Microsoft launched a fully-functional hibernate feature with Windows 2000. But many users complain about not having the feature on their Windows-powered system. Some are even confused about the use case of the hibernate feature.
If you are curious about what exactly hibernate is and how it works, your search ends here. We will discuss the hibernate feature on Windows in detail. You will learn about its use cases and how to enable it on your system. So, without further ado, let's delve into the details.
What Is the Hibernate Mode in Windows 11?
Hibernation in computing is much like the term we often hear in biology; it denotes a low-mobilization, power-conserving state. And the hibernation mode on Windows saves an image of all the files and apps open on your system on your hard drive. After that, it turns off the system power completely.
When you power on your system again, it fetches that hibernation image file and restores Windows to the state where you left it. So, you don't have to close any open apps or disturb your current work progress. You can use hibernate to power off your system without closing any open apps and docs, and then return when you need to resume work again.
What Are the Benefits of Using Hibernate Mode?
The biggest advantage of hibernate mode is that you don't have to shut down your system. You don't have to close all running apps and then reopen them during the next boot.
Suppose you are working on a project and your laptop displays a low-power notification. You don't have a power socket nearby to plug in your system.. When your system runs out of power and shuts down, it will close all apps and running processes. Thus, you will lose your work progress if you can't save it right now.
However, you can use the hibernate mode to get out of this problem. Hibernate mode will save all the running apps and processes in the hiberfil.sys file on your hard disk. Then it will power off the system. When you turn on your system again, Windows will use the hiberfil.sys file to restore to the point where you left off.
All your apps and files that were running will remain open. So, you can continue to work on whatever app/file you were working on before.
Apart from the low battery issue, you can even use the hibernate feature to extend your work timeline without closing any app or file. You can take a small hiatus and return without losing any progress. However, it is best to use hibernate feature only when necessary.
How to Check if Hibernate Mode Is Active on Windows 11
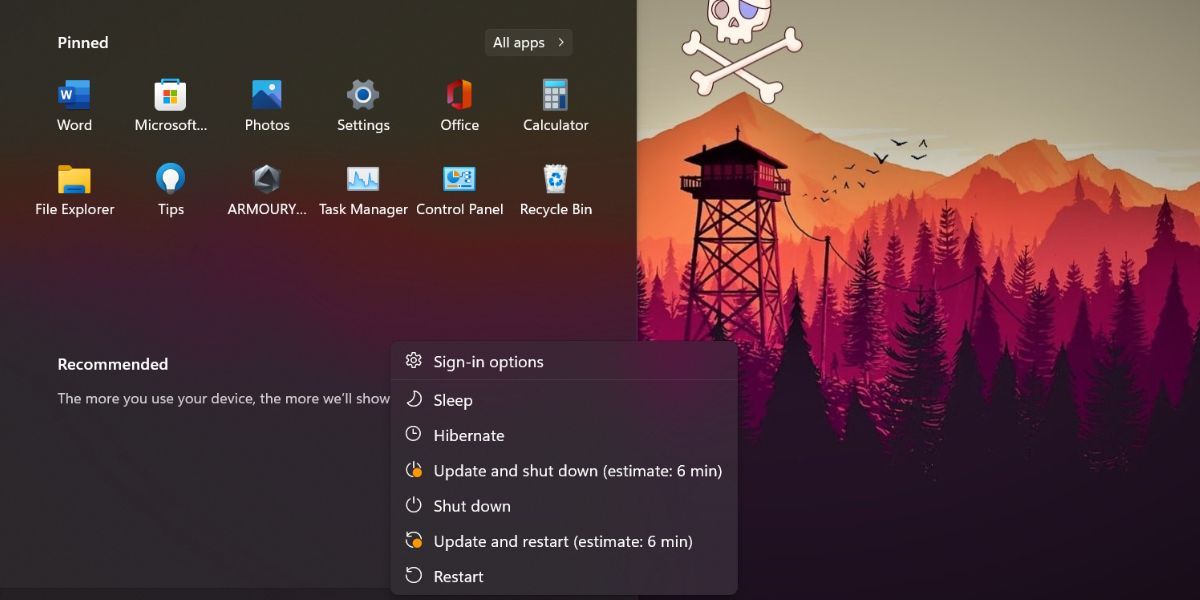
Microsoft does not enable the feature in Windows by default. So, if you have never seen or used the feature in power settings before, it is probably disabled. You can check it by launching the Start menu and clicking on the power button.
If you see a hibernate option along with sleep and restart in the list, it is active. Otherwise, you need to enable the feature on your system.
You can also check for it by pressing the Alt + F4 key combination to launch the Shut Down Window. Here, you can click on the drop-down list and check if hibernate option is present along with other power options.
How to Enable and Disable Hibernate Mode in Windows 11
There are multiple methods to enable hibernate feature on Windows 11. You can enable the feature using the control panel, command prompt, and tweaking the registry.
1. Using the Control Panel
Windows 11 introduced a UI revamp which sadly removed the old Control Panel power options shortcut. Instead, when you click on the power icon, it opens the power and battery settings page. There isn't an option to enable hibernate using this page. So, you need to access the control panel and enable the hibernate feature from there.
To enable hibernate feature using the control panel, do as follows:
- Press the Win key and search for Control Panel. Open the first search result.
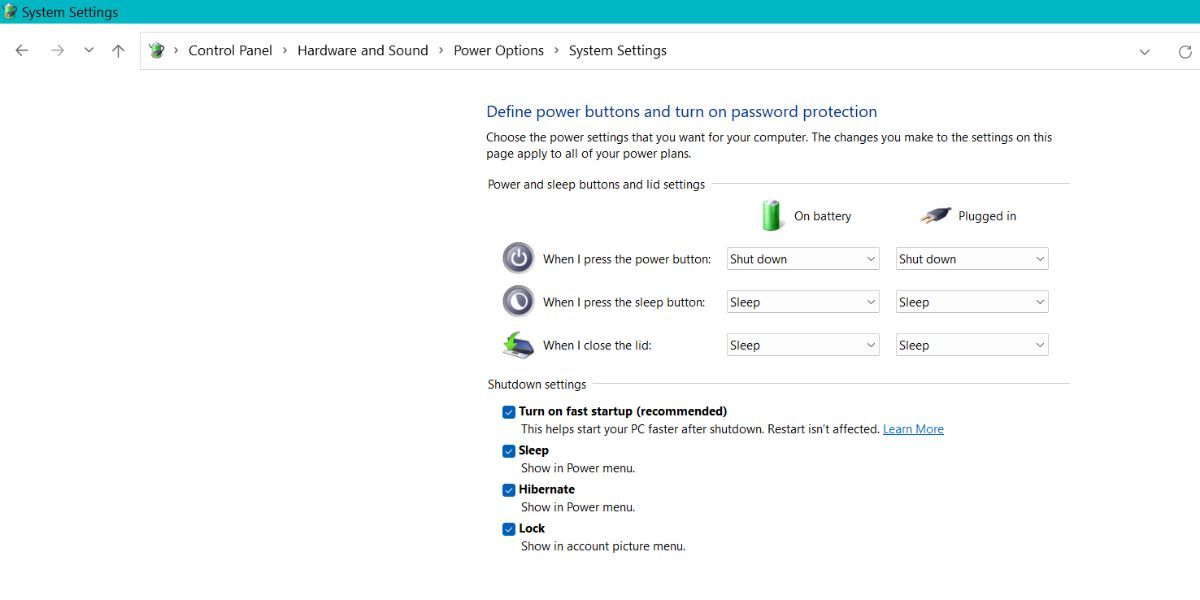
- Click on the System and Security feature. Then find the Power options feature and click on the Change what the power buttons do option.
- Now, you will see the Change settings that are currently available option at the top area. It will have the administrator icon next to it which means that you must log in as an administrator to make these changes.
- Click on the Change settings that are currently available option. You will notice that the power options that were inaccessible before are now interactable.
-
Click on the Hibernate checkbox and click on the Save changes button. Exit the Power options window.
- Press the Win key and click on the power button icon in the Start menu. You will see that hibernate option is available in the start menu now.
- If you want to disable the hibernate feature, retrace the above steps and uncheck the Hibernate checkbox. Then click on the Save changes button to disable the feature.
2. Using the Command Prompt
You can also disable the hibernate feature using the command prompt. Here's how to do it:
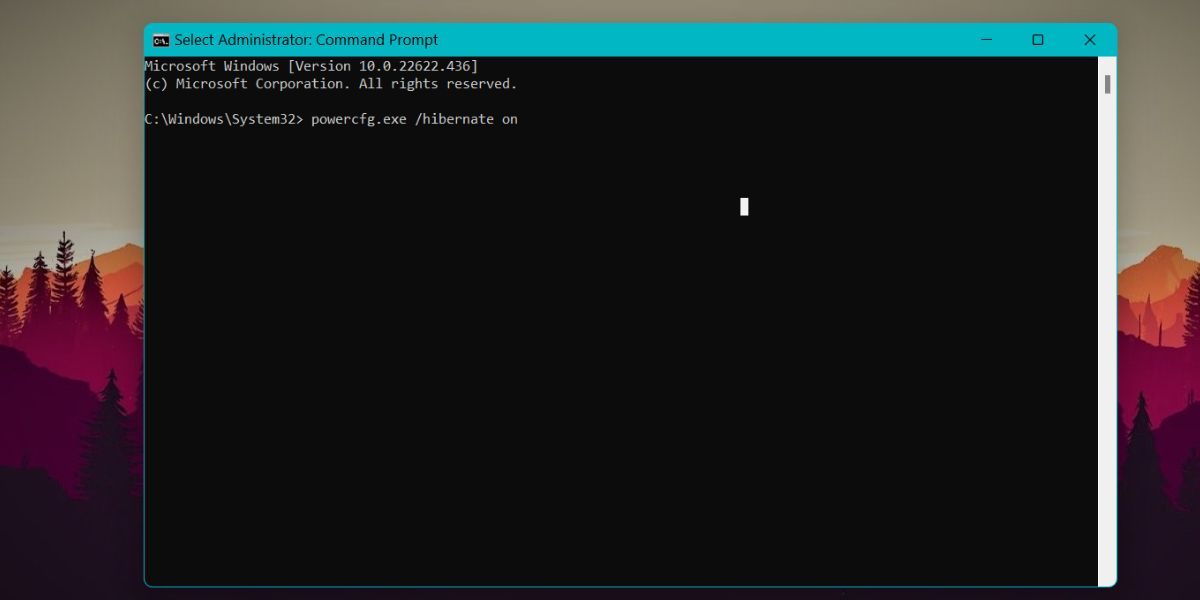
- Press Win + R to launch the Run command box. Enter cmd in the text box and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter key.
-
The command prompt will launch with administrator privileges. Now, input the following command: powercfg.exe /hibernate on
- Press the enter key to execute the command. Now, hibernate feature will be active on your system.
- If you wish to disable hibernate, relaunch the command prompt with administrator privileges. Then input: powercfg.exe /hibernate off and press the enter key.
3. Using the Windows Registry
You can even tweak the registry settings to enable the hibernate feature on Windows 11. Before making changes to your registry, always export a copy of it. Check our guide on how to back up your registry.
To enable hibernate using the registry editor, do as follows:
- Press the Win key and type Regedit. Right-click on the first search result and select the Run as administrator option from the context menu.
- The registry editor will launch on your system. Go to the top area and enter the following path: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power
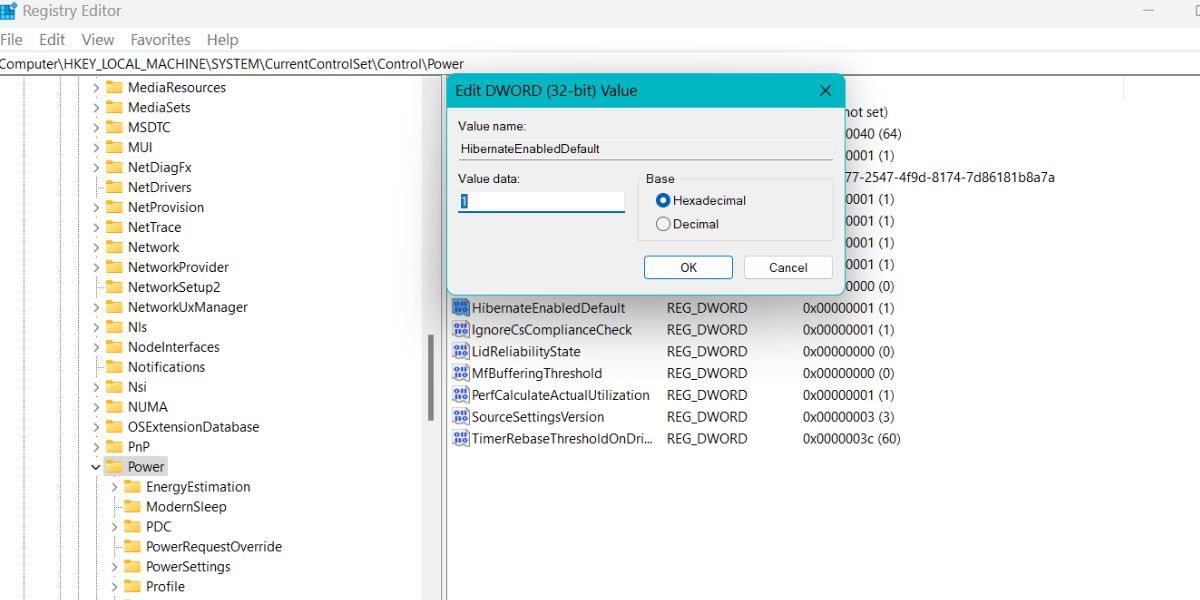
- Now, navigate to the right-hand side area and find the HibernateEnabledDefault value.
-
Double-click on it to open the edit window. Set the value data to 1. It will enable the hibernate feature on your system.
- If you want to disable hibernate, visit the same registry path again and set the HibernateEnabledDefault value data to 0.
Which Is Better: Hibernate or Sleep?
Sleep mode puts the computer in an extremely low power state and stores all the open apps and files in RAM. Hibernate, on the other hand, stores all the open apps and files on the hard disk. Then it shuts down the system.
Sleep mode is useful when you want to take a quick break and then resume work without powering off your system. Hibernate is useful when you will be away from the system for a while and cannot afford to close active apps and files.
Save the Current System State With Hibernate Mode
These were the multiple methods to enable or disable hibernate mode on Windows 11. Microsoft made some UI changes that removed the means to access power options directly from the taskbar. But, you can use the command prompt method or edit the registry key to activate hibernate mode on Windows 11.