Many vehicles on the road today have driver assistance features. These vary from basic cruise control and adaptive cruise control to vehicles that can change lanes for you and can even steer you around curvy back roads. Between Tesla's Autopilot and Mercedes' impressive self-driving technology, there needs to be an exact definition of how each vehicle fits each level of self-driving autonomy.
So, here's what we know so far regarding the categories and levels of self-driving vehicles.
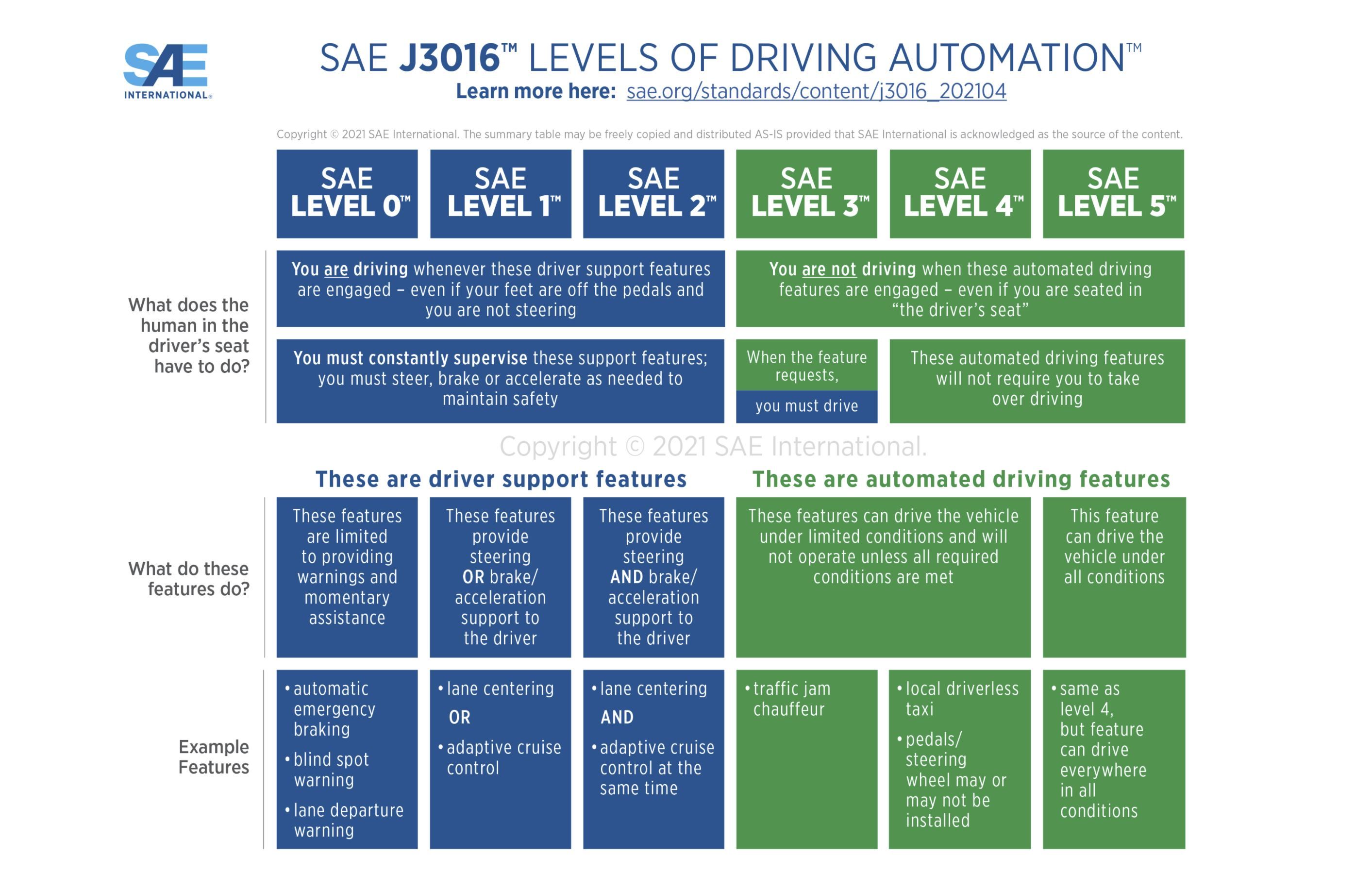
What Are the Levels of Self-Driving?
The Society of Automotive Engineers has released information regarding the different levels of driving automation. This information helps both consumers and governments better understand the technological complexities in each category. For example, some categories require the driver's full attention to the road, while other levels of autonomy have vehicles with no steering wheel or pedals, allowing the driver to essentially take a nap.
Here are the six levels of driving automation as we know today, from no driver assistance features to fully autonomous vehicles.
Level 0: No Driving Automation
This category is fairly simple. These vehicles do not have any sort of dynamic driver-assistance technology available. Instead, the driver performs all necessary tasks themselves, such as accelerating, braking, steering, parking, etc.
Level 0 vehicles can have some intervention from the vehicle, however. This includes things like automatic emergency braking, blind-spot monitoring, and even lane-keep assist. These driver assistance features are considered to be in the level 0 category because they do not drive the vehicle but simply alert the driver and can automatically brake in certain scenarios.
Level 1: Driver Assistance
This category includes simple features such as cruise control, adaptive or not, or assists the driver in steering or braking.
Although the vehicle will be able to change its speed and following distance based on the vehicle in front of them, the driver will need to continue to pay close attention to the road and their surroundings. They must intervene whenever something goes wrong.
Another driver assistance feature in level 1 autonomy is the ability to steer the driver back into the lane if they begin to drift over the line. A vehicle that has a combination of acceleration, braking, as well as steering assistance is considered level 2 driver autonomy, which you can read about in the next section.
Level 2: Partial Driving Automation
As stated above, a combination of a few driver assistance technologies such as adaptive cruise control and steering correction qualify as level 2 automation.
Another example of partial driving automation is highway driver assist. This feature is available in several vehicles, such as Hyundai and Mercedes. Highway driver-assist allows the vehicle to accelerate and brake automatically and keep itself in the lane all on its own. The assistance feature does, however, need the driver to temporarily put their hands on the steering wheel to make sure they are still attentive to the road around them.
Tesla's Autopilot features, as well as the FSD beta, are all categorized as level 2 automation. Unfortunately, legal disputes make level 3 automation difficult to bring to the open market.
Level 3: Conditional Driving Automation
Vehicles in the third level of driving automation can adjust their acceleration, braking, and steering based on environmental factors. These vehicles are built with extra sensors and cameras to detect changes in their environment. This additional equipment helps the vehicle sense cars in the lanes next to them, allowing the vehicle to change lanes for its driver automatically.
However, this level of automation still requires the driver to be attentive and intervene when the system inevitably makes mistakes.
A great example of this is Audi's Traffic Jam Pilot, which was designed to steer autonomously, accelerate, and brake in stop-and-go traffic up to 37mph and was to be first available in the 2019 A8L. Government regulations with self-driving technology made it difficult to release in the U.S and Europe, so the vehicles being sold to consumers ended up being limited to level 2 driving automation.
Level 4: High Driving Automation
Level 4 self-driving is what most dream of when it comes to the future of automated driving. Level 4 does not require driver intervention as the vehicle is programmed to stop in the event of system failure. This is the level of self-driving where a steering wheel and pedals are optional, and the driver may take a nap while the vehicle drives itself.
The closest we have to level 4 autonomy at the time of writing is driverless taxis, such as Waymo One in Phoenix, Arizona, that are mapped to a specific geographic location and are only designed for bringing passengers to a couple of determined destinations.
Human input is optional in case of emergencies.
Level 5: Full Driving Automation
This is the level of automation that movies depict in the future. No driver involvement is required. The vehicle can drive in all conditions and is not restricted to a certain geographic area. For level 5 driving automation to exist in our world, self-driving technology needs to be perfect.
When Will Fully Autonomous Vehicles Appear on the Road?
At the time of writing, it's difficult for cars with self-driving technology to move into level 3 of self-driving. Although the technology is there, governments are having a hard time wrapping their heads around the legality of who is at fault if the system fails and other factors.
The majority of vehicles on the road today are at level 0, meaning drivers make all the decisions. Distracted driving still results in thousands of accidents each year. So, until all cars on the road can drive themselves and are connected to one another, level 5 fully self-driving vehicles will remain a fantasy for years to come.