It's no surprise that powerful PC components like CPUs and GPUs require a ton of power to function at their full potential. However, a side effect of pumping several hundred watts into your CPU is the amount of heat that it generates.
While it's usually not a problem, excessive heat can lead to problems that directly impact the performance of your CPU. Thermal throttling might save your CPU from turning into an induction cooktop, but it won't do much good to your system's performance.
What Is CPU Thermal Throttling?
Whenever your computer runs resource-intensive loads like a heavy game or program, it uses more power to keep up with the level of performance demanded by such applications. The more power your CPU is pulling, the more heat it generates. Once this heat becomes too much for your PC or laptop's cooling system, the CPU starts being throttled.
CPU thermal throttling occurs when your CPU hits critical temperatures (usually around 194 Fahrenheit or 90 Celsius) and starts sacrificing performance to maintain or reduce that temperature. Temperatures beyond that point can damage the CPU, at which point your system will likely shut down to protect internal components.
If you're overclocking your CPU to get more performance, you also run a higher risk of thermal throttling. Since overclocking pushes the CPU to reach higher clock speeds, it pulls more power and generates more heat. This means it'll hit its thermal thresholds faster, meaning you need to upgrade your cooling solution accordingly to avoid throttling your precious CPU.
To be clear, thermal throttling itself isn't a bad thing. If you have an inadequately cooled CPU, thermal throttling might be the only thing keeping it from melting down. If you're using a laptop, thermal throttling can also ensure that it doesn't get so hot that you can't use the device properly anymore, as the CPU heat generated in laptops often heats the keyboard deck and especially the underbody.
Desktop CPUs are limited by their TjMax temperature, otherwise known as the Maximum Thermal Junction Temperature, where the CPU's internal thermal control mechanisms act to prevent component damage. On laptop CPUs, this TjMax value can vary by the device model and make, as well as manufacturer specifications.
You can find your specific CPU's TjMax value by checking the spec sheet or using freeware utilities like Core Temp or HWMonitor.
How Does CPU Thermal Throttling Impact Performance?
The main aim of thermal throttling is to cool down the CPU to a point where it doesn't go beyond a particular temperature threshold. This is done by lowering the CPU's core clock speed, which results in a lower power draw, eventually leading to less heat generation. As you can probably guess, since your CPU can't run at its maximum boost clock speeds anymore, that directly affects your system's performance.
The effect is especially notable on portable devices as they tend to have smaller power budgets and cooling solutions. However, regardless of whether you're using a laptop or PC, your CPU will generally throttle between its base and turbo frequencies.
Just how much performance you lose by thermal throttling comes down to factors like the load on the CPU, your cooling solution, the CPU's base and boost clocks, and the power it consumes. In terms of your gaming experience, expect to see sudden FPS drops as well as random lags and spikes during the game. It can also lead to games outright crashing in extreme situations.
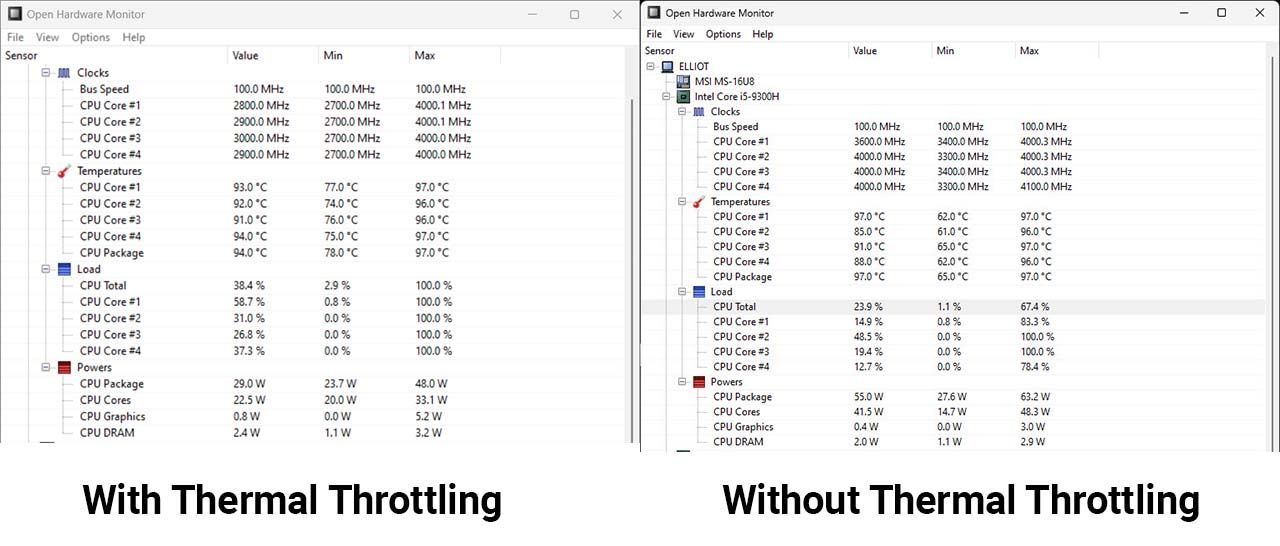
For example, my MSI laptop's 9th-Gen Core-i5 9300H was thermal throttling while playing Call of Duty Warzone 2.0, with the game running between 30-35 FPS on low settings. This was caused by a significant drop in the CPU's clock speeds, which dropped as low as 2.9GHz as compared to its regular boost clock of 4.0GHz. That's a significant loss in performance.
The CPU's power draw was also significantly reduced. When being throttled, it was pulling anywhere between 23-30W of power, while it can reach as high as 50W when running at full performance.
All this while, the temperature across all four cores was between 96-97 Celsius (204.8-206.6 Fahrenheit), just 3 degrees short of the processor's TjMax. It won't go any higher, as MSI has put restrictions in place to prevent the bottom of the laptop from turning into a frying pan.
Ideally, your CPU should be running at 50-60 Celsius (122-140 Fahrenheit) when under no load. My thermal throttled i5 9300H was sitting at near 80 Celsius (176 Fahrenheit), which didn't leave a lot of room for the CPU to maintain performance when under stress.
When I worked out the issues causing the throttling, performance increased to a much more stable 55-60 FPS, nearly double what I was getting with a throttled CPU.
Depending on your specific CPU load and degree of throttling, the mileage may vary. The point is thermal throttling affects your CPUs performance quite significantly, not to mention that constantly running a CPU near its thermal limit also massively impacts its longevity.
How to Check if Your CPU Is Throttling
Checking for CPU thermal throttling is actually quite simple. First up, to the keen-eyed, the drop in performance will be enough to indicate that something is wrong. Your PC will also show signs of struggle, meaning fans will run faster, producing more noise as your PC overheats.
For conclusive proof that your CPU is throttling, open any CPU monitoring program like OpenHardwareMonitor or HWiNFO while putting your CPU under stress with either a CPU-intensive game or stress test like Prime95 and watch the temperature, power draw, and core speeds.
If your CPU is thermal throttling, you'll see the temperatures rise up very close to your CPU's TjMax value while the power draw and core clock speeds will reduce significantly from what they should be under a heavy load. This will result in a performance loss and is a pretty solid indication of your CPU being thermally throttled.
How to Fix Thermal Throttling Issues
There are a number of ways you can fix your CPU's thermal throttling issues. Since the reason for thermal throttling is almost always an inadequate or faulty cooling solution, that should be the first area you check.
Dust is the number one enemy of your computer. Regardless of whether you're using a laptop or have a desktop, if your fan vents are clogged with dust, your system's thermal system won't be able to pull in as much cool air as it needs to cool down your CPU leading to thermal throttling. This also applies to water-cooled systems.
Ensure your fans have clear airflow access and the heatsinks aren't clogged up with dust, especially on laptops. It doesn't require much effort; a few carefully aimed compressed air or blower sprays will do the job in most cases. Laptops are a different story, though, as you might need to open them up to access the fans or get them to a repair shop if you aren't comfortable opening yours up on your own.
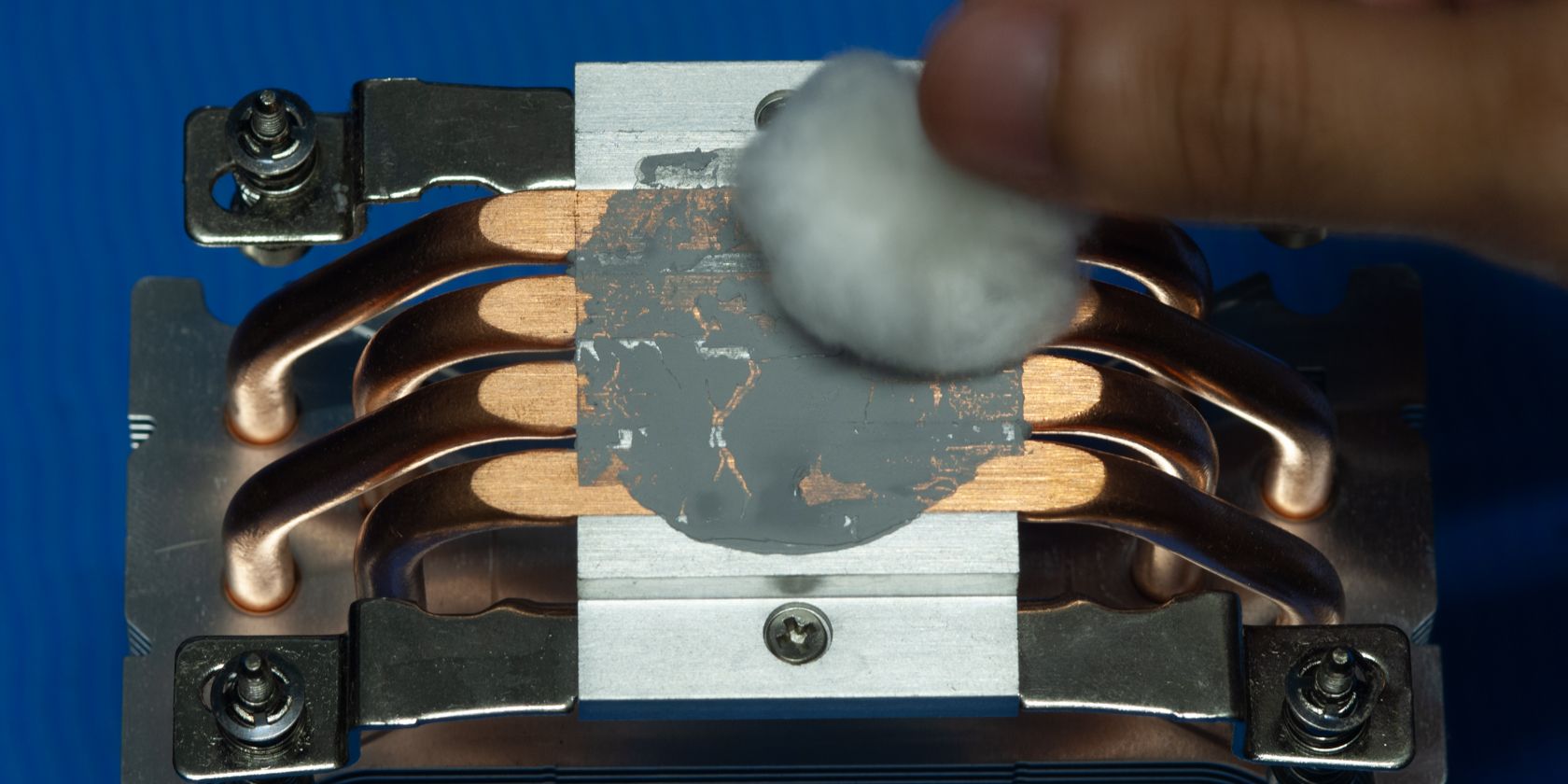
Thermal repasting can also help, as your thermal paste can dry out over time. However, note that you shouldn't have to frequently repaste your CPU as good quality thermal paste often lasts a pretty long time. Or if you're done with thermal paste, liquid metal is also an option.
If you're uncomfortable performing surgery on your computer, there are ways to fix or at least reduce thermal throttling on your CPU. Of course, the easy way is to reduce your CPU's load and not run demanding programs on your computer. But it is easier said than done for most of us.
Alternatively, you can also undervolt your CPU. Undervolting involves lowering your CPU's power consumption while maintaining consistent core and memory clock speeds. It's much safer than overclocking and, in some cases, can yield better performance than your CPU produces at stock settings. That said, it does require some technical know-how.
These methods also extend to other PC components and can also be used to prevent thermal throttling on your GPU.
Don't Let That CPU Run Hot
As modern CPUs get faster and more power-hungry, they will generate even more heat which means keeping issues like thermal throttling at bay and cooling your CPU properly will be of utmost importance to get the maximum performance possible.
It's not that hard, after all. Just regularly maintaining your computer will go a long way in ensuring you get the maximum performance and longevity out of your CPU.