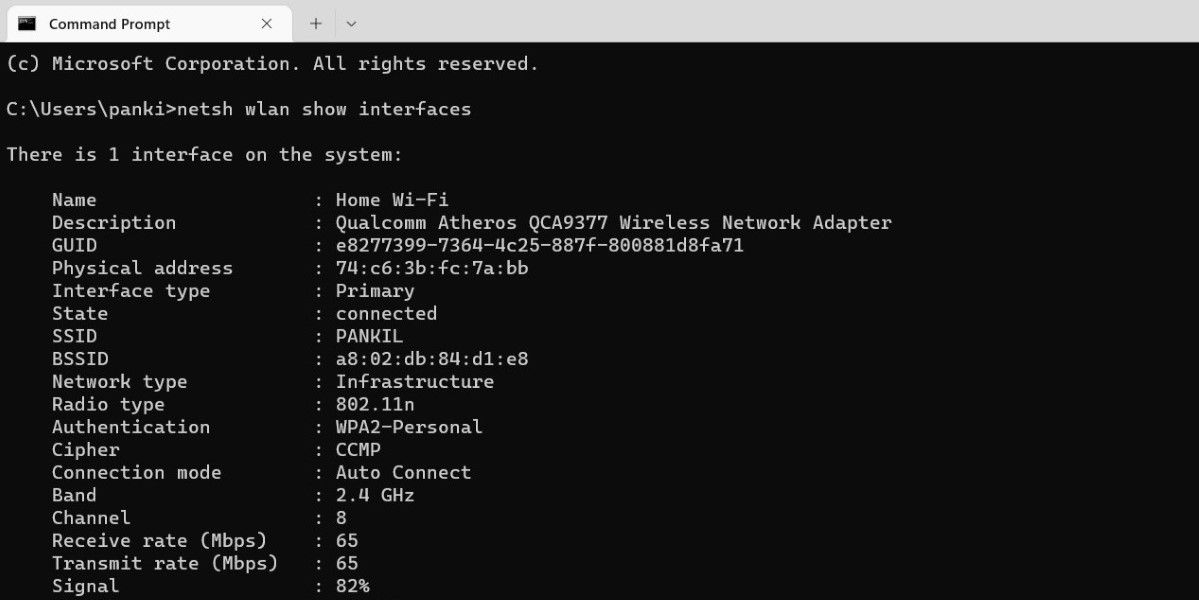
In the console, paste the following command and press Enter.
netsh wlan show interfaces -
Check the values next to Receive rate and Transmit rate to determine the speed of your network adapter.
Like using Command Prompt? Check our guide on how to master Command Prompt on Windows.
4. How to Check Network Adapter Connection Speed via PowerShell
PowerShell is yet another command-line tool you can use to interact with Windows. Although PowerShell is primarily used to automate tasks and troubleshoot errors, you can also use it to find system information such as the network adapter speed.
To check network adapter connection speed via PowerShell:
- Press Win + S to open the search menu.
- Type Windows PowerShell in the search box and press Enter.
-
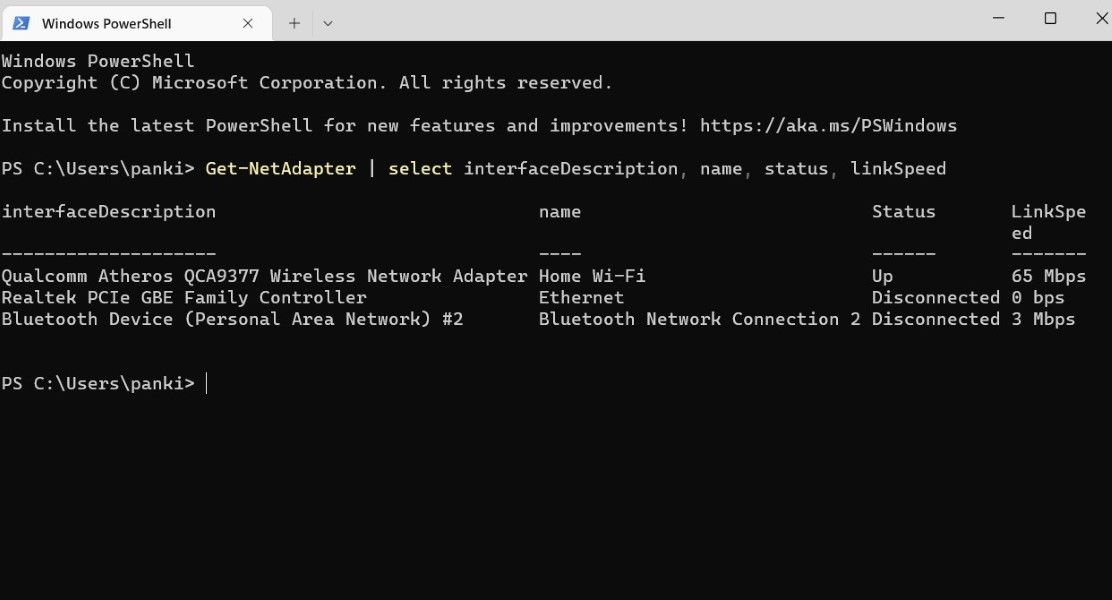
Paste the following command in the console and press Enter.
Get-NetAdapter | select interfaceDescription, name, status, linkSpeed
Once you run the above command, PowerShell will display a list of all the Ethernet and Wi-Fi adapters on your Windows computer, along with their link speeds.
Checking Network Adapter Connection Speed on Windows
As we just learned, determining the network adapter connection speed on Windows is relatively simple. Do you know what else is easy? Speeding up the internet connection speed on your Windows computer.