If the processor is the brain of your computer, the motherboard is the heart—it's where the different parts of a computer connect and talk to each other. So if your motherboard has a problem, it's a bigger issue than just replacing one part.
Usually, motherboards are sturdy enough to take over the ravages of daily use. But there are some things you can do to make sure it keeps running right. Protecting the motherboard from damage is paramount to protecting every other component.
Avoid some of these common mistakes that damage a computer motherboard, and you'll save yourself from serious headaches.
Why Do Motherboards Fail?
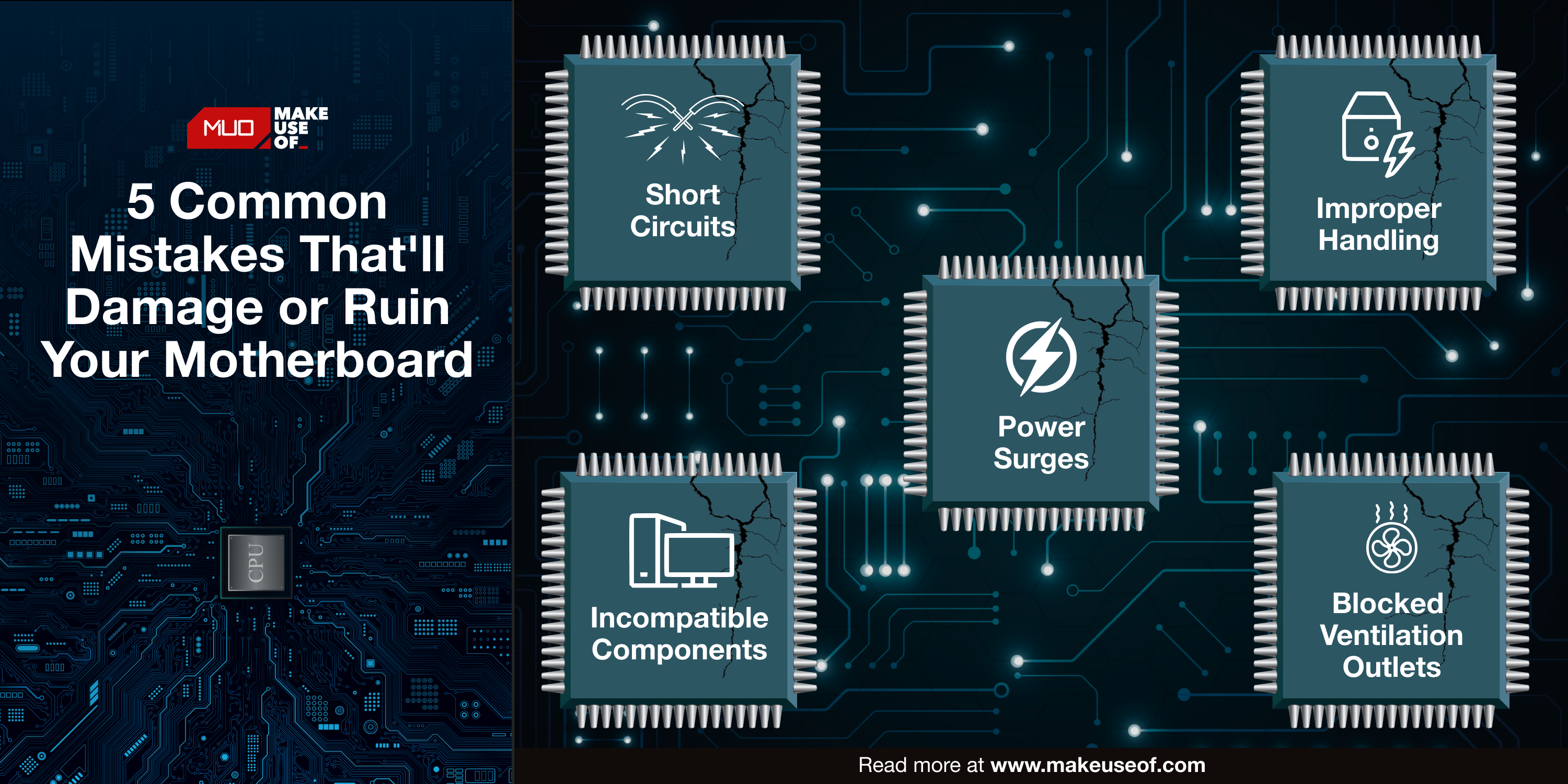
There are many reasons why a motherboard might fail, but they typically fail into five main categories:
- Short circuits
- Power surges
- Poor ventilation and overheating
- Incompatible components
- Improper handling
There are various issues that fall under each header (and sometimes straddle more than one!), but motherboard failures generally fit into these categories.
1. Short Circuits
Motherboard short circuits are more prevalent in desktop computers but also (yet rarely) occurs in laptops. Whether you like to build your own PC or buy one assembled from somewhere, there are chances of a short circuit if it hasn't been assembled properly.
Sometimes a loose CPU cooler results in irreversible damage to motherboards. This is why, when assembling and before switching on your PC, you must check for loose cables and ensure that the cables are attached to the correct ports.
In the course of assembling your PC, you need to fit the motherboard properly into the case. The motherboard screws that you use to attach it to the case. Make sure you use every screw and that it is tight. A single loose screw can result in a fried motherboard—it does happen!
In short, the inside of your computer should be neat and organized. If the motherboard ends up in contact with an unintended object, it can cause a short circuit, and a short circuit can fry your motherboard.
2. Power Surges
The motherboard is where your computer's power supply unit (PSU) is connected. It's important to buy the right PSU for your needs—if your components need more power than the PSU can provide, it will cause the components or the motherboard to fail.
But the more frequent problem for motherboards is power surges. Some electronics in your home are power-hungry, like air conditioners or refrigerators. Have you ever seen your lights flicker when these devices turn off? That's because they needed to draw more electricity, which caused a surge.
When they switch off, the current takes a few seconds to adjust. And in those few seconds, it gets redirected to other electronics, like your lights or computer. This is the most basic explanation of a power surge.
Most power supply units and motherboards adjust their voltages to accommodate small power surges. But if it's a big one, it can fry your motherboard and all the components connected to it. It's a big issue and one of those that we never tend to account for adequately. The only solution is to buy a durable surge protector or invest in a UPS for your computer.
3. Ventilation and Overheating
Heat is the enemy of electronics (along with its co-conspirator, dust). Computer components need to stay cool to run properly. But they generate a lot of heat themselves. That's why heat dissipation is crucial to computers, whether in the form of fans or heat sinks.
If your laptop or computer regularly runs hot, you need to clean its ventilation outlets. Excessive heat can sometimes damage the motherboard, leaving you with a shorted motherboard that is difficult to repair. Besides that, you can also change and install a better CPU cooling fan to keep the temperature in check.
To help you out, we've already discussed some useful tips for keeping your PC cool and at a safe temperature. Also, remember that a loose or improperly fitted connection is a ticking time bomb for your motherboard.
4. Incompatible Components
Another mistake that could damage your motherboard is trying to install incompatible or low-quality components. You must double-check whether all the parts are compatible before assembling a PC.
There are a plethora of websites that allow you to check for compatibility issues, such as PCBuilder and PCPartPicker. Also, ensure that you buy good quality parts for your motherboard. If you plan to build an expensive computer, don't cheap out on components such as high-quality RAM or a good PSU.
As mentioned earlier, heat is the enemy of computer components. Keep this in mind when buying parts such as graphics cards. Some graphics cards have a higher affinity for overheating due to fan design and other factors. Avoid these if you can, and keep your PC cool at all times.
5. Improper Handling
Are you curious as to how a motherboard gets damaged? Apart from the reasons mentioned above, another possibility is improper handling of a motherboard during installation. If you assemble your computer, make sure you have an anti-static wristband and an anti-static mat on hand.
Always keep your motherboard on an anti-static mat when handling it. A single static shock can cause irreversible damage to your motherboard, and this is one of the common mistakes made by beginner PC builders.
Another important thing to remember is to avoid touching the circuitry on the motherboard. Whenever you're lifting it, hold it using the edges. Furthermore, during installation, screw the motherboard by applying equal pressure on all corners, i.e., don't tighten a screw completely before moving on to the next one.
How to Check for Motherboard Damage
A damaged motherboard isn't as simple to diagnose as other computer parts. Generally speaking, it's quite easy to spot your PC for failing hardware. But you can't narrow it down to the motherboard immediately.
That said, there are a series of steps you can take to figure out the motherboard damage.
- Switch on the PSU and check for a green light on the motherboard. If there is no green light, the problem is with either the power supply or the motherboard. Check with a different PSU, and if the motherboard still doesn't light up, it's probably damaged.
- If the green light is coming on, check the bare basics of your PC components, i.e., the CPU and RAM. Connect only these two components and see if the motherboard is booting into the BIOS or UEFI.
- If it is still not booting, check the CMOS battery on your motherboard. If your computer is more than a few years old, chances are the battery may need to be replaced.
Most modern motherboards come with error lights that blink when the motherboard encounters an error or a component is malfunctioning.
Motherboard error lights or error codes vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, but there are some general motherboard troubleshooting tips that you can use to fix your motherboard.
What Happens When Your Motherboard Fails?
Unfortunately, if you've exhausted all troubleshooting methods and your motherboard appears to be dead, you're not left with many options. First up, you could try your local PC repair store to see if they can diagnose or coax it back to life. But otherwise, it's time to hit the shops and start looking for a new motherboard.