It has been a whirlwind few years for AMD in which the company has pushed its hardware back to the top of the computing pile. AMD's recent successes with its Ryzen CPUs and new 5000 and 6000-series GPUs are driven by innovation.
One such innovation is AMD Smart Access Memory, a process that allows its hardware to "harness the full potential of GPU memory." Sounds great, right? But what is AMD Smart Access Memory? Furthermore, how does AMD Smart Access Memory work?
Let's take a look.
What Is AMD Smart Access Memory?
On a Windows system, your processor can only address a certain amount of graphics memory (VRAM) at once. Typically, the CPU can access 256MB of VRAM at a time. The limitation is a quirk of the 32-bit era carried forward into the 64-bit era, where we now have more powerful hardware with much larger amounts of graphics memory.
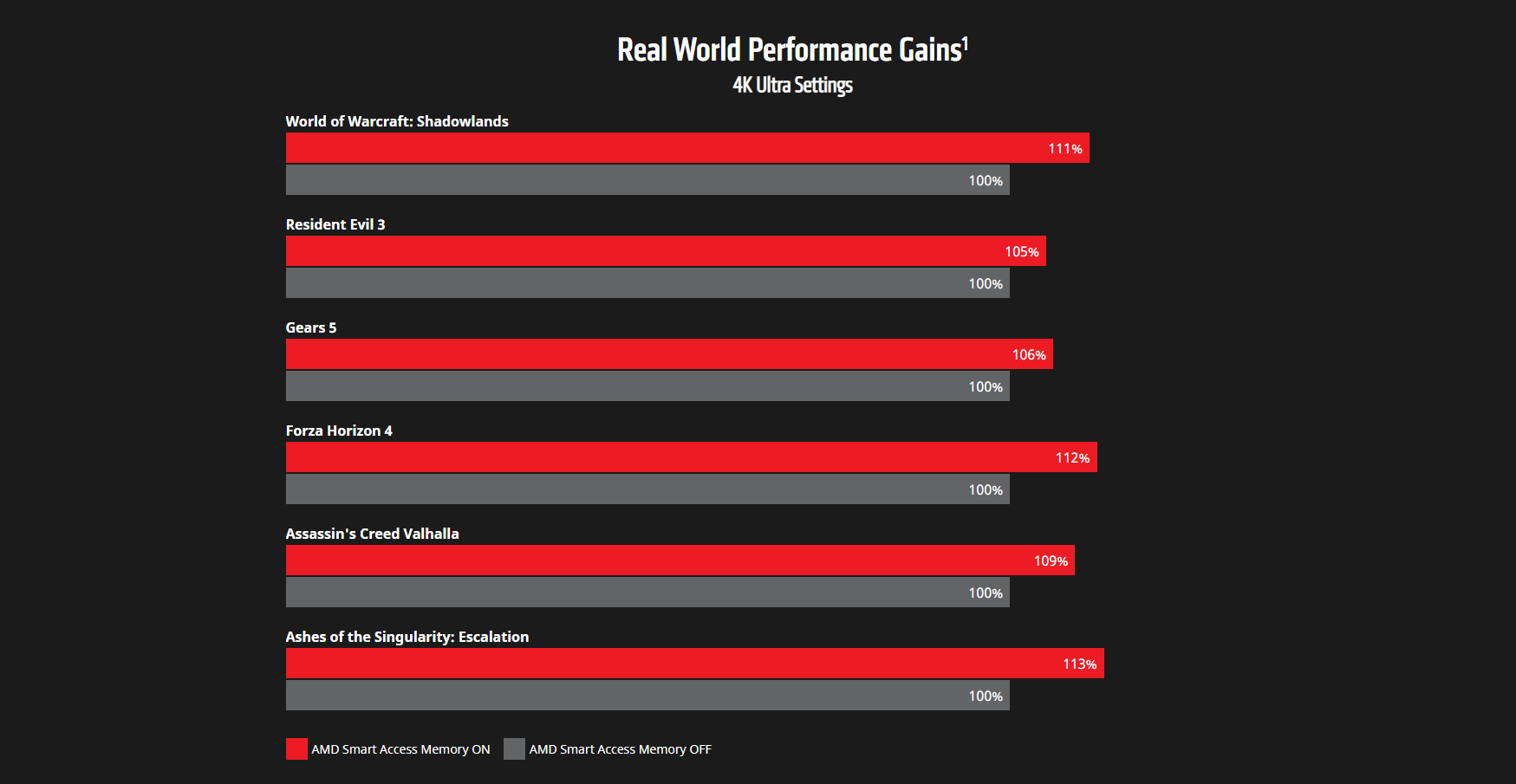
AMD Smart Access Memory (SAM) is AMD's solution for this quirk, opening up the entirety of the GPUs memory to the processor. With the CPU able to address all available VRAM, some games can receive a performance boost of up to 10 or even 15 percent.
In AMD's testing, Assassin's Creed Valhalla received a 9 percent performance increase while gaming on 4K Ultra settings, while Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation saw a 13 percent boost.
AMD Infinity Cache
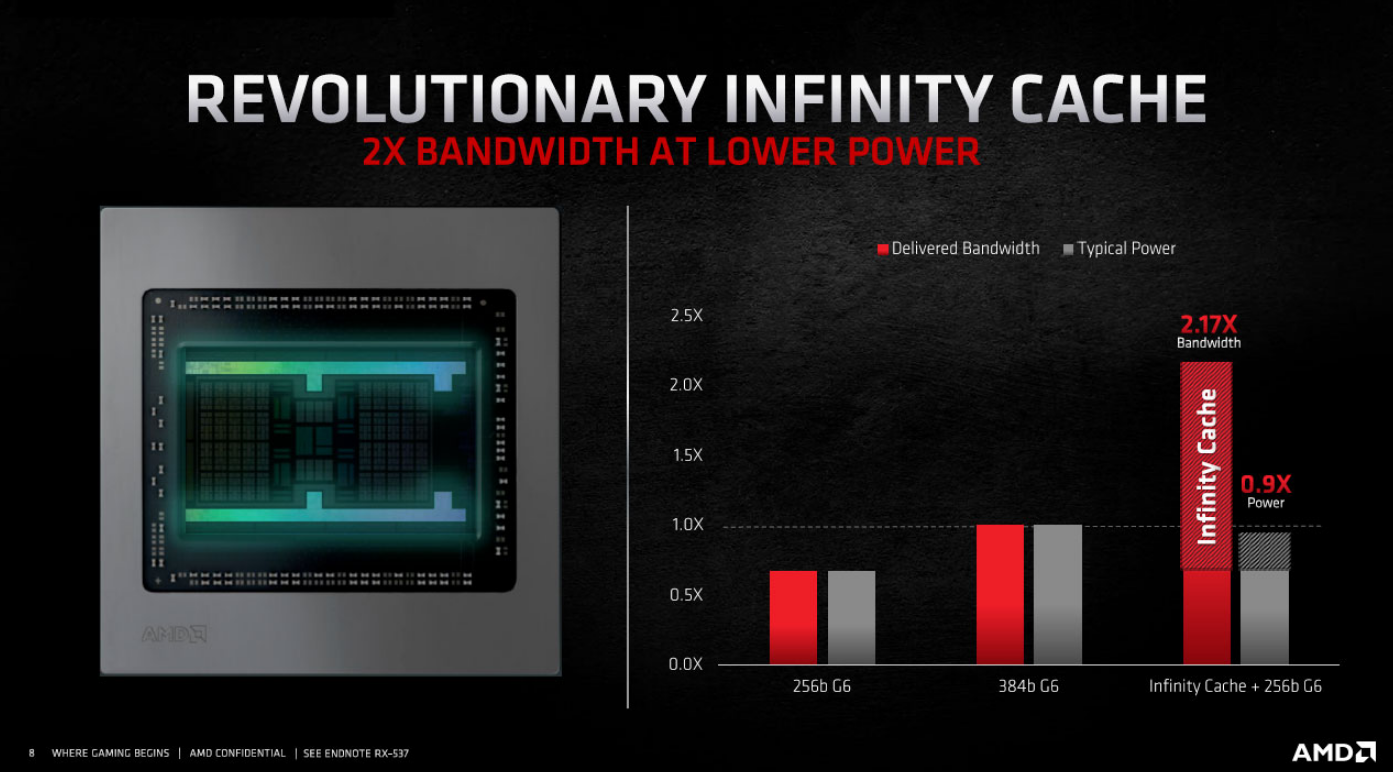
AMD Smart Access Memory's success ties into a graphics card innovation known as the AMD Infinity Cache, a feature exclusive to AMD 6000-series GPUs (which use the latest RDNA2 architecture).
The AMD Infinity Cache effectively sits between the L1 and L2 memory caches on your GPU but effectively works like a giant L3 cache. The overall effect is more efficient access to a wider pool of on-board memory, which in turn allows AMD Smart Access Memory to address more VRAM.
AMD's Infinity Cache is the first example of this architecture on a GPU. L3 caches are common in CPU architecture. For comparison, NVIDIA's highly rated Ampere GPUs use an increased L2 cache rather than an L3.
Because of this difference, the NVIDIA GPUs use a wider 384-bit or 320-bit memory interfaces (which require more power and are more expensive to manufacture) in comparison to the 256-bit interface found in the AMD 6000-series.
That's not to knock NVIDIA's 30-series GPUs. The NVIDIA 30-Series are clearly outstanding GPUs in their own right.
AMD Smart Access Memory Available on High-End Hardware
The success of AMD SAM isn't under question. Switching Smart Access Memory on demonstrably increases performance.
However, the feature is only available to AMD's top-tier hardware. The official AMD documentation indicates that the AMD Smart Access Memory requires the following hardware:
- AMD 500 Series motherboards
- AMD Ryzen 5000 Series CPU
- AMD Radeon RX 6000 Series GPU
This is all top-shelf computing hardware. However, it isn't quite as it seems.
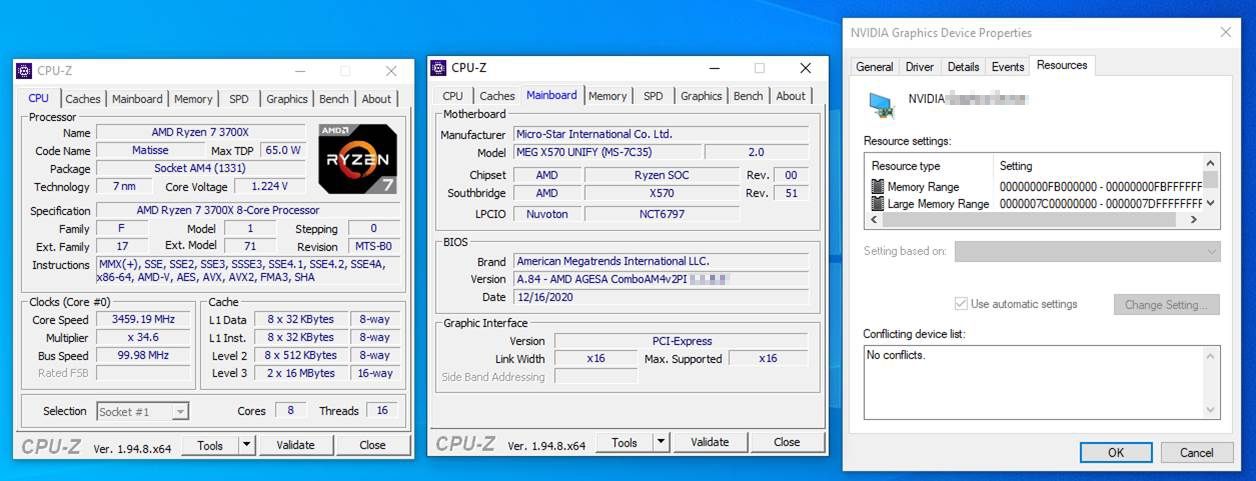
At the time of launch, AMD stated Smart Access Memory would only work with 5000 series CPUs. However, both Asus and MSI have enabled SAM on its respective hardware, sharing screenshots that show Smart Access Memory up and running with Ryzen 3000 CPUs and Ryzen 4000G APUs.
The images, first seen by Wccftech, confirm that SAM isn't out of reach for all AMD users. That said, neither MSI nor Asus are forthcoming with tweaking your system to enable Smart Access Memory use with the Ryzen 3000 CPUs and Ryzen 4000 APUs.
For now, the best bet for AMD Smart Access Memory (complete with the AMD Infinity Cache) is with the hardware listed above.
What Is AMD Rage Mode?
So, you know what Smart Access Mode and the Infinity Cache are. But what is AMD Rage Mode? Surely not another framerate boosting feature snuck into AMD's new hardware?
Well, you'll be pleased to know that's exactly what Rage Mode is: integrated performance presets that tune the GPU, adjusting power and fan levels accordingly.
For want of a better word, AMD Rage Mode is an integrated overclocking tool with preset performance levels. Currently, Rage Mode is only available to the AMD RX 6800 XT and the AMD RX 6900 XT, the top two cards of AMD's GPU roster.
The Rage Mode presets currently include:
- Balanced: The default preset which balances performance and power.
- Quiet: Delivers top gaming performance while keeping the fans quiet. AMD claims game performance "drops of only around 2 percent while the fan speed is reduced by almost 10 percent."
- Rage Mode: Ultimate, maximum performance, pushing the card to its limits.
AMD is marketing Rage Mode as an "XT" card exclusive. Of course, it didn't take hardware tinkerers long to bring Rage Mode to non-XT 6000-series GPUs. You can see how to enable Rage Mode in the following video.
Please note that as Rage Mode isn't officially supported, so your mileage may vary, and there is a chance you could damage your hardware in the process.
Disclaimer over, let's examine Rage Mode a little more. Rage Mode appears to be little more than the same "gaming modes" seen on previous hardware. Several tests from various hardware outlets found little actual gain when enabling Rage Mode.
Handy as focusing your hardware's capabilities are, your system and the GPU itself can already accommodate in-game requirements without being pushed to do so. You'll get much more mileage from a manual GPU overclock if you really do want to extract maximum processing power from your hardware.
Is AMD Smart Access Memory Worth the Money?
Looking at AMD Smart Access Memory as a single selling point for its new hardware isn't ideal. Smart Access Memory is just one of the many innovations that AMD has brought to its new GPU generation. You've now read about another one in the AMD Infinity Cache, which works with Smart Access Memory to deliver a better and faster experience.
One of the biggest things the introduction of SAM does is make building a complete AMD system an easier choice. In previous hardware generations, there was often a compromise for system builders between Intel and AMD hardware.
Now, with AMD's excellent Ryzen CPUs and new Radeon RX 6000-series GPUs, the choice is much easier to make, especially for those working to a specific budget.