Windows has dozens of processes running in the background, and you can see them in the Task Manager. One of them is the Client Server Runtime Process (CSRSS), and it is an integral part of the Windows Operating system.
Sometimes, the CSRSS can cause concern, making you think disabling it is a good idea. However, there are a few things you need to know before you attempt to kill it.
What Is Client Server Runtime Process?
The Client Server Runtime Process doesn't do much these days, but it was responsible for handling the entire graphical subsystem during the era of Windows NT 3.x. Part of its operation included managing windows and drawing things to the screen like window frames and menus.
When Microsoft released Windows NT 4 in 1996, it removed a majority of CSRSS's graphical operations. It did this to improve the OS's visual performance. Since Windows 7, the process is only responsible for handling the console and shutting down the graphical user interface (GUI).
CSRSS is a process that starts running as Windows is booting up – it can't run after. So if something unexpected happens and it fails to launch, you'll most likely get the infamous blue screen of death (BSoD).
To view the process, right-click the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
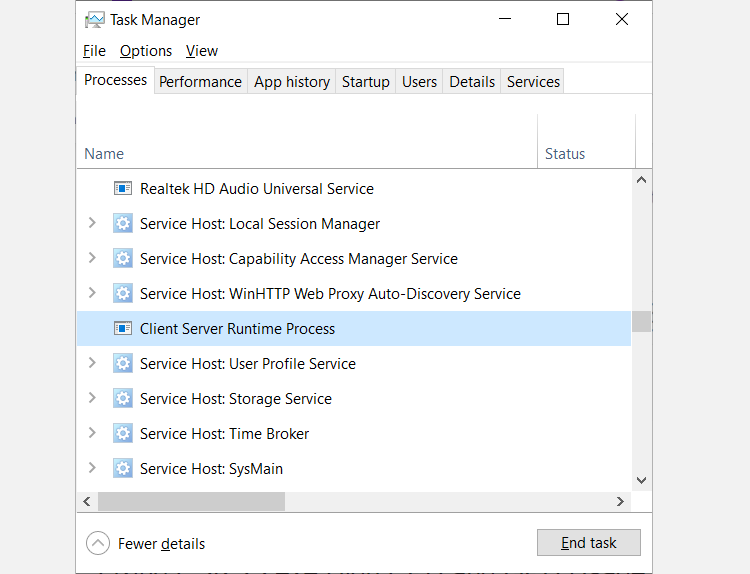
Select the Processes tab and scroll down until you see Client Server Runtime Process.
Is It Okay to Disable Client Server Runtime Process?
It's natural to want to kill a process when you want to boost performance or when it's causing problems, but CSRSS is one of those processes you never want to kill. It is such a critical system function that the OS won't let you randomly terminate it, making it virtually unkillable.
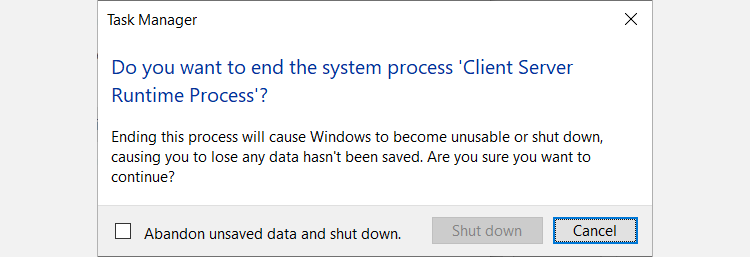
You can attempt to end the Client Server Runtime Process by selecting it in the Task Manager and clicking the End task button on the bottom right. You'll get a warning telling you that proceeding will make Windows unstable or shut down.
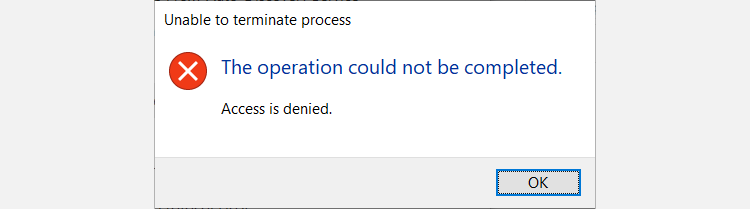
You can decide to continue by ticking the Abandon unsaved data and shut down checkbox and then clicking the Shut down button. However, you'll be greeted by another warning telling you that Windows could not complete the operation and is denying you access.
Why Do I See Two Instances of CSRSS Running at Once?
If you notice that there are two instances of Client Server Runtime running simultaneously, don't panic. When some people see this, they usually assume it's a virus. It's perfectly normal to have more than one of these processes active in the Task Manager without any of them being malware.
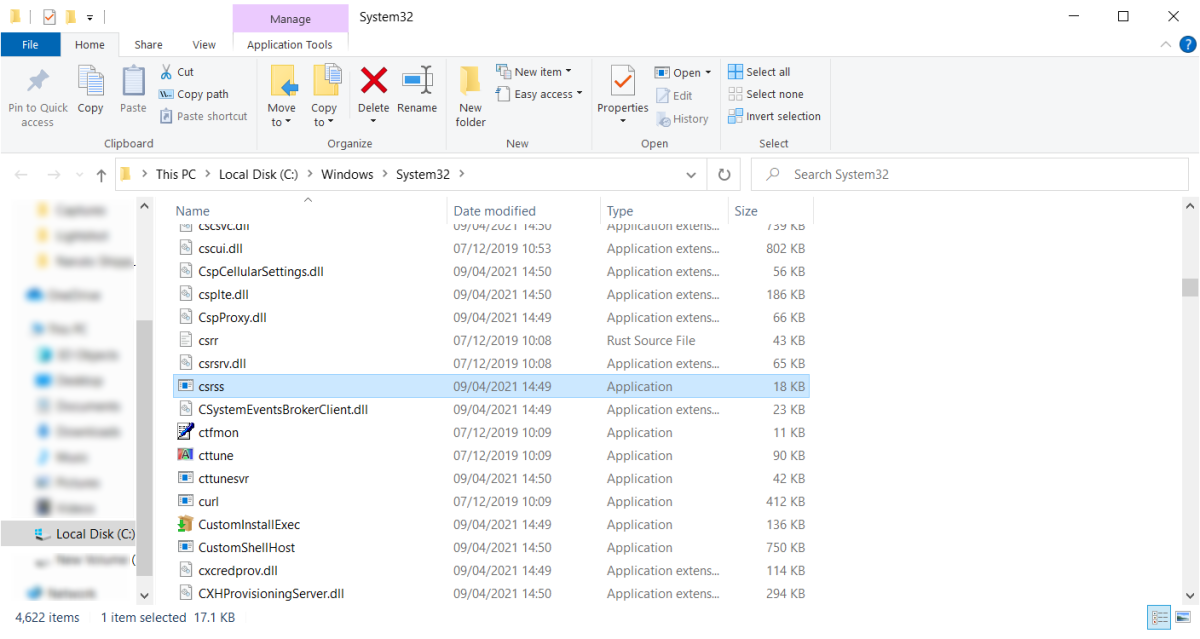
If you suspect one of the processes isn't legitimate, there's a simple way of verifying it. The executable file for the actual Client Server Runtime Process is in the following location: Local Disk (C) > Windows > System32. All authentic instances of this process originate from the System32 folder.
To verify, click on the Client Server Runtime Process in the Task Manager and select Open file location. Windows will redirect you to the System32 folder with csrss.exe chosen, meaning the process is legit.
If the redirection takes you elsewhere, then a trojan has most likely infected your system. To get rid of the trojan, open up your antivirus software (make sure it's up-to-date) and run a full system scan. The program will identify and remove all malicious software from your system, such as viruses, trojans, worms, and spyware.
Fixing CSRSS.exe High CPU and Memory Usage
Considering the Client Server Runtime Process isn't responsible for a lot, it shouldn't noticeably impact your computer's performance. However, some people report that the process can suddenly start using a large chunk of their CPU and memory. At best, it can make the PC sluggish, and at worst, the system can crash.
When CSRSS is misbehaving by hogging system resources, it is usually for two reasons: a malware infection or a corrupted user profile.
When It Is a Malware Infection
As mentioned in the previous section, a simple full-system scan can remove the harmful program affecting the Client Server Runtime Process. Therefore, as a preventative measure, it's a good idea to perform a full system scan at least once a week.
When It Is a Corrupt User Profile
If you've ruled out malware, then the second most likely cause is a corrupted user profile. Unfortunately, there's no way to uncorrupt it, meaning you have to create a new account and delete the old one.
Before proceeding, transfer any important files to a flash drive or external hard drive to create a backup. You can even create a cloud backup if you don't want to use physical storage devices.
To delete your old user profile on Windows 10, create a new user account (skip this step if you already have another profile on your PC).
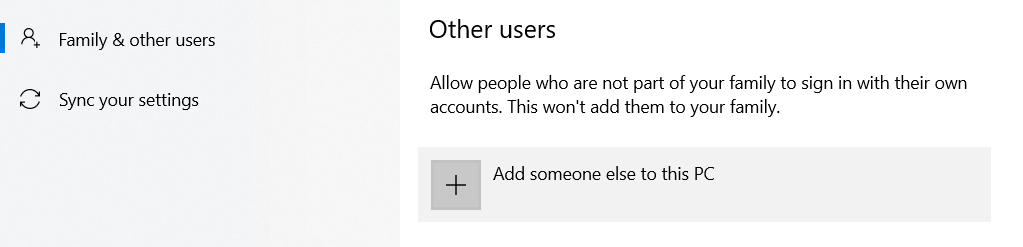
Go to Start > Settings > Family & other users and click on Add someone else to this PC.
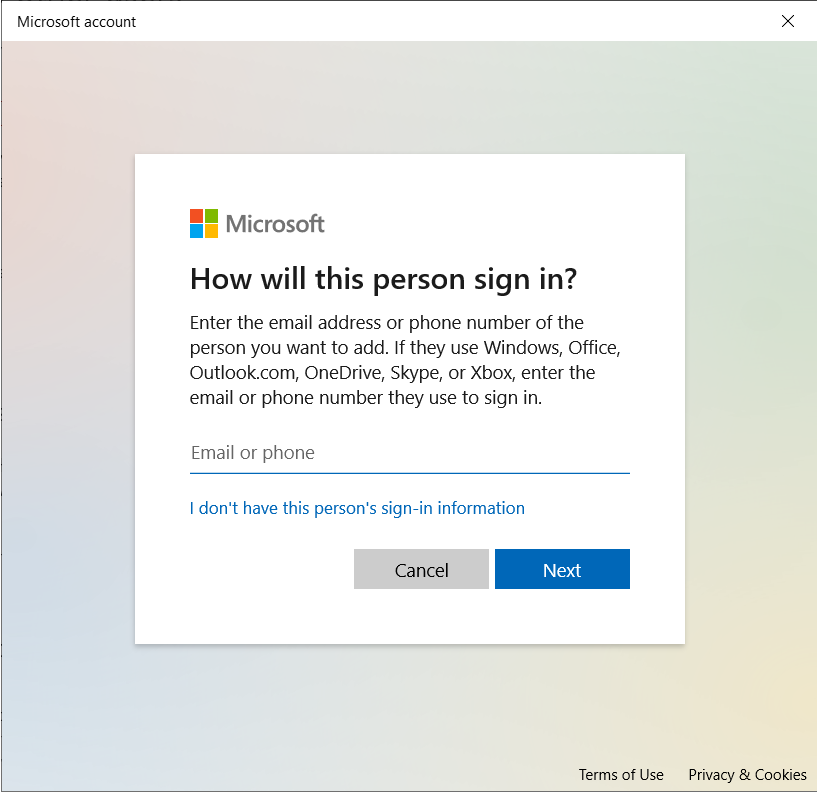
Windows will ask you to enter how the person will sign in. Click on I don't have this person's sign-in information.
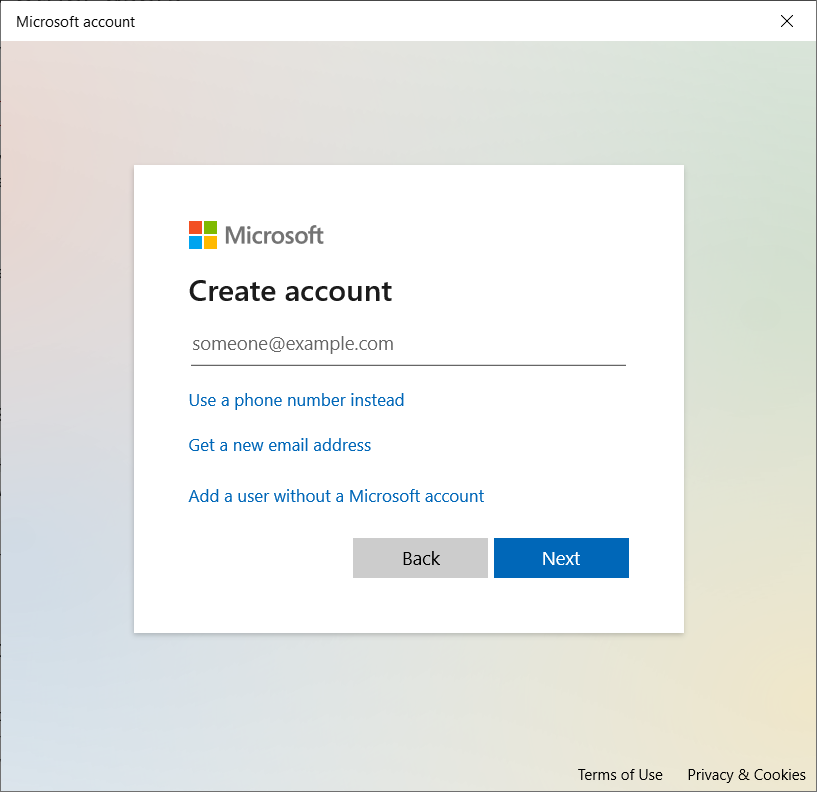
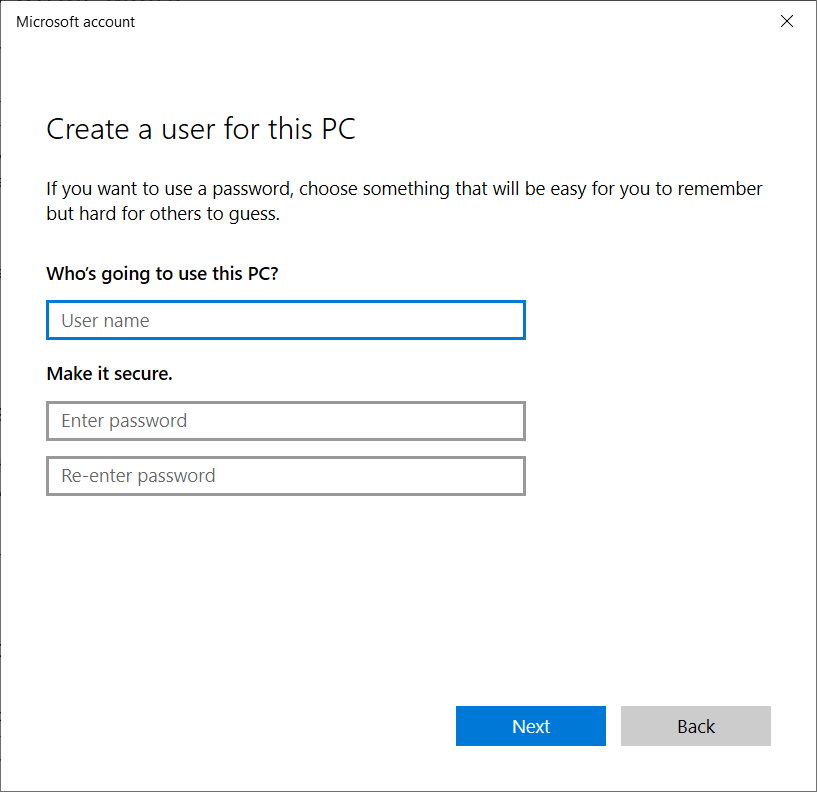
Now you can create a new account. Click on Add a user without a Microsoft account.
Enter the name of the new user, create a password and fill in the security questions. Then, click on the Next button to finish setting up the new account.
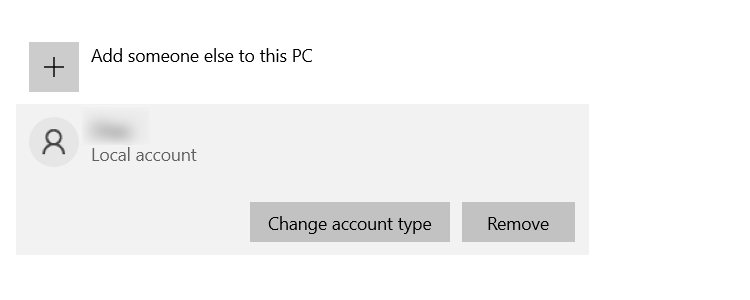
Now log out of your old account and log into the new one. Navigate to Family & other users. Click on your old account to expand the options and click on Remove.
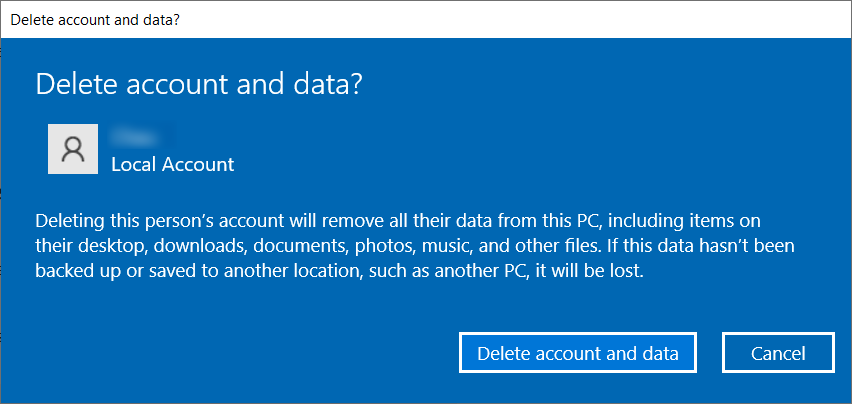
Then, click on the Delete account and data button to remove the profile from the system completely.
Client Server Runtime Process Demystified
If you aren't a Windows enthusiast, no one can blame you for not knowing what CSRSS is. Beyond being just another background process, it's critical to the operation of Windows. You can't disable the process, even when it's causing problems (Microsoft made sure of that).
But knowing what Client Server Runtime Process is and how to fix the common problems associated with it brings you a step closer to being a guru at handling Windows processes.