When it comes to cyberattacks, there are a wide variety of tactics that hackers use to disrupt networks and steal sensitive information. One such method is known as a smurf attack based on the smurf malware, which can cause significant damage to a target system.
Despite the name, a smurf attack has nothing to do with small blue creatures. Just as the cartoon characters take down larger enemies regardless of their size, this attack uses little packets to take down whole systems. It doesn't matter if you're here looking for information on cybersecurity or on Gargamel: everyone needs to know what a smurf attack actually is and how they can protect against one.
What Is a Smurf Attack?
A smurf attack is a distributed denial of service attack that occurs on the network layer and attacks by sending and overloading the victim's server with numerous Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo requests. These ICMP requests overwhelm the server, making it impossible for it to process all the incoming traffic. Hackers execute a smurf attack using malware called "DDOS.Smurf".
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a cyberattack where multiple systems are used to flood a target website or network with traffic, causing it to become unavailable to users. In a DDoS attack, the attacker usually gains control of a large number of computers and uses them to generate a high volume of visitors directed at the target.
The main goal of a DDoS attack is to overwhelm the target with so much traffic that it becomes unable to handle legitimate requests, making it difficult or impossible for users to access the website or network.
The History of Smurf Attacks
The first smurf attack was carried out in 1998 on the University of Minnesota. The code used to carry out this attack was written by a renowned hacker, Dan Moschuk. This attack lasted for more than an hour and affected the Minnesota Regional Network (the state internet service provider) and then, as a result, other large and small businesses and nearly all the MRNet customers.
What Is an ICMP Echo Request?
A smurf attack relies on ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) echo requests, but what does that mean? An ICMP request is a type of message sent from one device to another on a network to test the connectivity of the receiving device and to determine whether it is reachable and responsive. It is also known as a ping request, due to the command commonly used to initiate it.
When an ICMP echo request is sent, one device sends a packet to the receiving device containing an ICMP echo request message. If the receiving device is working, it responds to the request by sending an ICMP echo reply message back to the sending device, signifying that it is reachable and responsive.
ICMP echo requests and replies are commonly used by network administrators to troubleshoot network connectivity issues and diagnose problems. But they can also be used by attackers to probe and scan networks for vulnerable devices or to launch DoS attacks like ping floods or smurf attacks.
How Does a Smurf Attack Work?
Smurf attacks use numerous ICMP packets/echo requests to create a denial of service attack on a system. A smurf attack might sound similar to a ping flood, but it is even more dangerous.
The difference between a smurf attack and a ping flood attack is that the former uses amplification to increase the volume of traffic directed at the victim, while also making it harder for the victim to detect the source of the attack.
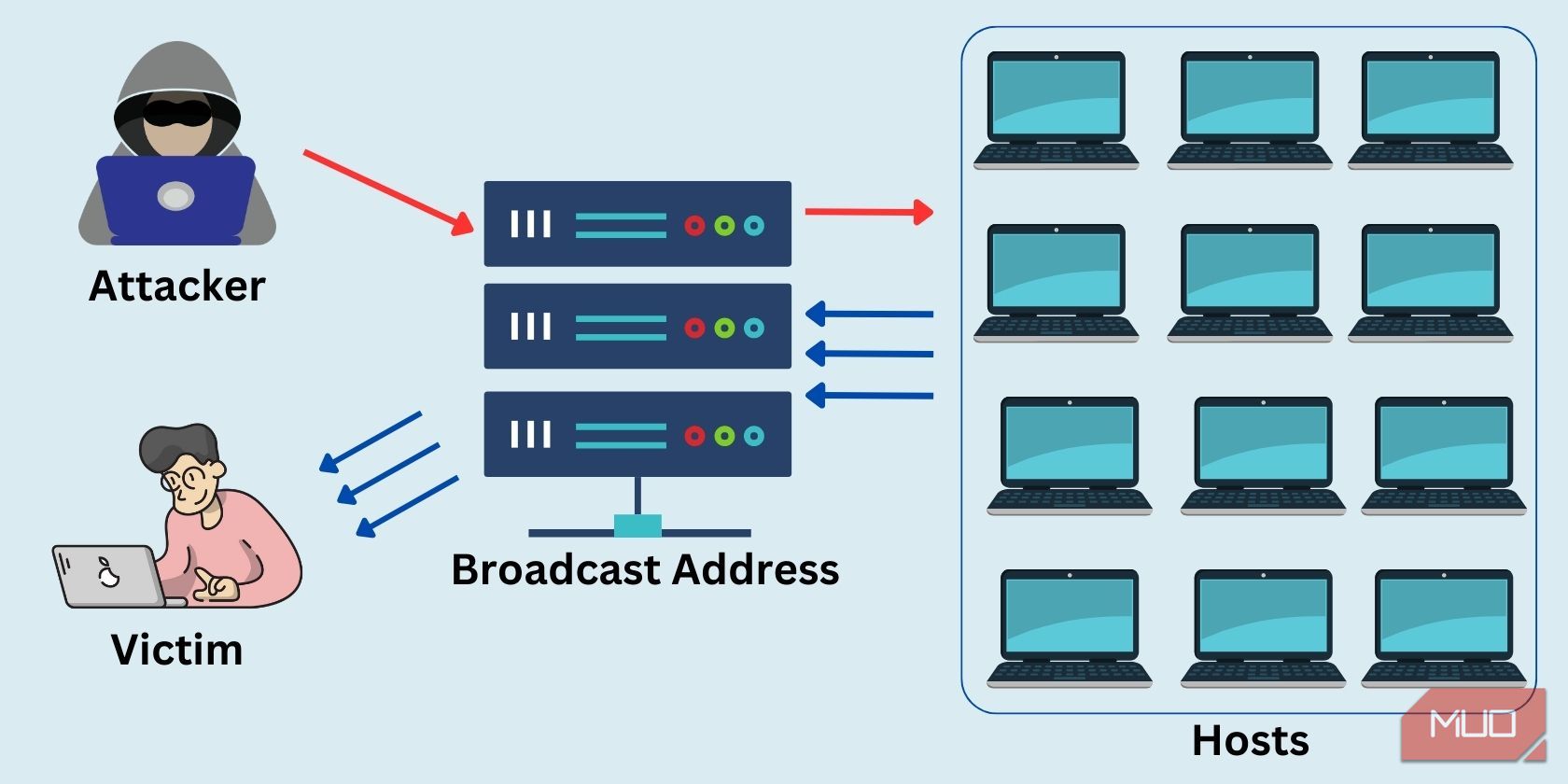
In a smurf attack, the cybercriminal sends numerous ICMP echo requests to the broadcast address of a network, with a spoofed source IP address that matches the victim's address. The broadcast address of a network is a special address that is used to send a message to all hosts on that network.
When these requests are broadcasted, all the hosts on the network will receive the requests and in turn reply to them with ICMP echo replies, which are then sent back to the victim's IP address.
Since the source IP address of the original ICMP echo requests is spoofed to match the victim's IP address, all the ICMP echo replies generated by the hosts on the network will go to the victim. This causes considerable amplification, where the amount of traffic directed at the victim is much greater than the original amount sent by the attacker.
So, if the attacker sends 100 ICMP echo requests to broadcast addresses containing 100 hosts each, the victim's IP address will get 10,000 ICMP echo replies. This amplification effect makes smurf attacks particularly effective and dangerous, as they can overwhelm a victim's network or server with a relatively small amount of traffic from the attacker.
How to Prevent a Smurf Attack
To prevent and defend against smurf attacks, it is important to use effective strategies to monitor traffic on your network; doing so will help you detect and contain malicious behaviors before they begin. Some other preventive measures against smurf attacks include:
- Disabling IP-directed broadcasts on all network routers. This stops attackers from using it to amplify their attacks.
- Configuring network devices to limit or disallow ICMP traffic in general.
- Reconfiguring your firewall to disallow pings that do not originate from your network.
- Using anti-malware and intrusion detection software.
If you visit a website and it's not loading properly, it could be down due to a DDoS attack. Or maybe for routine maintenance. In fact, there could be numerous reasons for a site not working properly, so just be patient, come back later, and maybe check social media to see if there are any announcements about downtime.
Strengthen Your Organization’s Security Posture
To prevent cyberattacks like the smurf attack, it is important you carry out routine assessments and evaluations of your business' security posture. This helps to pinpoint the weaknesses in your systems, and in turn strengthen them by fixing and improving your security. It is also necessary to implement proactive incidence response plans in the event of a cyberattack.
By prioritizing cybersecurity and continuously improving security measures, you can better protect your organization's sensitive data and systems.