A VPN is a secure connection between your computer and the VPN provider's server. It adds another layer of protection to your internet connection, delivering some privacy and security bonuses.
So, if that's what a regular VPN does, what does a decentralized VPN do? How does it differ?
Read on to learn how decentralized VPNs work, how they compare to a regular VPN, and whether a decentralized VPN is right for you.
How Does a VPN Work?
Before diving into how a decentralized VPN works, consider how a regular VPN works first.
A regular VPN creates a secure tunnel between two parts of the internet. Think about it like this: a tunnel that goes under a mountain. Both sides link to a direct path through the mountain. In this case, the mountain is the internet.
You use a VPN to increase your security and privacy online. A VPN uses powerful encryption to protect your data in transmission from prying eyes. Anyone snooping on your data will struggle to figure out what you're doing, as well as where your internet traffic has originated from (thus protecting your location and potentially your associated identity).
When you connect to a VPN service, data moves between your computer and the VPN services servers. Between your computer and the VPN server, your data is heavily protected. Once your data leaves the VPN server, it is back in the wild. The website server won't know the originating IP address and therefore won't trace you to a single location. However, if you connect to your Facebook account even while using a VPN, they still know that it is your Facebook account.
How Does a Decentralized VPN Work?
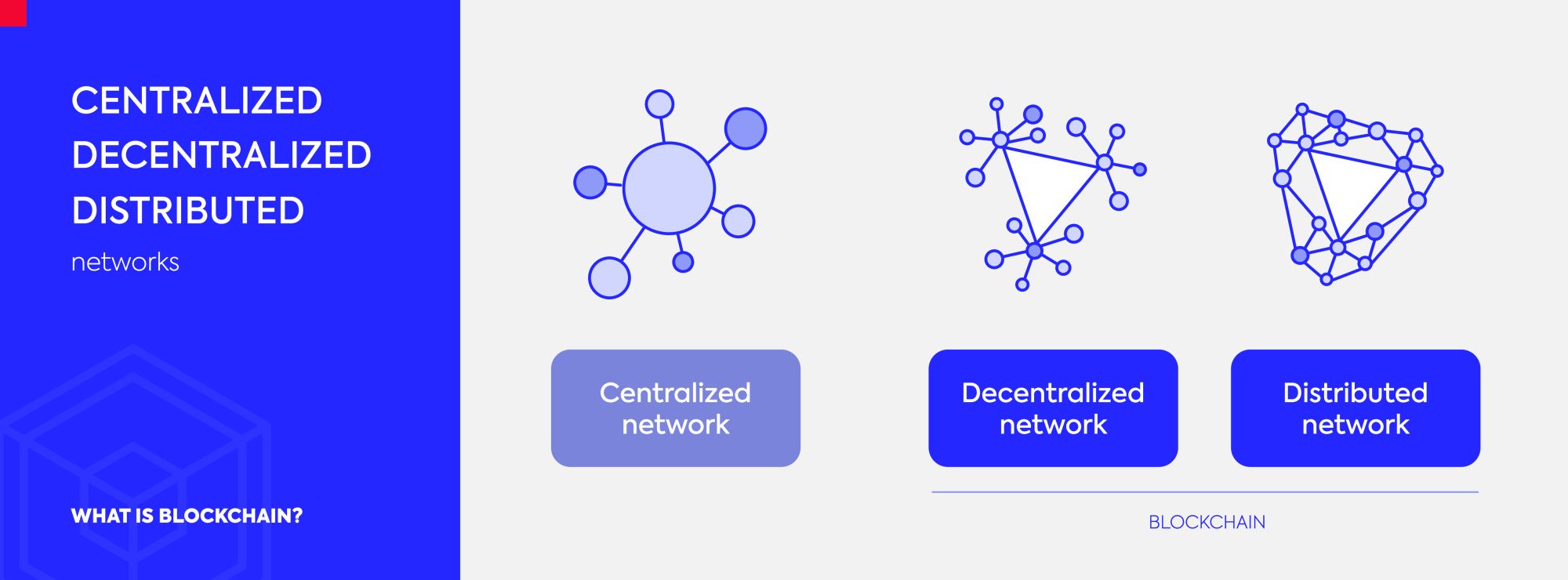
So, where a regular VPN connects you to a server, a decentralized VPN (also known as a dVPN or P2P VPN) connects you to a network node. The decentralized VPN node could be a server, desktop computer, smartphone, laptop, or even a tablet.
The owners of these devices allow access to their hardware in exchange for payment, usually in the form of an associated VPN network credit. Once they bank the decentralized VPN network token, they can begin using the decentralized VPN service themselves, keeping the decentralized VPN economy moving and, for the most part, circular. Decentralized VPN nodes offer up and advertise an available amount of bandwidth to the network, and if the offer is good and the node is trustworthy, users can take up the offer.
But if there is no centralized authority or controlling entity, how does the decentralized VPN service work?
For the most part, decentralized VPN nodes can set pricing individually, offering up an amount of bandwidth to the network in exchange for a set number of network tokens. There is no set fee to join the network or advertise bandwidth. Furthermore, as there is no up-front fee, you only pay for the decentralized VPN bandwidth you use.
Decentralized VPN vs. Regular VPN: What's the Difference?
The biggest difference between a regular VPN and a decentralized VPN is the network configuration.
With the regular VPN, you connect to a proprietary server owned and controlled by the VPN service. There are many no-log VPNs that do not collect data on your internet activity while connected to their service. Some logless VPN services have even gone so far as to invite third-party auditors to confirm their no-log claims.
Even still, the biggest single failure point of a regular VPN is its network configuration and the trust you must place in one service taking control of and protecting your internet data. If it turns out that the company was collecting your logs all along (or you were using a cheap or free VPN service to begin with), all of the data you thought was private and secure has been logged.
A decentralized VPN eliminates this point of failure through its distributed network of independent nodes. Data is unlikely to travel through the same node frequently, and there are more potential nodes to choose from (although this does depend on the number of decentralized VPN nodes available to the network, so it's not without issue).
Second, a decentralized VPN is an implementation of a decentralized app (dApp). Because dApps are open-source and run on top of a blockchain, the code they use is open for scrutiny and allows anyone with technical knowledge to assess the service's privacy and security credentials.
Is It Worth Using a Decentralized VPN?
A VPN should enhance your privacy and security online. So the biggest question you face is whether a decentralized VPN is safer than a regular VPN?
When you weigh up the facts, a dVPN does appear to be the safer option on the face of things. Who wouldn't want better privacy, more anonymity, and a reduced threat of data tracking?
However, things aren't as clear-cut as they might appear. As decentralized VPN services are still relatively new, there aren't many options available to users. And of those options, even fewer are fully operational and able to deliver a consistent dVPN service.
Orchid dVPN
Right now, Orchid is one of the most active decentralized VPN services. You can sign up to the service, buy some network credits, and begin using the decentralized VPN instantly. The connection speed is good overall, though, unlike a regular VPN, you don't choose the location of the dVPN server. Therefore, it's somewhat pot-luck when it comes to exit nodes which will be an issue if you're attempting to access a service in a specific country.
During my brief test, it connected me to a device located in North Carolina, which is definitely not where I'm writing from, so that's a good start!
At the time of writing, there is no published number of Orchid dVPN nodes. The Orchid app has been downloaded over 100,000 times for Android, but there are no available stats for iOS or macOS.
Neutrality Way
Launching in 2022, Neutrality Way aims to become the first free decentralized VPN, echoing the free regular VPN services available now but with a significant twist: Neutrality Way cannot track and log your data in exchange for the service.
Neutrality Way solves this problem by creating the first decentralised VPN that does not require "trust" and operates transparently from within Ethereum blockchain, uses entirely open-source code and offers the unlimited data and time-based access plans that VPN users are accustomed to.
The free decentralized VPN service will be subsidized in part through its premium plans, with a small number of network tokens going towards the free dVPN's running costs. Although the free version will be a lightweight option, Neutrality Way hope that its existence will help onboard more users.
VPN or dVPN?
Whether you make the switch to a decentralized VPN will likely come down to the service on offer. If a dVPN allows the same range of choice as a regular VPN in terms of selecting a node in a specific location, more users are likely to make the switch, especially if prices remain low.
In the meantime, it might be worth waiting until more dVPN services come online, increasing your options and hopefully your security and privacy with them.