Vector databases have gained a resurgence due to the widespread availability of pre-trained AI models. Although the concept of a vector database has been around for several decades, it is only now, in the age of large language models (LLMs), that vector databases can be used to their full potential.
Vector databases are particularly helpful in applications such as recommendation systems, image similarity search, anomaly detection, face detection, and natural language processing applications.
So, what exactly is a vector database? How does it work, and when should you use them to boost AI capabilities?
What Is a Vector Database?
A vector database is a way to store information through the use of vectors. Unlike the usual form of databases that organize data as tabulated lists, vector databases organize data through high-dimensional vectors. These vectors can then be represented in mathematical space as vector embeddings.
Vector databases are important as they hold these vector embeddings and provide features such as indexing, distance metrics, and similarity search based on vector embeddings.
Vector databases are services that can easily be integrated with a pre-trained model, many of which will need an API key to access the service.
What Are Vector Embeddings
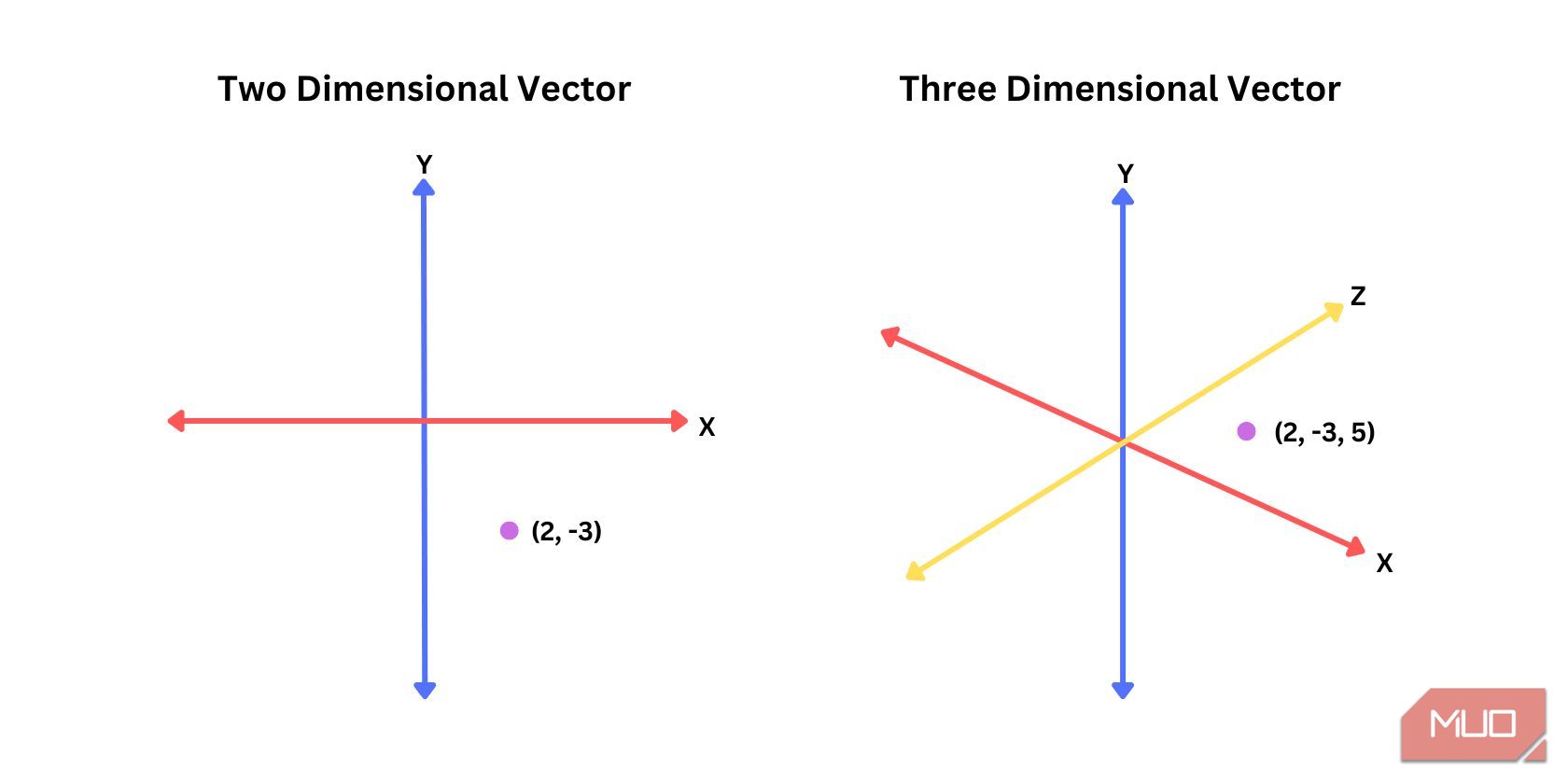
In simple terms, vector embeddings, or simply embeddings, are numerical representations of a subject or a word. For example, a two-dimensional embedding might look like "2, -3", where 2 represents two units in the positive direction along the x-axis, while -3 represents a negative three units along the y-axis. While a three-dimensional embedding would look like "2, -3, 5", where five places the data point 5 units in the positive direction of the z-axis.
Having more dimensions provides more context to what a piece of data is supposed to be. The number of dimensions used in vector database often range from 100 to 300 dimensions for NLP and several hundred for computer vision.
Generation of vector embeddings requires the use of vector embedding models and tools such as BERT, CNNs, and RNNs.
Why Are Vector Embeddings Important?
Having the ability to plot the location of data in mathematical space allows computers to understand the relationship between data points and how strongly correlated they are to each other. By knowing the degree of correlation between each data point, an AI model will have the capability to understand queries in a contextual manner like a human would.
Without understanding semantics or context, an AI may provide logically correct but contextually wrong answers. For example, the AI may misinterpret the phrase "He had a heavy heart as he walked away" as a guy with a heart condition instead of a guy feeling sad or burdened.
How Vector Databases Help Boost AI
Vector embeddings are important components in training various types of AI models. Having a specialized database that can store, index, and query vector embeddings is essential to maximize the benefits of using vector embeddings. Furthermore, vector databases boost your AI by being a fast, reliable, and scalable database that can continuously help grow and train an AI model.
Since vector databases can expand the capabilities of an AI model, businesses and organizations may use a vector database for various applications, including:
- Search Engines: Sometimes, people don't know which keywords to use when querying. A vector database helps the system understand your query by analyzing the context and retrieving the closest keywords with the strongest correlation to your query.
- Recommendation Systems: With vector databases extremely efficient at storing and retrieving data in combination with a large language model and memory, an AI system may learn things a person likes over time. This can then be automatically queried by an application to recommend various things that may interest a person.
- Image and Video Analysis: With video and image embedding models, AI models can be fine-tuned to work with images to find items that look similar to the query. This is currently being implemented in many online shopping apps and websites.
- Anomaly Detection: By recording actions as embeddings, an AI model can make the world more secure by detecting anomalies and certain outliers based on the norm. AI Anomaly detection is now a popular tool for fraud detection, system monitoring, and network intrusion.
How a Vector Database Works
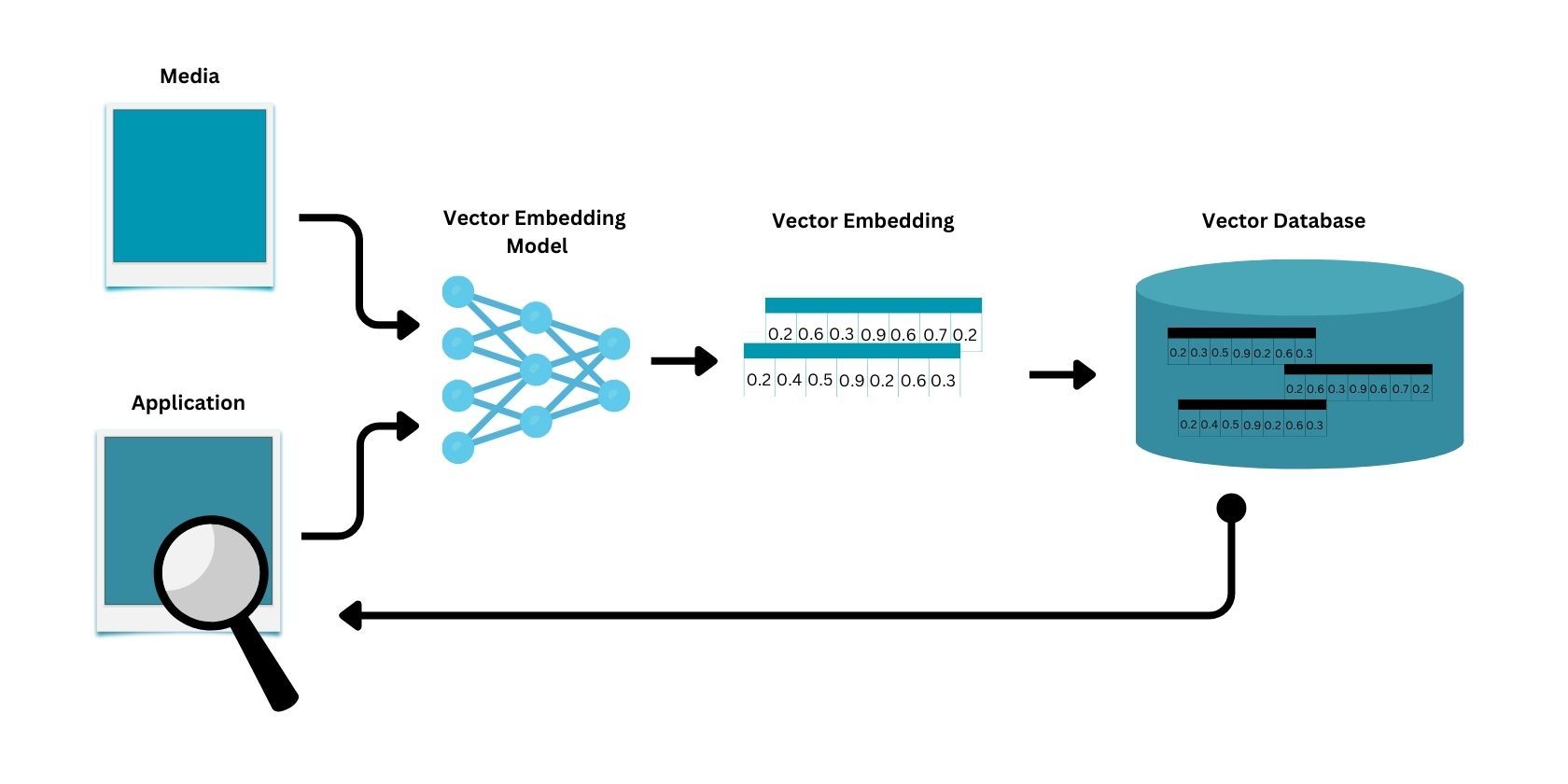
From generating vector embeddings to querying data from a vector database, your data undergoes a three-step process:
- Creation of vector embeddings: Based on the type of data, a vector embedding model is used to generate vector embeddings to be indexed. These embedding models are what turn words, images, videos, and audio into numbers/embeddings.
- Indexing: Once vector embeddings have been generated, they can now be stored on a vector database such as Pinecone, Milvus, and Chroma. These vector databases use various algorithms, such as product quantization (PQ) and locality-sensitive hashing (LSH), to index each embedding for quick and efficient storing and retrieval of data.
- Querying: When an application issues a query, the query must first go through the same vector embedding model used to generate the stored data on the vector database. The generated vector query is then placed on the vector database, where the nearest vector is then retrieved as the most fitting answer to the query.
Popular Vector Databases
With the explosion of publicly available pre-trained models, vector databases rapidly gained popularity as expanded the capabilities and rate of fine-tuning of these models. And with such high demand for vector databases, many companies have started their own vector database services; here are some of the most popular ones:
- Pinecone: A cloud-native vector database designed for fast similarity search. It features high scalability, analytics, and real-time insights, which is excellent for recommendation systems and image searches.
- Milvus: An open-source vector platform built with similarity search and AI applications in mind. It provides quick and efficient indexing and search capabilities for high-dimensional vectors. In addition, Milvus supports multiple indexing algorithms and offers SDKs for various programming languages.
- Redis: A high-performance vector database capable of supporting real-time applications, session management, and high-traffic websites. Redis is often used for real-time analytics, similarity search, and recommendation systems.
- Weaviate: Offers schema discovery, real-time updates, semantic search, and contextualizing data. With these features, Weaviate is often used to create personalized experience systems for applications.
The Future of Vector Databases
With the continuous growth of high-dimensional data types for images, videos, and text, vector databases will play a crucial role in improving and expanding the capabilities of current AI models. Through constant development with vector databases, we can expect better services in the fields of healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and cybersecurity.
If you want to experience and try a vector database for yourself, you can try installing Auto-GPT and implementing a vector database such as Pinecone. Of course, you will need an API key to use their services.