Following months of rumors and potential leaks, AMD officially announced its latest Ryzen Z1 Series APUs on April 25, 2023. Based on the existing Zen 4/RDNA 3 microarchitecture and built using TSMC's N4 (4nm) process node, both the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme are specifically designed from the ground up to power high-performance handheld gaming devices.With ASUS' ROG Ally being the first Windows-based handheld console to integrate these brand-new chips, let's look at how AMD's Ryzen Z1 stacks up against its "Extreme" variant in terms of specifications, performance, and value.
AMD Ryzen Z1 Series: Specifications and Features
Regarding specifications, AMD's Ryzen Z1 has been equipped with six Zen 4 CPU cores for a total of 12 logical threads that run at an advertised base clock of 3.2GHz and a maximum boost clock of 4.9GHz. The custom SoC incorporates a more modest RDNA 3 iGPU, notably the Radeon 740M, with four compute units (256 shaders) operating at a core frequency range of 1.5GHz-2.5GHz.
Meanwhile, the Ryzen Z1 Extreme features an eight-core/16-thread layout with a base frequency of 3.3GHz and a boost frequency of up to 5.1GHz. Besides bumping up the core/thread count and clock speed, the Extreme variant also packs in a more powerful RDNA 3-based Radeon 780M with 12 compute units (768 shaders) clocked at around 1.5GHz-2.7GHz.
Even though both APUs remain identical in their configurable TDP range of 9W-30W, the Ryzen Z1 Extreme benefits from a slightly larger cache size than the standard Z1 chip. Owing to its inclusion of two additional cores, the Extreme variant takes advantage of 24MB of combined (L2+L3) cache, whereas the Ryzen Z1 utilizes an overall cache size of 22MB.
Like AMD's consumer-grade CPUs from the Ryzen 7000 Series, the vanilla Ryzen Z1 and its Extreme counterpart offer native support for dual-channel LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 memory controllers. Given how crucial it is for APUs to rely on high-bandwidth system memory, both variants should be able to deliver improved performance and reduced latency in the vast majority of AAA games.
Moving on to the platform level, AMD's Ryzen Z1 Series APUs support the latest USB 4.0 interface, allowing for much faster data transfer rates (up to 40 Gbps) and easy connectivity for external storage and display devices. Furthermore, it is possible to enhance your gameplay experience with AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition using proprietary technologies such as Radeon Super Resolution, Radeon Chill, Radeon Anti-Lag, Radeon Boost, and AMD Link.
|
Specifications |
AMD Ryzen Z1 |
AMD Ryzen Z1 Extreme |
|---|---|---|
|
Platform |
Handheld |
Handheld |
|
Architecture |
Zen4/RDNA 3 |
Zen 4/RDNA 3 |
|
Process Node |
TSMC N4 (4nm) |
TSMC N4 (4nm) |
|
Cores/Threads |
6/12 |
8/16 |
|
Base Clock |
3.2GHz |
3.3GHz |
|
Boost Clock |
4.9GHz |
5.1GHz |
|
L1 Cache |
512KB |
512KB |
|
L2 Cache |
6MB |
8MB |
|
L3 Cache |
16MB |
16MB |
|
cTDP |
9W-30W |
9W-30W |
|
GPU Compute Units |
4 |
12 |
|
GPU Clock Frequency |
Up to 2.5GHz |
Up to 2.7GHz |
|
FP32 (Single Precision) Performance |
2.8TFLOPs |
8.6TFLOPs |
|
Memory Support |
LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 |
LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 |
|
Launch Date |
04/25/2023 |
04/25/2023 |
When we look closer at the core specifications of both APUs, it becomes apparent that the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme bear striking similarities to a couple of AMD's upcoming Ryzen 7040U Series chips for ultraportable laptops. Silicon enthusiasts pointed out that the standard Ryzen Z1 aligns closely with AMD's mid-tier Ryzen 5 7540U, whereas the Extreme variant sits next to the top-tier Ryzen 7 7840U.
In response to these queries, AMD clarified that while the Ryzen Z1 Series APUs adhere to the same hardware configuration as the Ryzen 7 7840U/Ryzen 5 7540U, they have been purpose-built to meet the unique requirements of handheld gaming devices in mind. As a result, the engineering team had to validate an entirely new power profile with further optimizations for maintaining the right voltage curves.
Compared to the Ryzen 7040U lineup, which is limited to a restrictive TDP range of 15-30W, AMD's Ryzen Z1 Series APUs can consume as little as 9W in less demanding scenarios or as high as 30W during intensive workloads. In addition to these adjustments, Team Red's XDNA AI engine has also been disabled (not removed at the hardware level) on the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme, facilitating a lower manufacturing cost.
AMD Ryzen Z1 Series: Gaming Performance and Power Efficiency
On paper, AMD's Ryzen Z1 can offer up to 2.8 TFLOPS of theoretical performance, similar to the desktop variant of Nvidia's GeForce GTX 1650. Meanwhile, the Z1 Extreme boasts a massive compute throughput of 8.6 TFLOPS, making it comparable to the GeForce RTX 3050 in terms of rasterization.
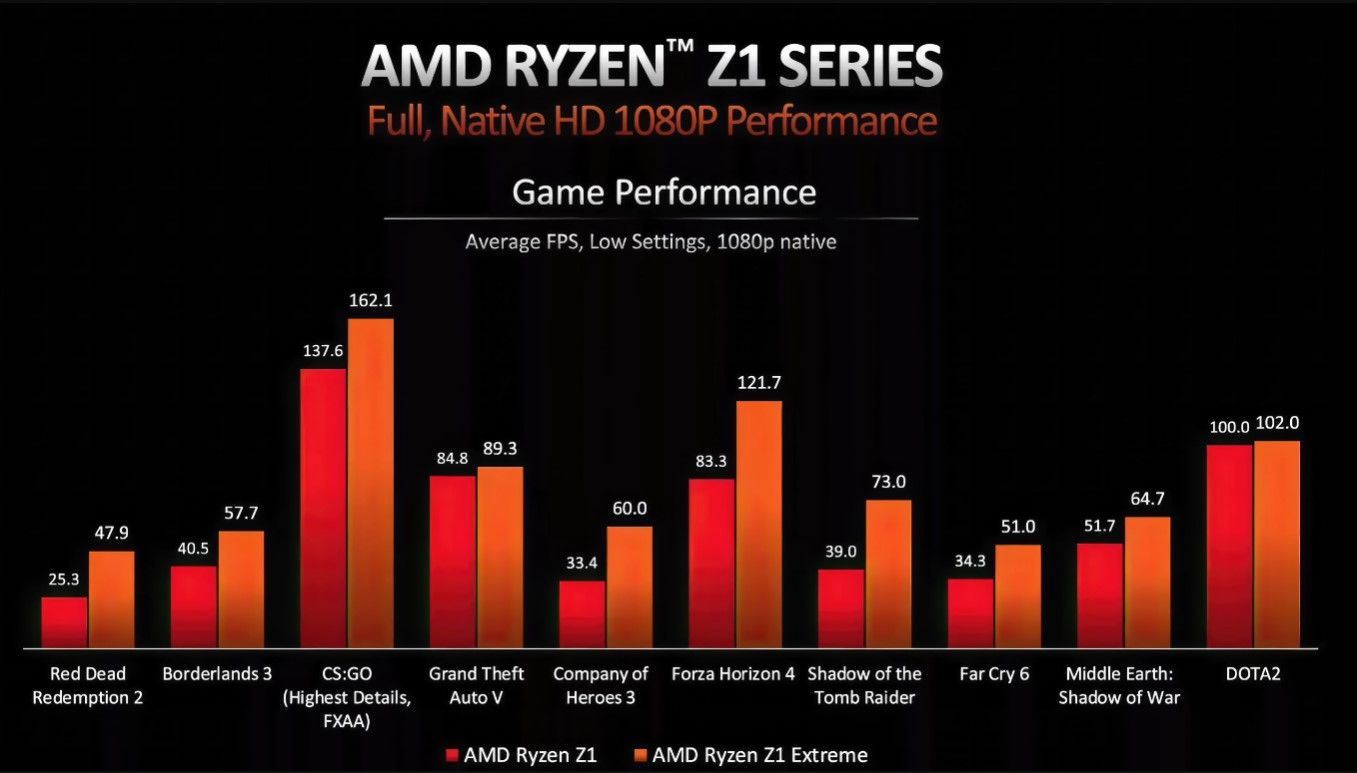
By comparison, Valve's Steam Deck (our Steam Deck review) with a custom Zen 2 plus RDNA 2 SoC can only manage 1.6 TFLOPS of graphics performance. In contrast, current-gen consoles like the Xbox Series X and PlayStation 5 reach up to 12.1 TFLOPS and 10.3 TFLOPS respectively. Since raw TFLOP ratings aren't an accurate measure of gaming performance in real-world scenarios, Team Red backed up its claims by sharing internal benchmarks of both APUs in a handful of popular AAA titles.
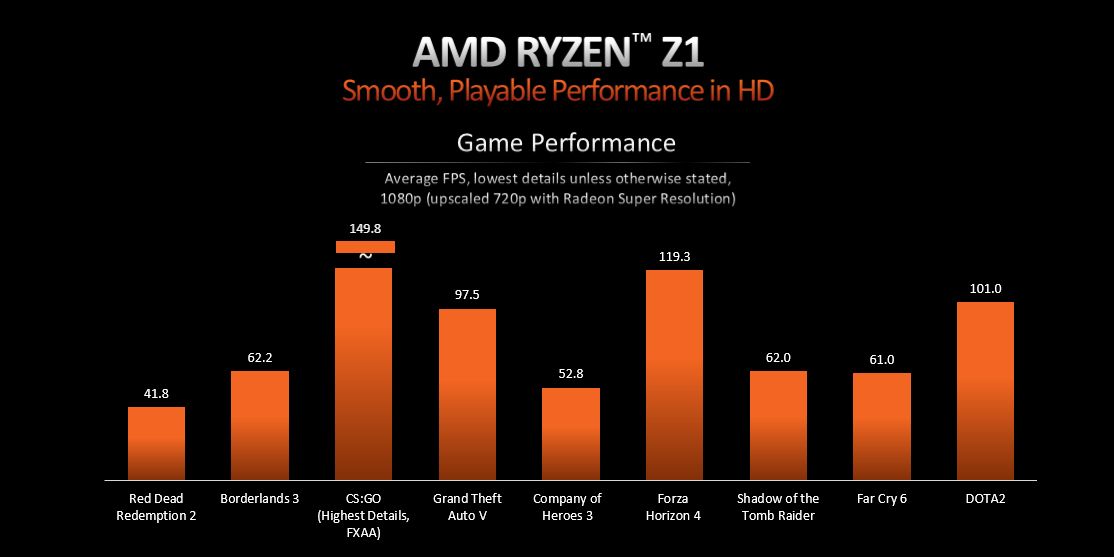
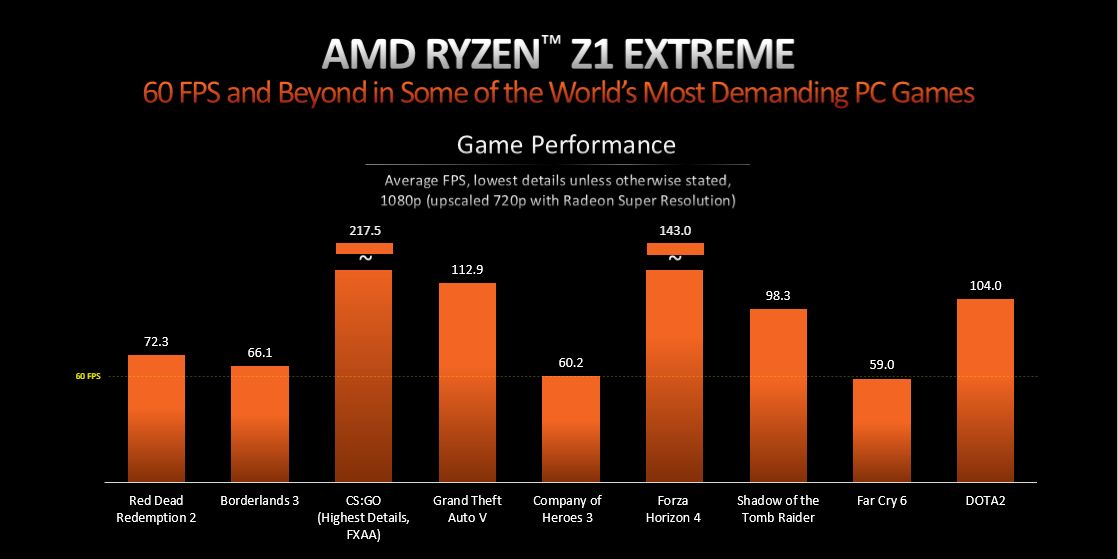
According to AMD's presentation slide, all the benchmarks listed throughout this chart were conducted at 1080p using low graphical settings. As is evident from the test results, the Ryzen Z1 maintains an average frame rate of 54 FPS, while the Extreme variant crosses the 60 FPS mark in all but the most demanding AAA games.
Although it remains unclear whether the games tested were based on the Low preset or the lowest possible settings, both APUs should be able to outperform the venerable Steam Deck by a considerable margin. Alongside the 1080p data, AMD showcased comparative 720p performance on both chips by utilizing its RSR (Radeon Super Resolution) upscaling technology.
With the 720p output upscaled to 1080p, the vanilla Ryzen Z1's average frame rates increase by about 18%, even in graphically intensive titles like Far Cry 6 and Red Dead Redemption 2. As for the Z1 Extreme, it delivers a more responsive gaming experience across the entire suite of benchmarks.
While the test results seem impressive at first glance, it should be noted that both APUs were running at their maximum TDP limits of 30W (Turbo mode). As soon as we drop to Performance mode with 15W of available power, the ASUS ROG Ally handheld console provides reasonable, though not exceptional, improvements over the Steam Deck.
However, when we switch to Silent mode, which locks the TDP at just 9W, the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme struggle to perform on par with AMD's aging yet competent Aerith SoC. Given the power-hungry nature of both APUs in this regard, we recommend setting a frame-rate cap and a fixed TDP limit of around 18W, especially if you're planning to game untethered.
AMD Ryzen Z1 vs. Z1 Extreme: Which APU Offers the Best Value for Money?
Considering the specifications, performance, and efficiency standards of both APUs, we believe that the ASUS ROG Ally, powered by AMD's Ryzen Z1 Extreme, offers a better price-to-performance ratio than the standard Z1 model. However, despite gaining a competitive edge over the Steam Deck in processing power, the Ryzen Z1 falls way short of expectations in its graphical capabilities.
Nevertheless, with a few minor tweaks to power management and pricing structure, the vanilla Ryzen Z1 could be a compelling option for future handheld devices primarily aimed at retro gaming.