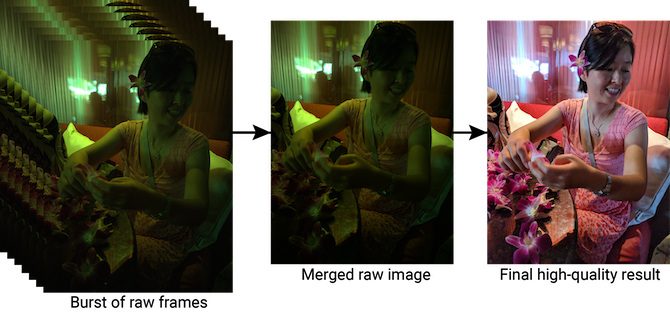Since its inception, the camera has remained the cornerstone of the Google Pixel line of phones. By leveraging the heaps of data it collects, Google has been able to push the boundaries of mobile photography. Through software, the company managed to replicate advanced features, normally for which other OEMs bundle two, three, or in some cases, four cameras on the rear.
So how do those camera modes function without special hardware? Here we explain the Google Pixel's best camera features.
1. HDR+
HDR+ is Google's take on the traditional HDR mode found on most smartphones today. It's important to understand the latter before we dive deeper into how Google approaches the concept.
In HDR photography your phone, instead of taking a single picture, takes multiple shots at varying exposure levels. That allows the camera to gather more data of the scene and produce a result that more accurately renders the highlights and shadows. It does so by mashing those different frames together through complex algorithms.
So for instance, there are scenarios where you're trying to capture an image of someone standing in front of a bright background and in the outcome, either your friend is completely in the shadows or the background has been blown out. This is where HDR comes in and balances your frame's lightest light and darkest dark.
Since on phones, this whole process is automated, it can be a little tricky for companies who don't have an enormous dataset to train their algorithms. There are other shortcomings as well. Compared to professional cameras, your phone sensor is much smaller which leads to noise when it stays open for too long.
Google's HDR+ tries to solve all of this. It too involves capturing a bunch of pictures and processing them later. But unlike the rest, Google's phones take several underexposed shots and merge them through algorithms that are trained on a massive dataset of labeled photos.
Since HDR+ doesn't go through a wide spectrum of exposures like traditional systems, there's also much less motion-blur in pictures and noise. To ensure all those computations don't slow your phone down, Google has even begun to integrate a dedicated, proprietary chip called the Pixel Visual Core from the Pixel 2 series.
2. Night Sight
Arguably, the most impressive piece of camera tech developed by Google's software team is titled Night Sight. When enabled, the feature is capable of taking nearly-dark scenes with almost no light and magically yielding a well-lit picture.
Night Sight, which is even available on the first-gen Google Pixel, is built on top of the company's HDR+ technology. Whenever you hit the shutter button with Night Sight turned on, the phone clips numerous shots at a bunch of exposure settings.
The information processed is then passed on to the algorithms for understanding the scene's various details like the shadows, highlights and how much light there actually is. Through this learning, the camera app stitches together a much more illuminated picture without amplifying the grain.
3. Super Res Zoom
Digital zoom is another critical drawback of mobile photography Google has tried to tackle with software instead of dedicated hardware like others.
Called Super Res Zoom, the feature promises up to 2x digital zoom without compromising any details. It uses the same burst photography technique Google employs for HDR+ and Night Sight. But here, it doesn't go for a range of exposures.
For Super Res Zoom, the camera captures multiple shots at various angles. So does that require you to move physically? Not at all. In the case of zoomed-in pictures, even the slightest hand movement is enough for a different angle. So Google is essentially using your hand tremors to accumulate more information.
Google has a solution for if your hands are too stable or for when your phone is mounted on a tripod as well. In those scenarios, the lens will actually wiggle a bit to replicate hand movements which is simply astonishing.
The phone utilizes all that data to capture a photograph with far more details digital zoom normally would have produced.
4. Portrait Mode
While the majority of manufacturers include additional cameras for depth-sensing, Google achieves Portrait Mode with software. For this, the camera app begins by taking a normal photo with HDR+. Then, with the help of Google's trained neural networks, the phone tries to figure out the primary subject. That could be a person, a dog or just about anything else.
To ensure it doesn't mess up the edges, Google's Portrait Mode benefits from a technology called Dual Pixel. In layman's terms, it means every pixel the phone captures is technically a pair of pixels. Along with better focus, the phone, therefore, has two viewpoints for evaluating the distance between the background and foreground.
This is crucial because Pixel phones don't have multiple sensors for calculating the depth. Lastly, the phone blurs everything except the subject mask it has finalized.
Wondering how to get the feature on your phone? Here's an easy guide to use Portrait Mode on any Android phone.
5. Top Shot
With Pixel 3, Google introduced a new, clever camera feature called Top Shot. As the name suggests, it lets you select a better shot than the one you clicked.
To do that, the camera takes up to 90 images 1.5 seconds before and after you tap the shutter key. And when it detects flaws such as motion blur or closed eyes, it automatically recommends an alternative picture. You can manually choose one from the lot as well, although only two of them will be high-resolution ones.
Since Top Shot is an extension of Motion Photos, it doesn't affect your camera's performance.
Simple Tricks to Boost Your Smartphone Photography
While there is a lot Google's software does for you, a few complicated scenarios still demand some extra effort on your side. To master those shots, we recommend mastering these simple tricks that can significantly boost your smartphone photography skills.