When your Windows computer works hard, whether you’re using it for work or for play, the CPU generates heat. To keep things cool, your computer needs to maintain a fine balance between the fan and processor speeds. And that’s where the system cooling policy comes in.
We’re going to discuss what the system cooling policy is and how to set it so it best suits your Windows PC.
What Is the Windows System Cooling Policy?
The system cooling policy is a set of configurations that keep your Windows computer's internal temperature cool by automatically adjusting the CPU’s clock speed and the PC’s fan speed. When your computer is doing something processor intensive, and you hear your PC’s fan start to spin louder, that is the system cooling policy at play.
There are two options when it comes to setting the system cooling policy: Active and Passive. The Active cooling policy makes the fan faster before slowing down the processor. On the other hand, Passive does the reverse – making the processor slower before speeding up the fan.
The policy you set will depend on what you want to prioritize between performance and power. So, for example, if you want to conserve battery power on your laptop, you might want to go with the Passive cooling policy.
How to Set the System Cooling Policy on Windows
To set a system policy, start by opening the Control Panel. Press Win + S to open Windows Search, type control panel in the text box, and click on Control Panel in the results. For more ways to launch it, please read our guide on how to open the Control Panel.
Next, go to Hardware and Sound > Power Options, and then click Change plan settings next to the power plan you’re using.
Click Change advanced power settings to open the Power Options menu.
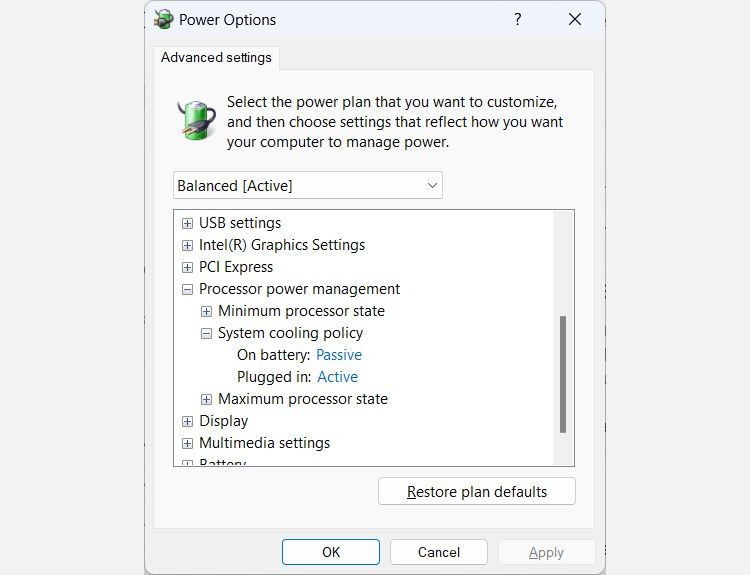
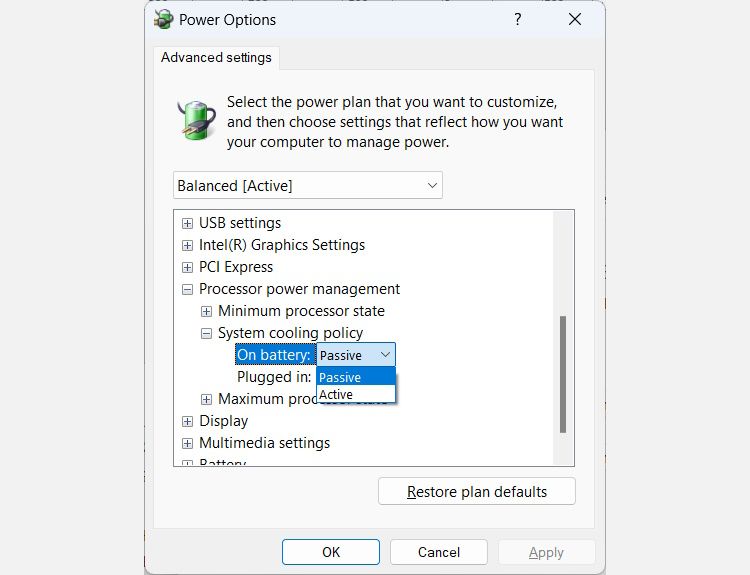
Expand Processor power management by clicking the plus sign on the right, and you will see System cooling policy. Expand that too.
You will then see how the cooling policies are set – of course, what you see will depend on whether you’re on a desktop computer or laptop. To change them, click on the cooling policy’s link – so if On battery is set to Passive, click on Passive. This will turn it into a dropdown, so click on that and select the other cooling policy.
You can set the cooling policy for all your power plans. And if you’re changing the cooling policy to save battery power, consider reading our guide on creating a custom power plan on Windows as well.
Set the System Cooling Policy You Want to Use
Remember, the Active cooling policy prefers performance, while the Passive cooling policy prefers battery consumption. You can change the policy as often as you need in the advanced power settings for your preferred power plans.
And while you’re there, you can even tweak the minimum and maximum processor state.