So you've done your reading and your research and you've finally decided to take the leap and install Fedora Linux. Like most users, you were probably pleasantly surprised at how easy it was to install the world's best-known “bleeding-edge” Linux distribution.
We know Fedora runs great and provides plenty of power out of the box. But who wants an out-of-the-box experience? Isn't that why you left Windows? Let us show you how to make your system truly your own. Here are eight things you should do right after you install Fedora.
Don't Fear the Terminal Command Prompt!
For the sake of speed and efficiency, some of the points will include typing commands in the terminal. Don't let this intimidate you if you've never used the Linux command line before. We'll show you exactly what to enter, step by step. None of the commands listed here are destructive.
The easiest way to follow along is to copy the commands given here and paste them into your terminal. You can right-click and select Copy, or hit Ctrl + C to copy the text you've selected on this page. Then, in your terminal window, right-click and select Paste or press Ctrl + Shift + V to paste the commands. So, let's open the terminal app and get started.
1. Maximize Download Speed for Updates
Fedora's package manager comes with a pretty conservative configuration to make sure that it will work well for the majority of users. By making a small change to one of the options, however, users with a fast connection can significantly increase the speed at which the system downloads updates.
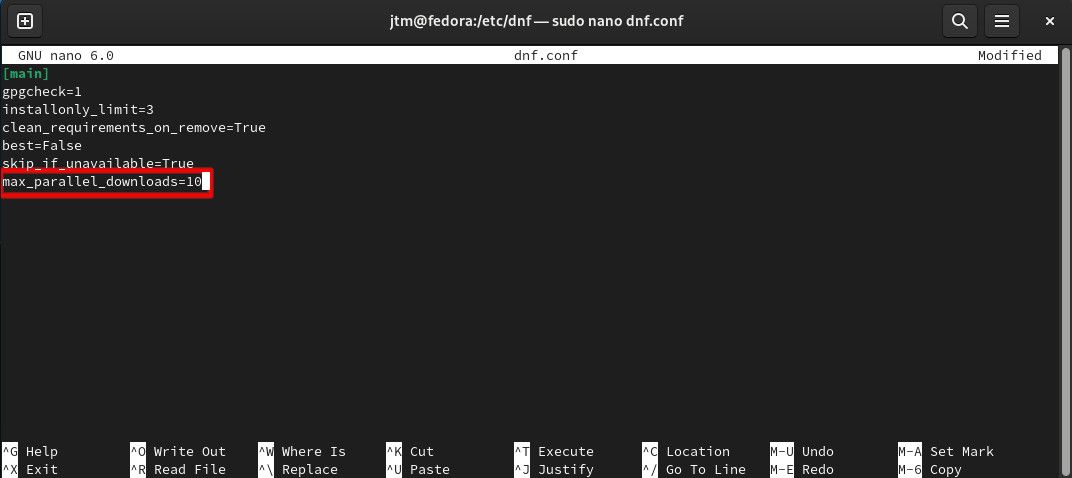
By default, when installing or updating anything, Fedora will download a maximum of three files at the same time. With some packages requiring the download of hundreds of files, increasing the number of simultaneous downloads will greatly increase installation speeds if you have a fast internet connection. So, let's raise that number to 10.
First, change into the directory where the configuration file resides, using the cd command. Then, open the dnf.conf configuration file in the nano text editor by entering the following commands (enter your password when prompted):
cd /etc/dnf
sudo nano dnf.conf
The configuration option you need to change is max_parallel_downloads. Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to move the cursor. If the max_parallel_downloads option is already there, simply change the number "3" to "10." If it is not there, enter the following after the last line of the file exactly as it is written here:
max_parallel_downloads=10
After making the change, hit Ctrl + X to exit, enter yes when asked to save the file, and then hit Enter to confirm the name of the file to save. The change will take effect immediately.
2. Check for System Updates
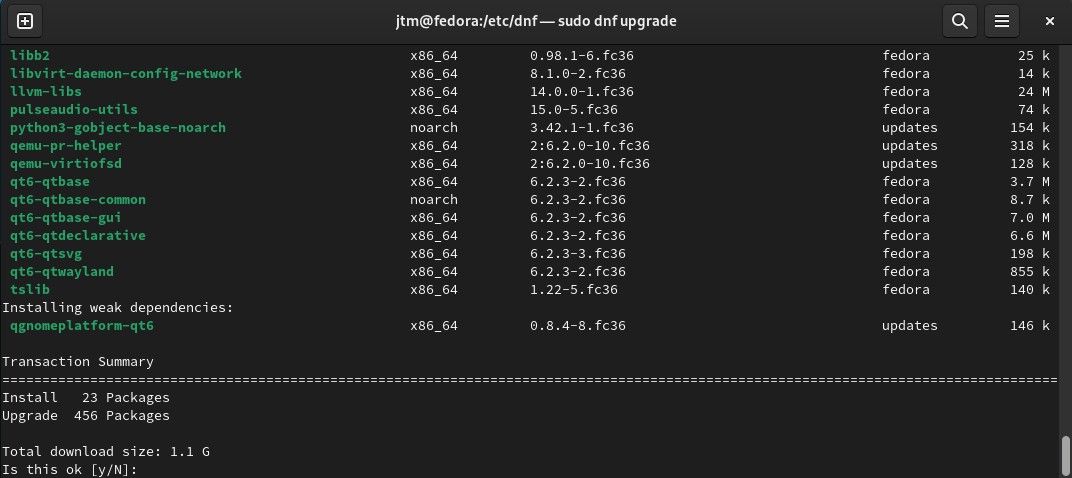
Now that we've increased the package manager download speed, it's a good idea to run a system update. The ISO image you installed the system from is most likely a bit behind the most current version of the operating system and applications.
sudo dnf upgrade
Enter the command above (enter your password if asked) and answer "yes" if any updates are found. This will bring everything on your system up to the latest version.
3. Install RPM Fusion Software Repositories
The RPM Fusion software repositories provide a wide variety of applications, utilities, and drivers that will greatly improve your Fedora experience. Most of what RPM Fusion offers is free software that can not be distributed with Fedora for one reason or another. For example, some licenses forbid distributing software as part of another package. Others are not fully open source or conflict with Fedora's packaging standards in some way.
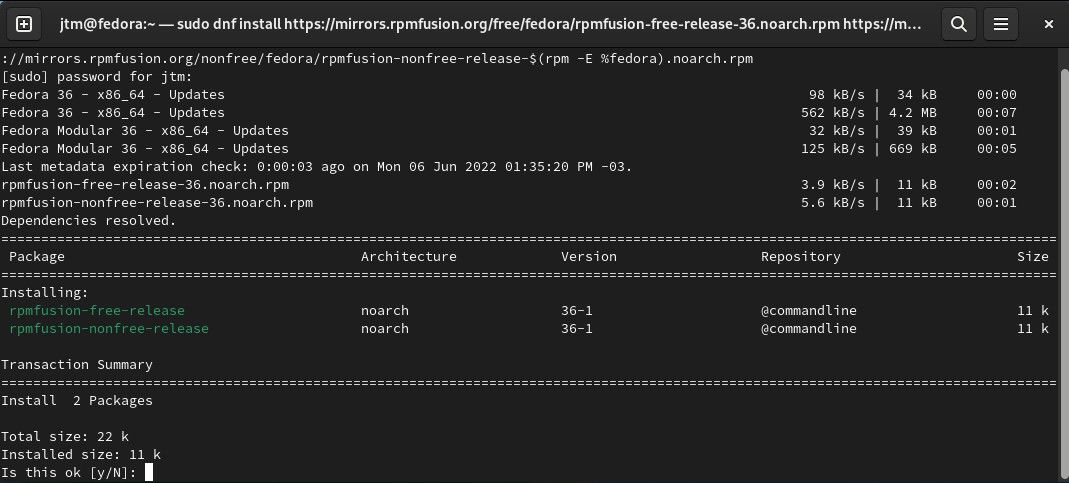
Installing these repositories is a multi-step process, but don't let that scare you. There is very little interaction. All you'll need to do is enter the following commands in order, enter your password if required, and answer "yes" to any installation questions:
First, to set up the repositories (copy and paste this as one line):
sudo dnf install https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
To update application data:
sudo dnf groupupdate core
Install extra sound and video packages:
sudo dnf groupupdate multimedia --setop="install_weak_deps=False" --exclude=PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin
sudo dnf groupupdate sound-and-video
Install extra drivers and libraries:
sudo dnf install rpmfusion-free-release-tainted
sudo dnf install libdvdcss
Install extra firmware utilities:
sudo dnf install rpmfusion-nonfree-release-tainted
sudo dnf install \*-firmware
4. Install GNOME Tweaks
GNOME Tweaks is a small application that will allow you to, well, tweak many GNOME settings that aren't available in the default system settings. You'll be able to add considerable customization to the look and feel of your system.
sudo dnf install gnome-tweaks
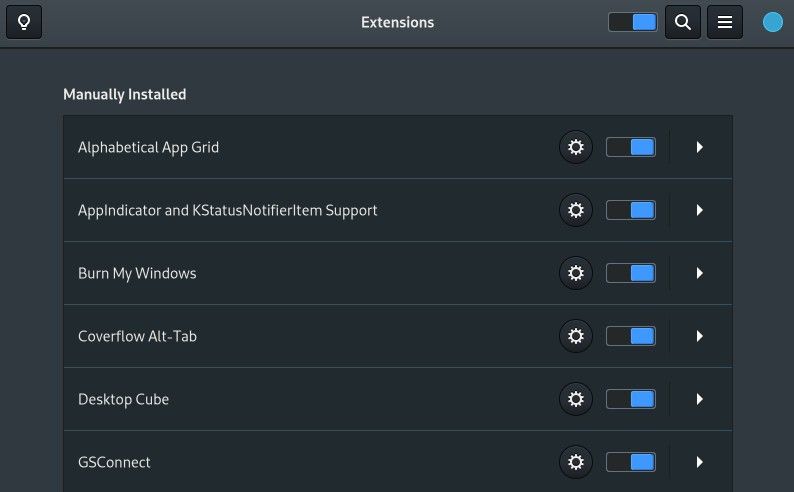
5. Install the GNOME Extensions App
This app will make it easy to manage and configure GNOME extensions, adding even more opportunities for customization. Refer to the next point to help find and install extensions on Fedora.
sudo dnf install gnome-extensions-app
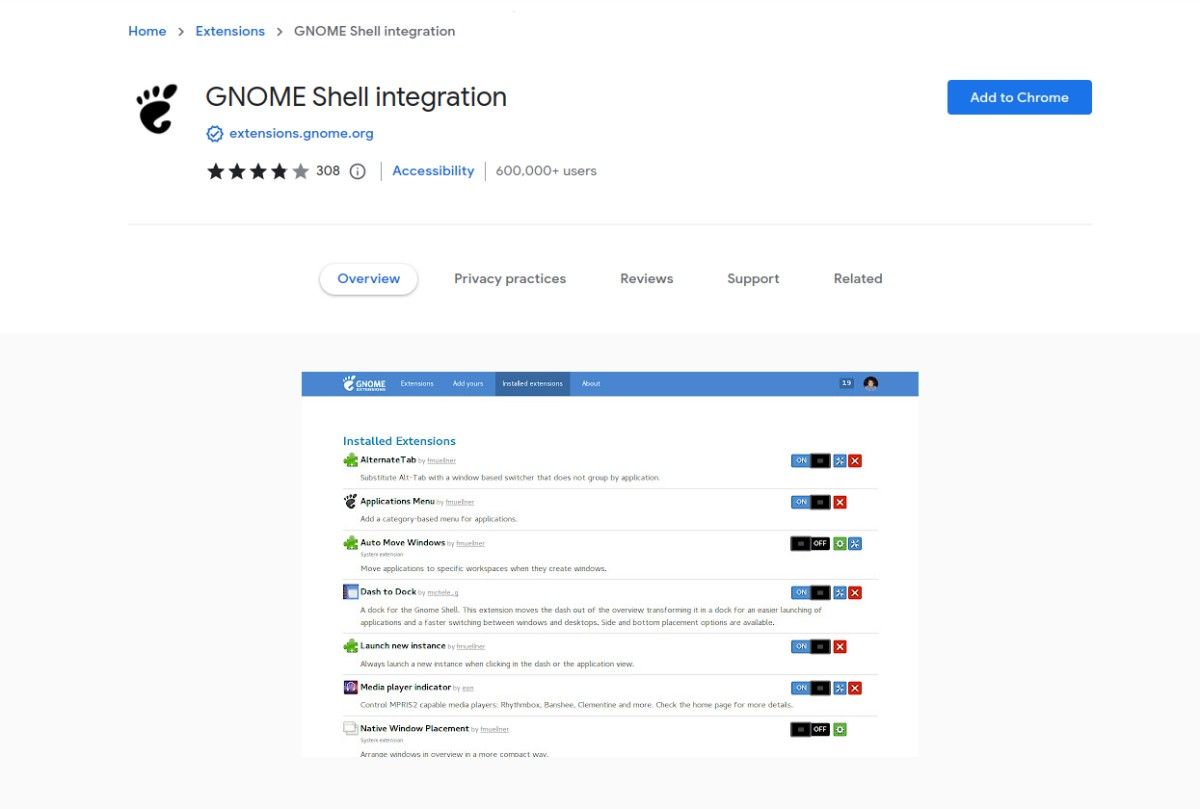
6. Install the GNOME Shell Browser Integration
The GNOME Shell integration extension will allow you to easily browse and install the best GNOME Shell extensions online from the official repository. By simply clicking in your browser you'll be able to add, remove, and configure any of the available extensions.
The integration extension is available for both Chrome and Firefox browsers. With the extension installed, visit the GNOME extensions page to start browsing.
7. Install GSConnect and KDE Connect
KDE Connect is made up of a mobile device app and a desktop app that work together to give you exceptional integration between the two devices. You'll be able to easily copy files back and forth, use your mobile as a remote input device, share notifications, make calls, and much more.
KDE Connect, as you might have guessed, is designed for the KDE desktop. GSConnect is a port of this wonderful program in the form of a GNOME extension that allows you to achieve the same integration with GNOME Shell.
First, grab the GSConnect extension from the GNOME extensions site. Then, install KDE Connect on your Android or Apple mobile device. Follow the instructions on your mobile device to pair it with your laptop/desktop and enjoy.
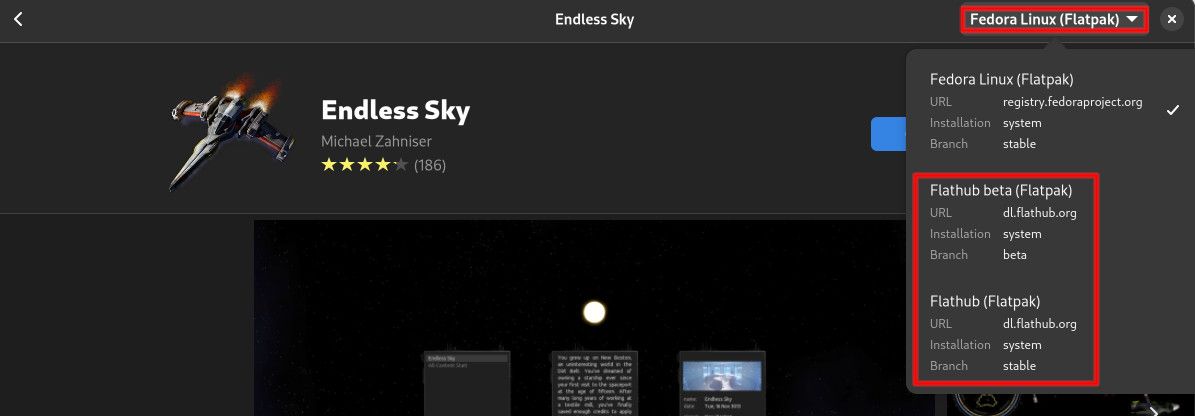
8. Install the Flathub Flatpak Repositories
Fedora comes with Flatpak support built-in and enabled. Depending on your installation choices, however, you may not have the Flathub repository enabled on your system. The Flathub repository will increase the amount of Flatpak software available to you through the GNOME Software Center considerably.
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub-beta https://flathub.org/beta-repo/flathub-beta.flatpakrepo
To verify that the Flathub repositories have been enabled correctly, open GNOME Software, click on any app, and then click on the dropdown menu at the top-right. You should see the repositories listed as shown in the picture above.
You can now install Flatpak-packaged software directly from the GNOME Software Center or by browsing the catalog at flathub.org.
Welcome to the Wonderful World of Fedora Linux!
You now have a complete Fedora Linux system with all the bells and whistles enabled. We're sure that you'll find Fedora to be incredibly powerful yet extremely user-friendly. Welcome to the world of Linux. You are now running one of the most advanced personal computer operating systems in the world!
If for some reason, you don't find the default GNOME desktop on Fedora exciting, you can always switch to another desktop environment.