A Virtual Private Network (VPN) helps you browse the internet anonymously while encrypting your data. Whether you are connecting to an unsecured Wi-Fi network at a coffee shop or trying to log into a secured corporate network, a VPN is vital in protecting your privacy. But as important as VPNs are, sometimes they don't work as planned. In fact, most users occasionally face the dilemma of having no internet when connected to a VPN.
So, what good is connecting to a VPN if you cannot browse the internet? Why is there no internet access after connecting to your VPN?
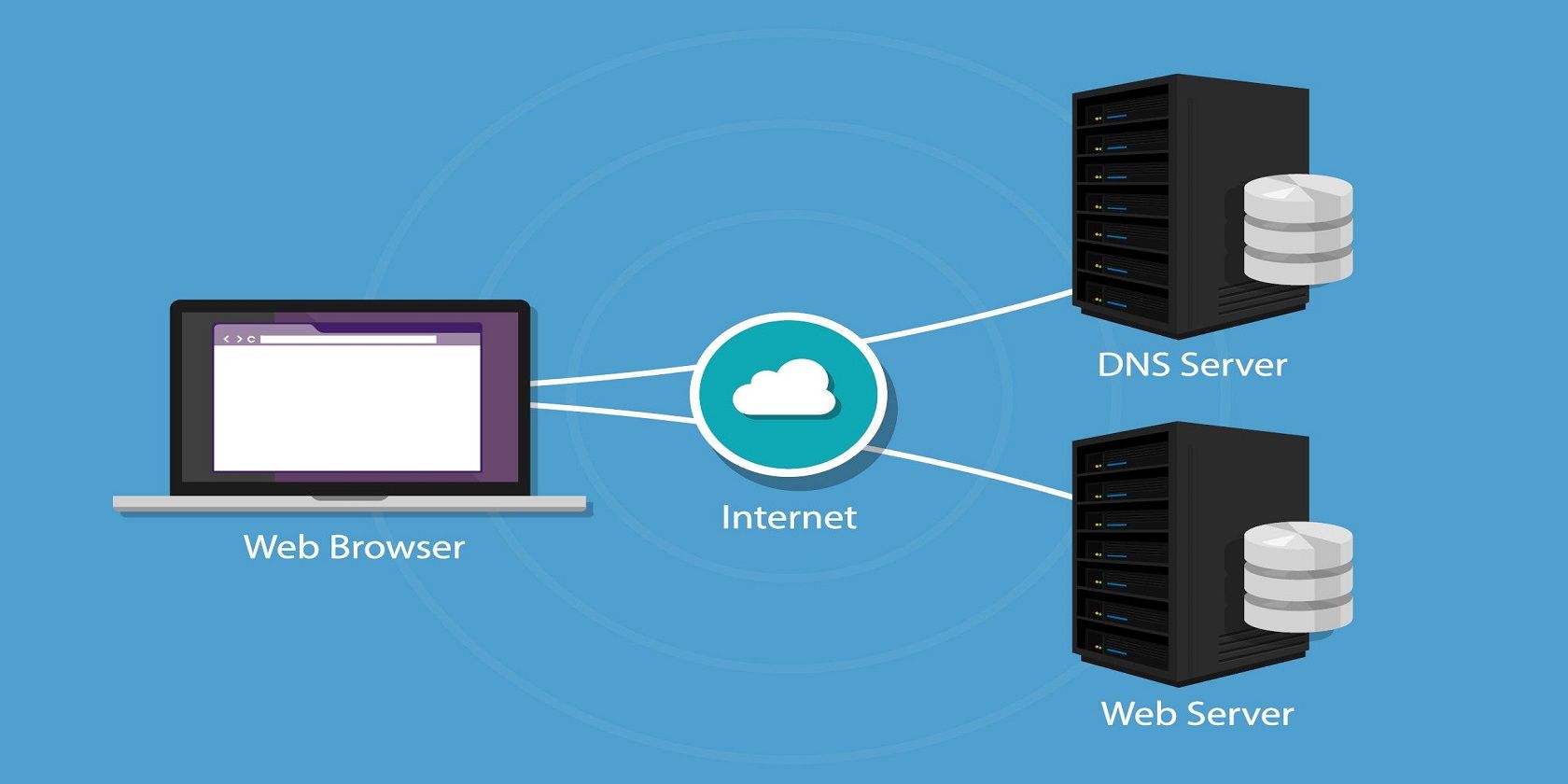
How Does a VPN Route Traffic?
A VPN creates a secure tunnel of communication between your internet connection and the remote network without compromising security or speed.
It achieves this security level by shielding your IP address and routing the internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel that is created between your originating traffic and the destination.
This way, the VPN server becomes the source of your data every time you browse the internet by severing you from the rest of the unsecured public internet.
A VPN also keeps your online activities anonymous so that no one, including the Internet Service Provider (ISP) that determines where your internet comes from, can see which websites you visit or what you download.
The VPN also works as a filter that makes your data undecipherable as it travels through the encrypted tunnel. Encryption makes it hard for even the cleverest online intruders to decode your data.
Why Is There No Internet When My VPN Is On?
While a VPN is a great asset when you want to extend a private network across a public one, things don't always go as planned. Not being able to connect to the internet while your VPN is turned on is frustrating yet very common.
Here are some potential reasons behind this problem.
1. Bad Internet Connection
A bad internet connection can prevent you from connecting to the internet with or without a VPN.
To confirm the source of the problem, disconnect your VPN connection and then try to access the internet. If there is still no internet access even after disconnecting your VPN, then the problem is with your network.
Generally, rebooting your device and checking your network status can alleviate this problem. If not, you can contact the internet providers to get a solution. We also have a detailed guide on fixing a bad internet connection which you can check out for further assistance.
2. DNS Configuration Issues
The most common reason why you cannot browse the internet when connected to the VPN is a DNS configuration issue.
Every website or domain name such as google(dot)com has an associated IP address. But humans are not good at memorizing IP addresses, so the DNS (Domain Name System) converts and translates those domain names into IP addresses, so we can surf the internet with ease.
However, faulty DNS settings can cause issues and prevent you from going online once you are connected to a VPN server. To fix this problem, you will need to change your DNS settings manually.
3. Bad Server Choice
If you are connected to a VPN server that is down, blocked (some countries block VPN connections), or has other issues, then it might prevent you from getting connected.
Generally, VPN providers offer hundreds of different servers, so trying to reconnect to a different one might just get around this problem.
If you can access the internet after switching the VPN server location, then most likely there was a temporary issue with the server location you selected originally.
4. Incorrect VPN Protocol
A routing protocol is a set of rules that determine how your data travels from source to destination; VPNs support different types of routing protocols. However, if your VPN uses the UDP protocol by default, it may be blocked in some countries.
To ensure the best outcome, open your VPN’s options or settings and select Protocol from the list. Then choose the protocols below in the following order of preference:
- OpenVPN TCP.
- L2TP.
- PPTP.
5. Incorrect VPN Port
The flow of traffic to and from a VPN server is managed by VPN ports. Just like VPN protocols, some ports might also get blocked, causing no internet access when connected to VPN.
Finding and switching to the correct port is important. But ports can be a bit challenging. It's best to contact your VPN provider, so they can suggest the port that is suitable for your needs.
6. Default Gateway Settings
The default gateway settings should be left unchecked if you are having issues connecting to the internet while your VPN is turned on. This is because if you have configured your VPN connection to use the default gateway on the remote network, then this setting overrides the default gateway settings that you specify in your TCP/IP settings.
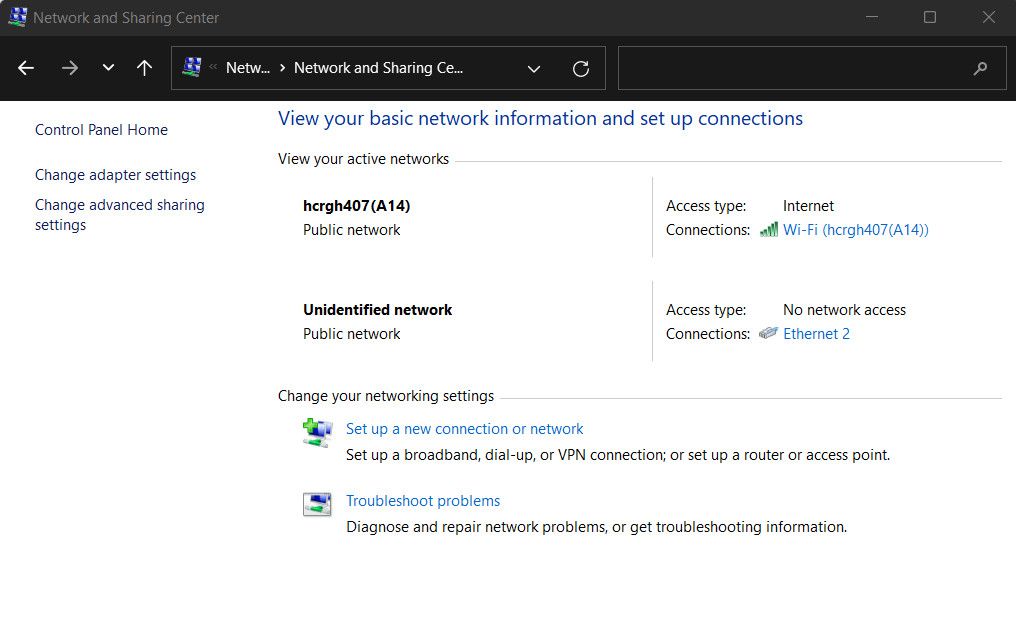
To uncheck the default gateway option, here are the steps to follow if you are a Windows user:
-
Go to Start > Control Panel > Network & Internet > Network & Sharing Center > Change Adapter Settings.
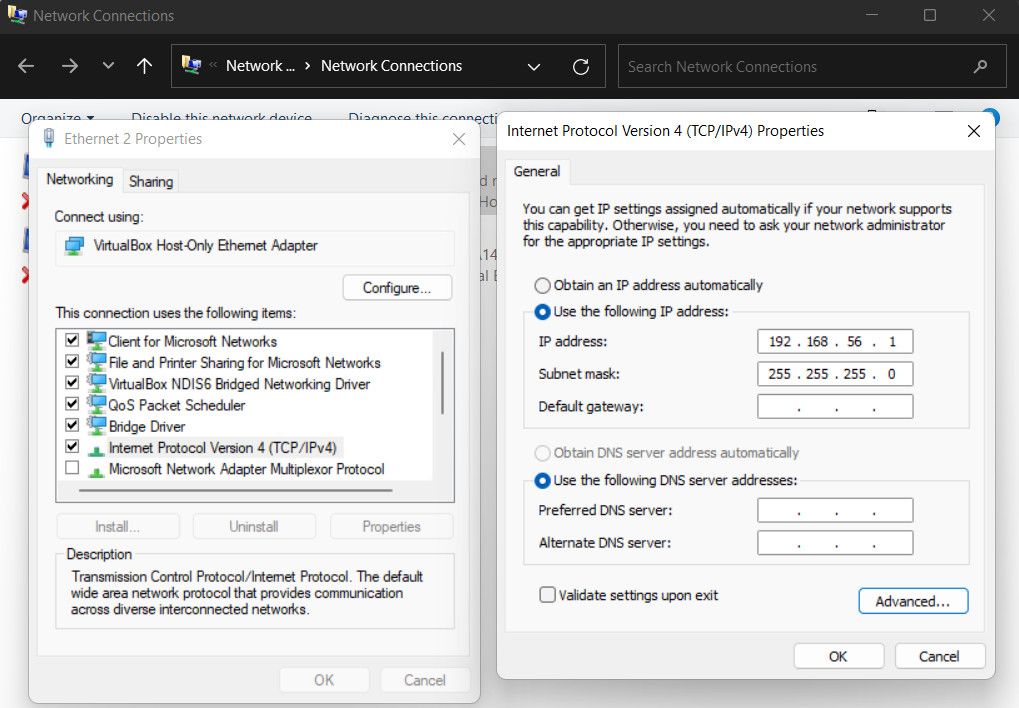
- Right-click the VPN connection adapter and then click Properties.
- Click the Networking tab.
- Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) option.
-
Choose Properties > Advanced and go to the IP Settings tab.
- Uncheck the Use default gateway on the remote network option.
- Click OK three times.
7. Proxy Server Settings
A proxy server acts as a middleman between your computer and the internet. It is often used to hide your real location, so you can access websites that would otherwise be blocked based on your geographical location.
Sometimes, a web browser’s proxy settings may block access when a VPN connection is found. Disabling or changing proxy settings may resolve this problem. Fortunately, you can h.
8. VPN Kill Switch Turned On
A VPN kill switch is a special VPN feature that automatically disconnects your device from the internet when your VPN connection goes down. It is done to prevent the possibility of accidentally exposing your IP address while the VPN is down. This may be a reason why after connecting to VPN, the internet is not working.
You might face internet connection problems if your VPN comes back online, but the kill switch is still enabled. To fix the issue, manually check if the kill switch is enabled and then disable it to get back online.
9. Using an Older VPN Version
If the internet is not working when you're connected to VPN, using an older VPN version might be the reason.
Having an updated VPN is important to avoid connection issues. If you are running an outdated version, update it. You can also re-install the VPN software again.
Here are the steps to follow in Windows:
- Go to Start > Control Panel > Programs & Features.
- Right-click on your installed VPN client, then select Uninstall.
- If prompted, confirm your action in the User Account Control prompt.
- Once the program is uninstalled, visit your VPN provider's website and download the newest version of the software.
- Restart your computer.
10. Incorrect Date and Time Settings
In some instances, incorrect date and time settings might lead to your VPN blocking the internet.
To check for misconfigured time and date settings, follow these steps:
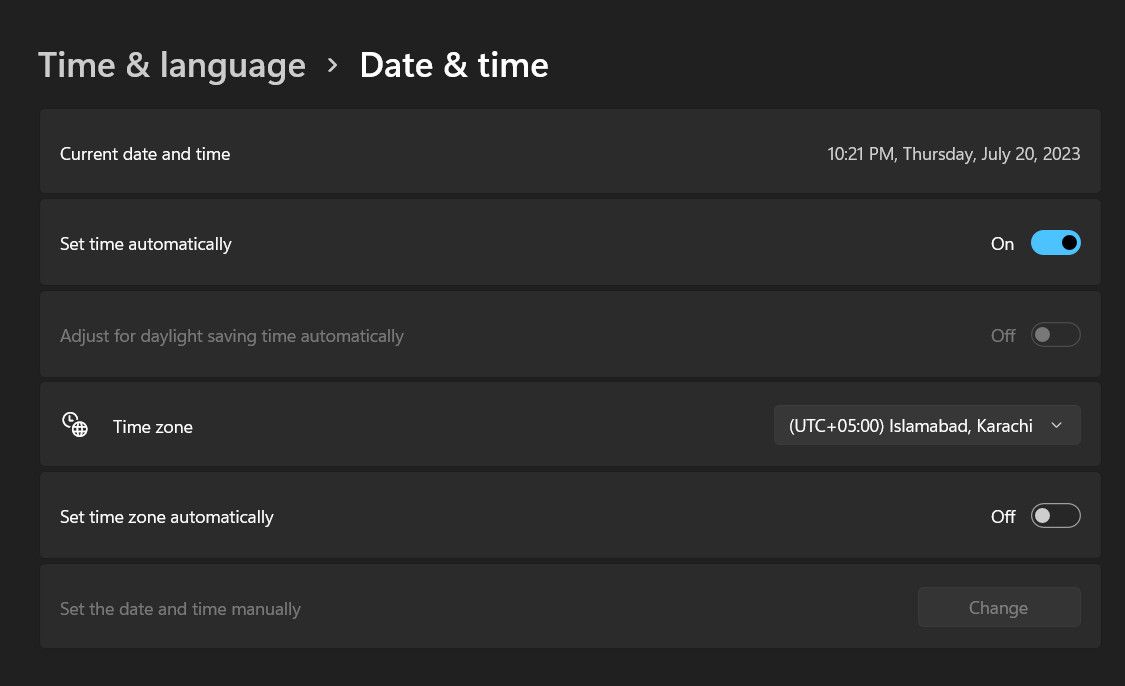
- Go to Start > Settings > Time & Language > Date & Time.
-
Select Change under Change date and time, and update it with the current date and time. Alternatively, you can turn the toggle on for Set time automatically if you don't want to do it manually.
- Click the dialog box under Time Zone to check if it's set correctly.
Be Wary of Free VPN Providers
The best things in life do not come without a price tag. So you should always be wary of free VPN providers.
Along with having servers that can get quickly overloaded due to a high influx of traffic, free VPN providers cannot necessarily be trusted with your private data. Not only do you suffer from a spotty internet connection, but you are also putting your precious data at risk, as free VPN providers are more likely to track your data to cover their operational costs.
So, if you are still at crossroads between getting a free VPN provider or a paid service, always go with the latter if you can afford it. Paid versions sometimes show glitches like having no internet access when connected to a VPN, but these issues are fixable and are much more reliable with data security.