With the internet getting ever faster it can be easy to forget about the structure behind it. Away from the physical infrastructure of cables, telephone lines, and routers, a digital structure exists that directs all your traffic around the web.
One of the most underappreciated parts of that digital infrastructure is the Domain Name System (DNS). DNS is often referred to as the phonebook of the internet, but it is far more than just a lookup service.
What Is DNS?
The DNS's main function is to turn an easy to remember URL into the IP address for the site. Your default DNS server will usually be the one provided by your internet service provider (ISP).
Type www.makeuseof.com into the address bar of your browser and a request is sent to your DNS server to get the site's IP address. If your ISP can find the site in its DNS database then it will send the site back to you.
With billions of websites, your ISP won't maintain a comprehensive list of every DNS record in the world. If the site isn't listed in your ISP's database then it will request the record from other servers. The record is stored a cache so that requests to that site are quicker in the future. If after trying a number of DNS servers it can't find a record for the website, you will be presented with a name_not_resolved error.
Most of the time leaving your ISP's DNS server as your default will do just fine, but there are some surprising benefits to shaking things up and trying out alternative servers.
1. Supercharge Your Browsing
It takes less than a couple of seconds usually for a website to load, which isn't an unreasonable amount of time. But if you had the option to speed it up for free it would seem like the obvious thing to do. Changing your DNS provider can improve loading times for many different reasons. There are a lot of variables in the system but the main difference is that a separate DNS server is likely to have more sites cached than your local ISP.
A program like NameBench can compare your DNS lookup performance to other public DNS options, and recommend which server would speed up your connection the most.
2. Add Network-Wide Parental Controls
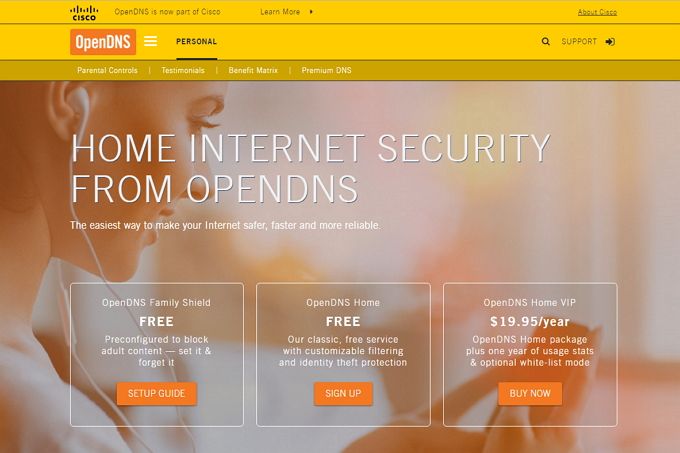
OpenDNS is a DNS server owned by networking giant Cisco, and incorporates adult site "blacklists". When a request is made for a lookup to one of the blacklisted sites then the request is blocked.
Many home routers will allow you to change the network's default DNS server, which means you could set up the OpenDNS on your entire home network giving you the ability to blacklist sites to protect your kids while they are online. Family Shield is OpenDNS' free server, but they also offer Home and VIP Home options if you want more customization on the filters.
3. Bypass Geo-Restrictions
There are many reasons that you may legitimately want or need to bypass geo-restrictions to access region-blocked video and music. While you could use a VPN for this, there is another simpler way.
Services like UnoDNS are able to unblock region-restricted content by replacing your IP address with one of theirs during a DNS lookup. This tricks the website into thinking you are in a location where the content isn't blocked. If you change to UnoDNS on your router then the content is unblocked without you having to do anything.
4. Avoid Censorship
Censorship is used by oppressive governments around the world in order to try and restrict the speech of its citizens. No individual government has the power to "shut down" parts of the internet. What they really do is block the site at the local ISP level. When Twitter was blocked by the Turkish government in 2014, some surprising graffiti started to show up.
The numbers in the graffiti were 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 -- Google's public DNS servers. By spreading the word through graffiti, Turkish citizens were able to undermine the government's attempt to block the social network.
5. Increase Security
In recent years we have grown used to hearing about website hacks and data leaks. An often overlooked problem is when a DNS server is hacked or goes offline. In October 2016 a large DDoS attack took down Dyn DNS for a number of hours. Some of the largest websites in the world like Twitter, Spotify, Reddit, and others use Dyn as their upstream DNS. The DDoS attack meant that some of the most popular services were inaccessible.
Without changing your server, you would just have to wait until your DNS server comes back online. If the attacker is particularly malicious they may even change DNS records to redirect to phishing or malware-ridden pages. By choosing a DNS server that has a good track record of security -- like Google's Public DNS or OpenDNS -- you minimize the chances of being victim to these attacks.
Time to Give DNS a Shot
One of the best parts of the DNS is how straightforward it is to change your DNS server. It means that you can experiment, and maybe even have different DNS servers for different situations. If you don't get the result you were looking for, it only takes a few seconds to change it back.
Changing your DNS can make a huge impact on your browsing speed, improving your security, bypassing censorship and geo-restrictions. So before jumping to more complicated solutions, try changing your DNS server as a free and easy way to improve your internet experience.
Have you tried any of these DNS tips? Did they make the improvement you were hoping? Do you think we missed any? Let us know in the comments below!
Image Credit: asharkyu via Shutterstock.com, Phantom Open Emoji via Wikimedia Commons