Did you know that there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins? Not one more, not one less—this is the reason why Bitcoin is becoming digital gold: its supply is finite.
We’ve discussed before that miners on the blockchain are technically able to mint as many coins as they possibly can, so how does Bitcoin manage to maintain its 21 million token hard cap?
This is all thanks to a major event called Bitcoin Halving that takes place once every four years.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving, or just simply “the halvening,” is an event where Bitcoin’s supply gets cut in half. This is a process that is unique to Bitcoin.
Bitcoins come into circulation thanks to miners who use expensive hardware (like ASIC miners) to solve complex mathematical solutions that link the transaction blocks together. Each block of transactions processed by Bitcoin miners earns a “block reward" along with any transaction fees. So, when the Bitcoin halvening happens, the block reward earned by the miners is halved.
But why do so? This can be traced back to Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto’s view on digital scarcity based on supply and demand theory. Nakamoto believes that by creating scarcity for Bitcoin, its value will appreciate.
This method of creating scarcity stands in marked contrast to the way fiat currencies work, where the federal government controls inflation by fiscal and monetary policies, i.e. deciding on interest rate for loans and how much money should be printed. Fiat currencies like the US dollar are inflationary in the long run, but Bitcoin is the complete opposite thanks to Bitcoin halving; it is guaranteed to be deflationary.
How Is Bitcoin Halved?
Bitcoin halving is carried out for every 210,000 blocks mined, which translates to roughly every four years. There is no central authority that decides the date of a halvening as this goes against the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. Bitcoin’s protocol is already designed in such a way that all miners agree to follow the rules.
The halvening will continue until each block reward reaches the smallest possible unit of Bitcoin, which is close to 0.00000001 BTC. As of now, about 18.7 million Bitcoins have been mined and are circulating in the cryptocurrency market (though many millions are irretrievably lost). This is equivalent to approximately 89% of the total supply of Bitcoin.
So, there’s really not much left waiting to be mined, which is all the more reason for Bitcoin Halving to take place: it reduces the number of block rewards earned by miners, slowing down the entire mining process.
Is Bitcoin Halving Good or Bad?
Like the Olympics, Bitcoin halving happens once every four years and is thus a highly anticipated event—the Bitcoin Block Reward Halving Countdown website is counting down to the next halvening.
All past Bitcoin halvings have been received positively by both miners and Bitcoin investors, with the value of the coin skyrocketing after every halving event.
In turn, although the supply of Bitcoins is halved, miners are still be incentivized to mine for more because ultimately, the value of Bitcoin has increased.
As lucrative as it sounds, there is also a drawback to the halvening. Miners make huge preparations at the eve of halving events. They spend large amounts of money (tens of thousands for some) to buy the most powerful mining hardware. This is because after each halving, it becomes more difficult and time consuming to mine for a Bitcoin, so miners need to be equipped with the most advanced mining tools in order to continue with their job.
However, as block rewards are halved, some miners may decide to give up on mining entirely due to excessive computational and electrical costs. For example, in the Bitcoin whitepaper, Nakamoto compared the mining process to mining for gold:
The steady addition of a constant amount of new coins is analogous to gold miners expending resources to add gold to circulation. In our case, it is CPU time and electricity that is expended.
Therefore, as more Bitcoin Halvings occur, BTC mining will become a more difficult task.
Past Bitcoin Halving Events
Every time a Bitcoin Halving event occurs is a big deal and is thus well documented. Here are the past Bitcoin Halving events that took place in the community, in chronological order:
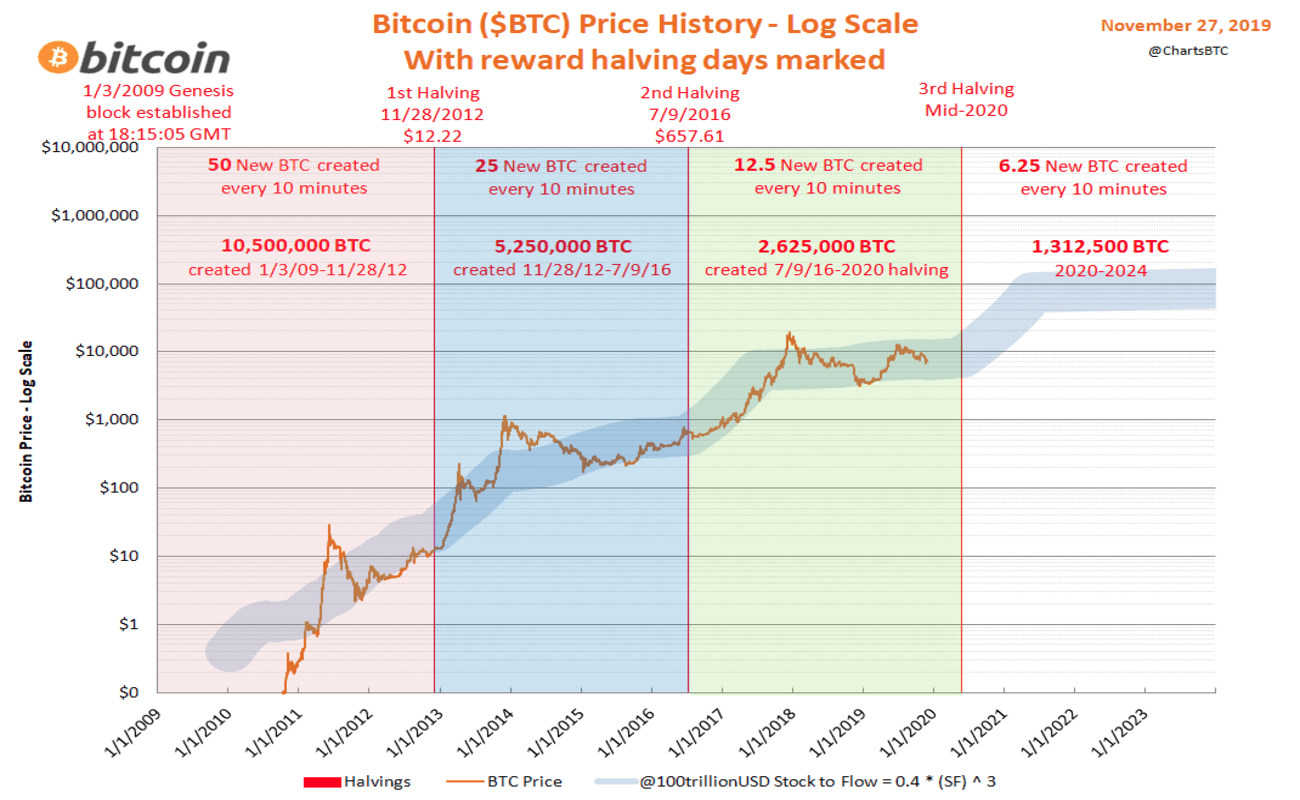
- 2009: This is Bitcoin’s pre-halving era. Block rewards begin at 50 BTC.
- 2012: the first halving occurs at block number 210,000. Block rewards dropped to 25 BTC. Bitcoin’s value increased from $12 to $1,207.
- 2016: the second halving occurs at block number 420,000. Block rewards dropped 12.5 BTC. Bitcoin’s value increased from $647 to $19,345.
- 2020: the third halving occurs at block number 630,000. Block rewards dropped to 6.25 BTC. Bitcoin’s value increased from $8,821 to $63,558.
Of course, other market movements during the time affected Bitcoin’s price. But Bitcoin halving certainly plays a significant role in Bitcoin’s meteoric price rises and is responsible for a bullish crypto market.
At this rate, the next halving will take place in 2024, when the block number reaches around 840,000. Over 99% of Bitcoins will be mined by 2032, and the block rewards will decrease to 0.78125 BTC by then.
The final halving will occur in the year 2140, until no new Bitcoins can be mined and miners will only receive transaction fees as rewards. Transaction fees currently take up less than 10% of a miner’s block reward income, but as we get nearer to the year 2140, the proportion of transaction fees distributed to miners will likely grow.
No one knows what will happen after all Bitcoins are unearthed, but it is possible that Bitcoin’s blockchain protocol may have gone through dramatic changes by then, so a new way of mining for Bitcoin may be introduced.
Mining for Digital Gold
Bitcoin halving is a major event that generates a lot of excitement in the crypto space. Bitcoin jumps dramatically in value after every halving, which is really a win-win situation for everyone involved. The very existence of such an event also shows that creating a scarce commodity in the digital world is possible through blockchain technology, and this could potentially change the way we perceive and use money in the real world.