Power interruptions can cause big problems for many of us who rely on computers for work, school, business, and finance. We may lose data, forfeit crucial transactions, and unintentionally exit important meetings. They can even damage computer hardware which can further delay us from making progress on our tasks.
As a solution, many people started to buy uninterruptible power supplies, also known as UPS. These devices have proven to be so effective that they have become a staple in many businesses and institutions. But what exactly is a UPS? And how does it work? Let's find out!
What Is a UPS?
A UPS or uninterruptible power supply is a device used to maintain power during power disturbances such as power dips and power outages. A UPS essentially acts like a power bank for your computer but with an automatic transfer switch (ATS) that provides instant power should a power failure occur.
A UPS is often used in business facilities, hospitals, schools, etc., and is becoming increasingly common in households as many people see the benefits of a UPS.
Benefits of Having a UPS
Having a UPS beside your computer is a great way to ensure you can continually work on your tasks even when power fails. Aside from providing power during an outage, here are a few other benefits that make a UPS the best backup power supply:
Continuity: Although there are other ways to power your PC during a power outage, a UPS utilizes a special switch that instantly provides power without your computer noticing the swap between primary to backup power. This prevents your PC from immediately turning off, which allows you to work continuously without needing to boot the computer and load applications.
Data Loss Prevention: A UPS provides uninterrupted power. During a power failure, a UPS provides instantaneous power to your PC and notifies you when backup power is activated. This gives you time to save your data or continue working until the battery runs out of power.
Hardware Protection: Depending on what kinds of UPS you get, you can expect various levels of protection from all kinds of power disturbances. This ensures that the delicate components in your computer are always operating within the electrical tolerances they are designed for.
How Does a UPS Work?
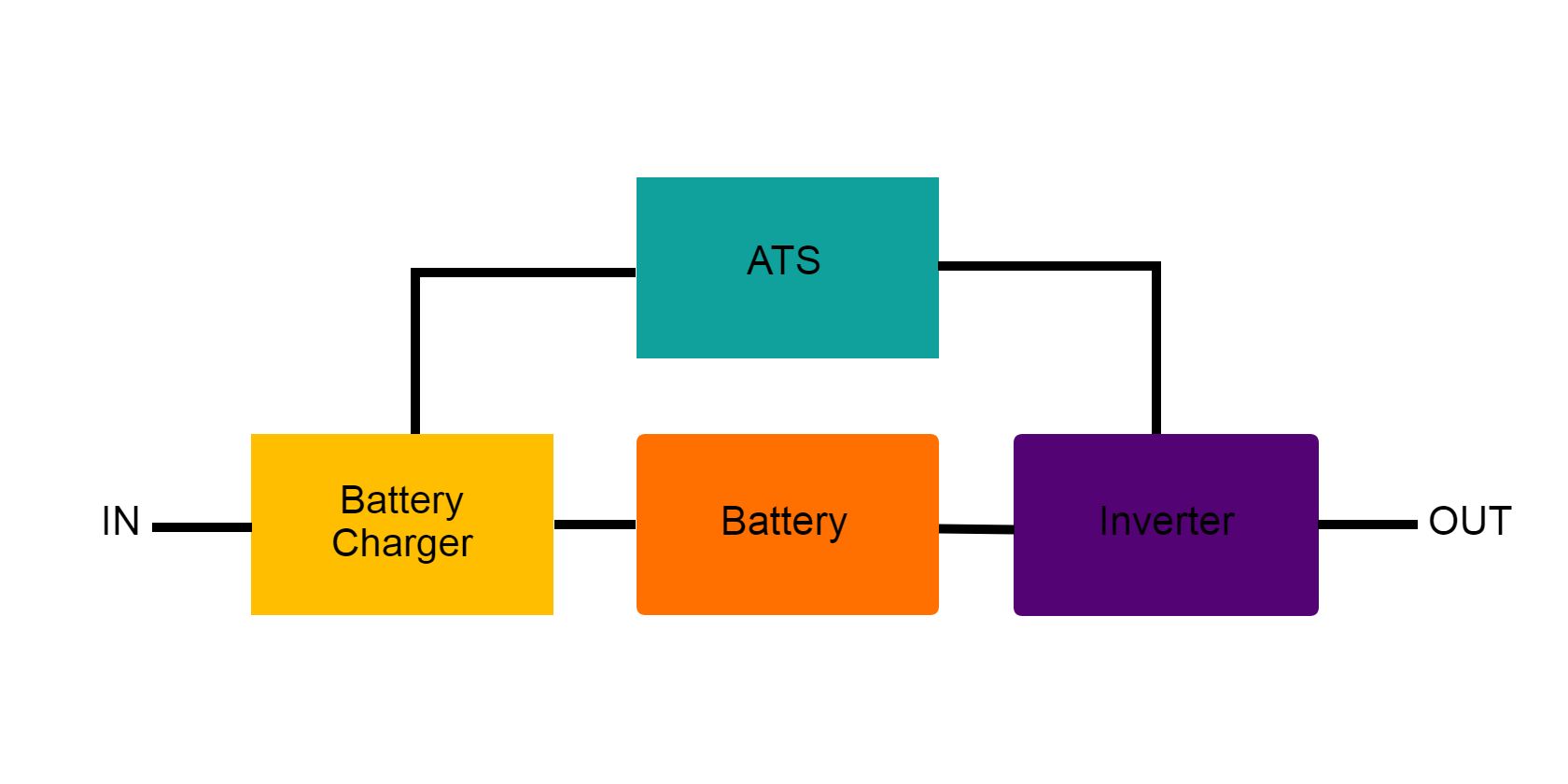
A UPS is basically a short-term battery power supply with a fast switch that provides instantaneous power. The essential components within a UPS are a battery, battery charger, inverter, and automatic transfer switch (ATS).
To set up the system, you simply plug your computer into the UPS and power the UPS through a wall or convenience outlet.
During normal operation (when power is available), the UPS passively charges your battery through the battery charger while simultaneously powering your computer. When a power outage occurs, the ATS automatically cuts off power from the house and switches to the backup power coming from the battery and inverter.
Depending on the type of UPS, there may also be other modes to prove uninterrupted power to your computer.
Common UPS Configurations
There are quite a few power disturbances that may damage your computer or other sensitive electronic devices. These disturbances are categorized as line noise interference, undervoltage, overvoltage, power sag, power surge, and power outage.
To combat these disturbances, manufacturers have started coming up with different types of UPS with varying degrees of protection. These UPS configurations are offline/standby UPS, line-interactive UPS, and online/double conversion UPS.
To know which UPS is better suited for your use case scenario, let's talk about each UPS configuration, its benefits, and how it works. Let's start with the most common, the offline or standby UPS:
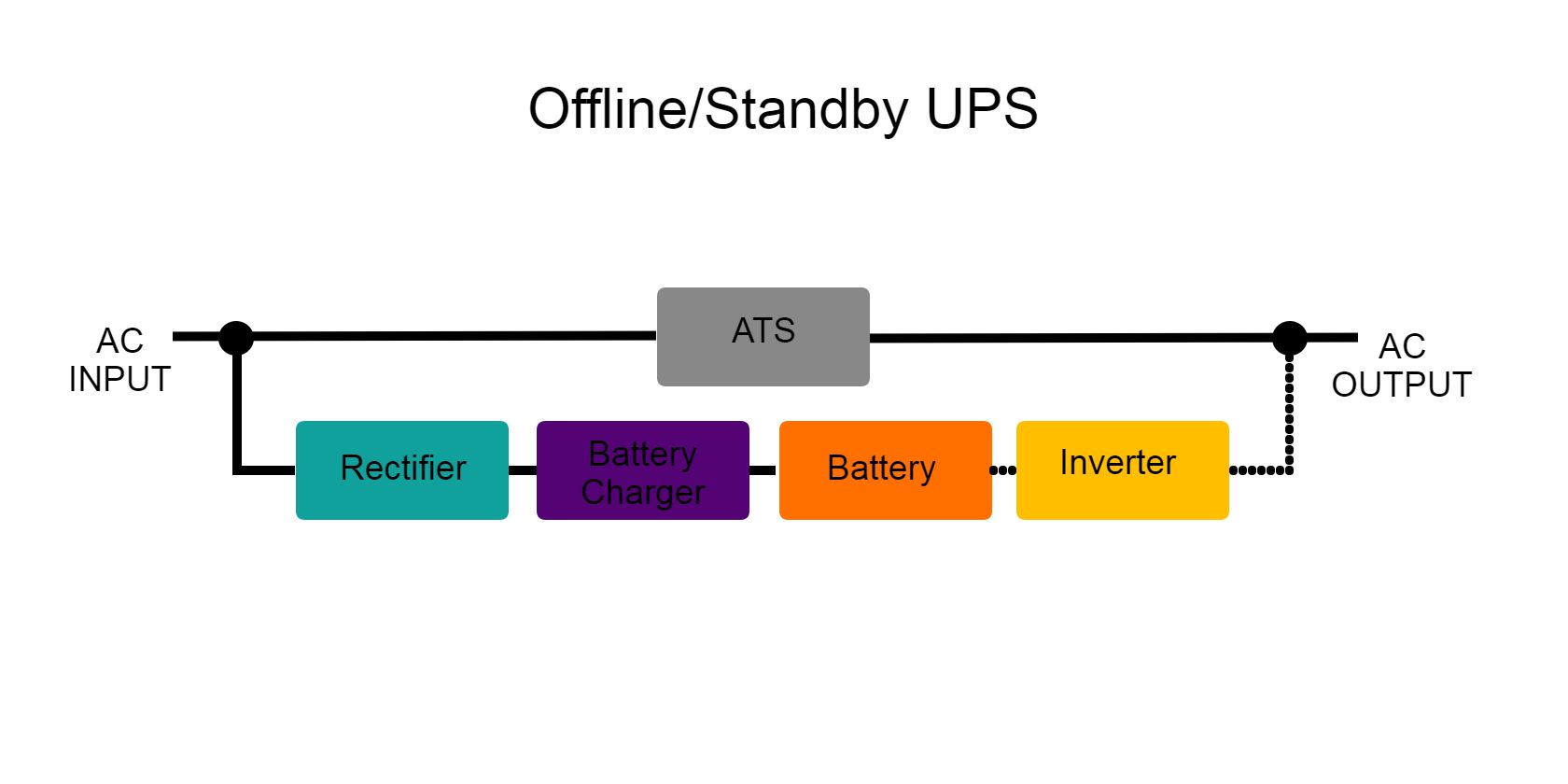
1. Offline or Standby UPS
An offline or standby UPS is the most common UPS in the market. It protects against power outages with its standard configuration of a battery charger, battery, ATS, and inverter.
Although it only provides the most basic protection, its cost-effectiveness in preventing data loss and continuous short-term power makes it common among households. Since this type of UPS only provides minimal protection, you should consider getting a surge protector.
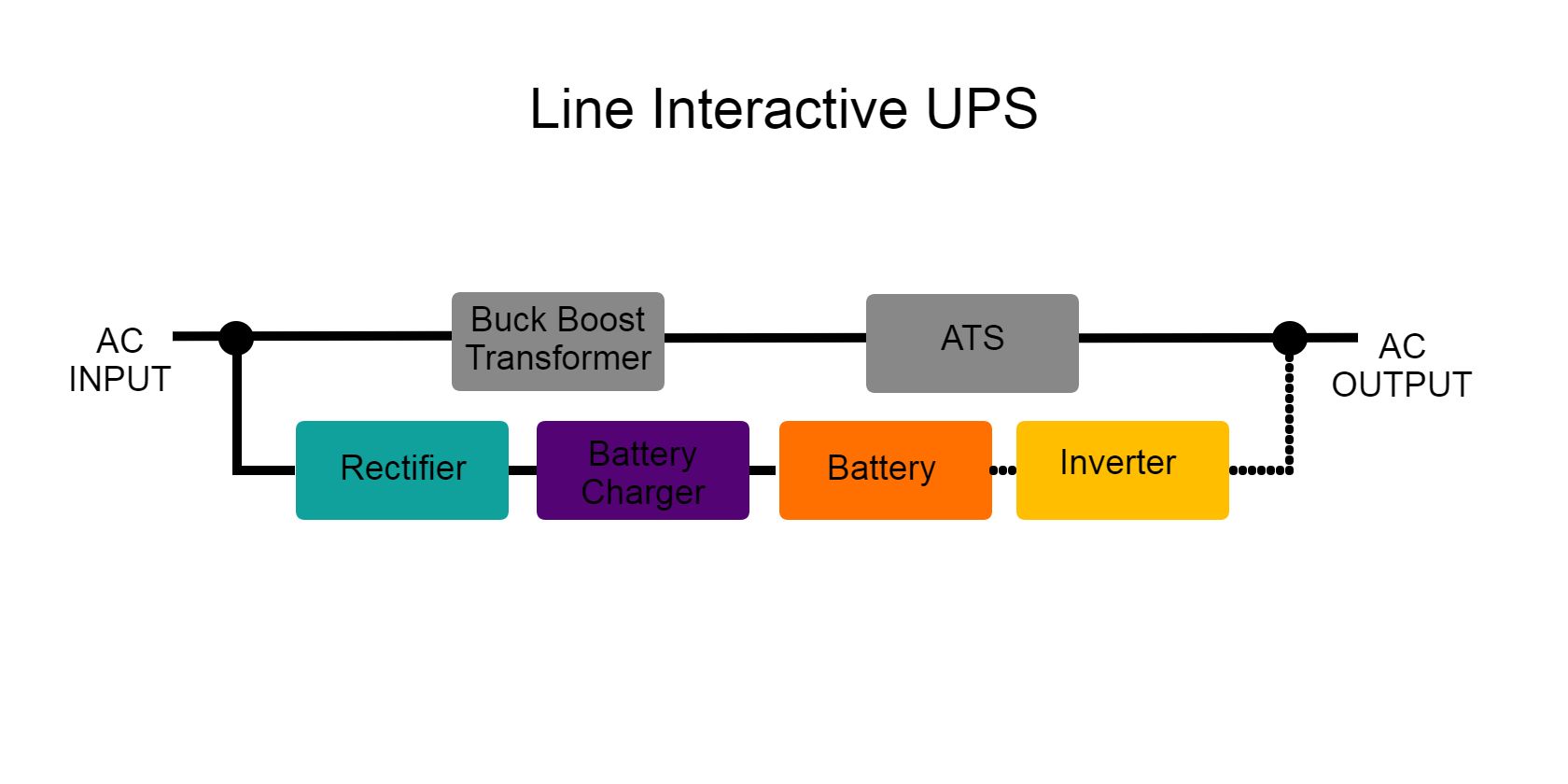
2. Line-Interactive UPS
Line-interactive UPS provides significantly greater protection as it negates the effects of power outages, power surges, power sag, overvoltage, and undervoltage to your electronic devices. These types of UPS are commonly found in high-scaling businesses but are also getting popular in common households.
A line-interactive UPS is composed of the same components as an offline UPS but with the addition of a buck-boost transformer. This type of transformer balances out noticeable power attenuations before reaching the device or equipment.
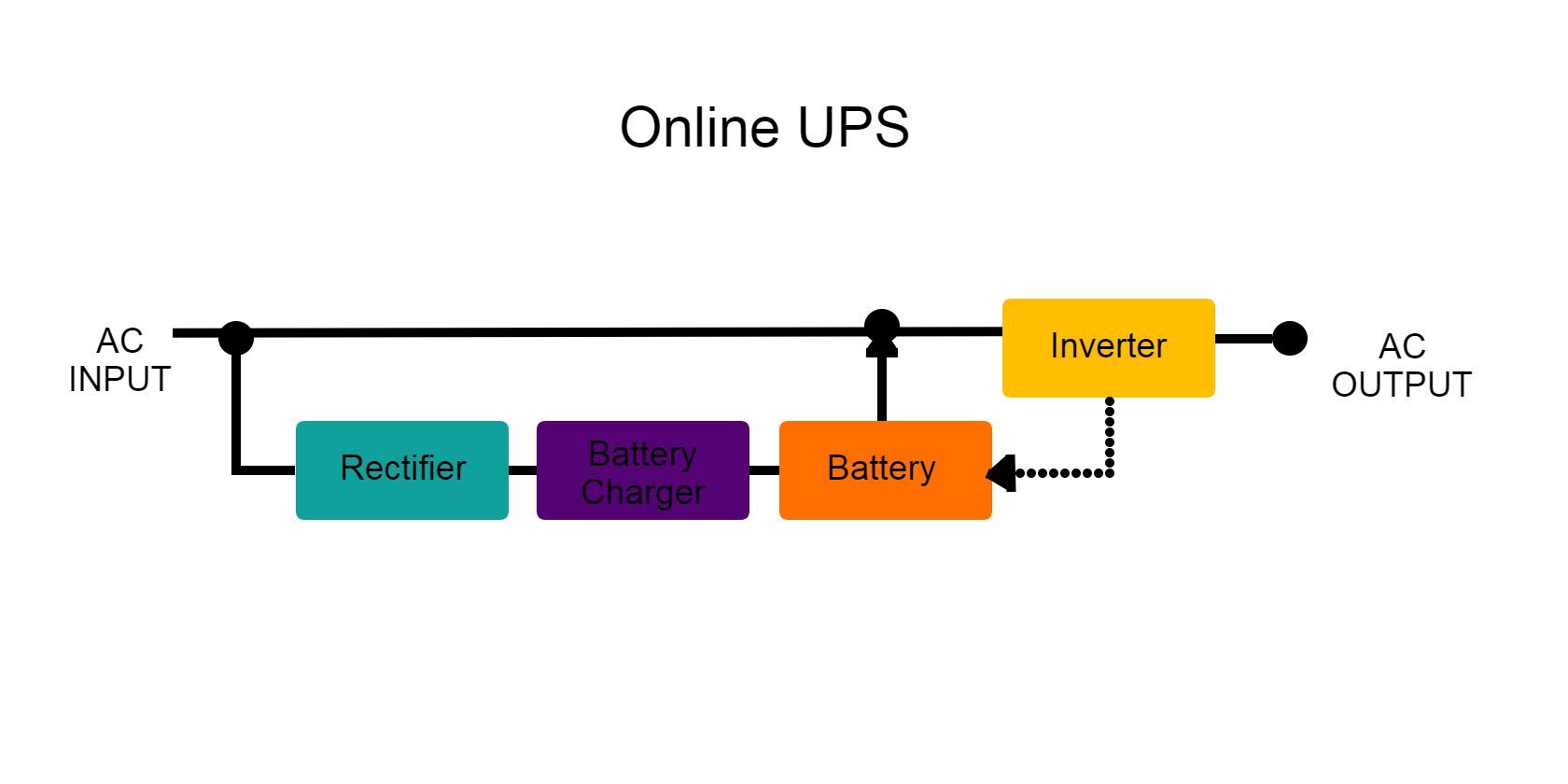
3. Online or Double Conversion UPS
An online or double conversion UPS is reserved for sensitive devices used in mission-critical applications such as medical equipment, online banking systems, and emergency communication equipment. This type of UPS isn't for household use as it's typically big, heavy, and expensive to buy and maintain.
An online UPS is unique as it mainly has a full-bridge rectifier, a battery charger, and an inverter. The idea of this UPS is to power devices only through the batteries installed inside the UPS with no direct connection to the power grid. This essentially sandboxes any device powered by the online UPS, effectively protecting against all power disturbances, including line noise interference.
How Does a UPS Compare to a PPS?
Aside from UPS, you could go for another popular backup power supply known as a portable power station (PPS). A PPS is much like a UPS but without an ATS, preventing it from providing instantaneous power to your devices. A PPS, however, has its own advantages, such as higher watt outputs, portability, and significantly bigger batteries.
If you're looking for a backup power supply for emergencies and weekend glamping trips, then a PPS is a good option you should be considering. But if you're specifically looking for something to protect your data, work progress, and device hardware from power disturbances, then a UPS should be the best companion for your device.
Although both provide backup power, PPS and UPS are different devices used for different purposes. Since UPS provides uninterrupted power and a PPS provides longer-lasting power, getting both backup systems will always be the best option.
UPS Protects Your Computer Round the Clock
Uninterruptible power supplies are essential devices that every person with a desktop computer should have. Not only does it ensure you get uninterrupted power, but it also protects your devices from harmful power disturbances.
But remember that a UPS isn't a PPS, and it must be plugged into a wall outlet 24/7 to ensure your PC gets round-the-clock protection. Although pricier, it may also be best to spend more on a line-interactive UPS than an offline UPS if you care about the longevity of your devices.