There are many good reasons to upgrade your router. You'll get lots of potential benefits: you can get faster speeds, improved range, and new features. It'll also ensure maximum compatibility with your latest gadgets.
But to get the best out of it, you also need to set it up properly. It's not difficult—adjust the hardware, tweak a few settings—but the results are well worth it. Here's what you need to do when changing routers.
1. Find the Right Position
The first—and most important—thing to do when setting up a new router is to find the best position for it. You can subscribe to the fastest internet provider and use the most up-to-date and powerful hardware, but it'll all be in vain if you put your router in the wrong place.
Wireless routers use radio waves which can be weakened (or even blocked) by obstacles like brick walls, and they also get weaker the further they travel. The weaker the signal, the slower your connection.
There are several golden rules for router placement:
- Place it near the center of your home.
- Don't place it on the floor—a desk, table, or shelf is ideal.
- Don't place it right next to a wall, which will absorb the signal.
- Don't place it near other devices that emit wireless frequencies, like microwaves or cordless phones.
2. Adjust the Antennas
How do you know if you need a new router? One sign is constant slow speeds. The latest routers support newer specs as well as improved antenna design for more efficient performance.
If your router has internal antennas, then you should sit it in whatever position it was designed. Don't sit a vertical router on its side just because it fits on your shelf better.
If your router has external antennas, you should make sure they're pointing in the right direction to optimize range and performance. Most of us naturally position the antennas facing upwards, but a former Apple Wi-Fi engineer, Alf Watt, recommends positioning them perpendicular to each other (i.e., one facing up and another facing out).
This is apparently because radio reception is better when both the sending and receiving antennas are positioned along the same plane—and some devices may have antennas positioned horizontally.
3. Change the SSID and Password
To access your router's admin settings, type the address for the router into a web browser. This is normally an IP address like
192.168.0.1
Or, in the case of Netgear, a more traditional URL like
routerlogin.com
Not sure what it is for your router? You'll find it in the manual.
Enter the admin username and password when prompted, which you'll find in the manual too. If you don't have the manual anymore, you may be able to find it online.
Each model of router uses the same default login details. If you know which brand of router your neighbor uses, then there's nothing to stop you from looking up the password on the internet and logging in.
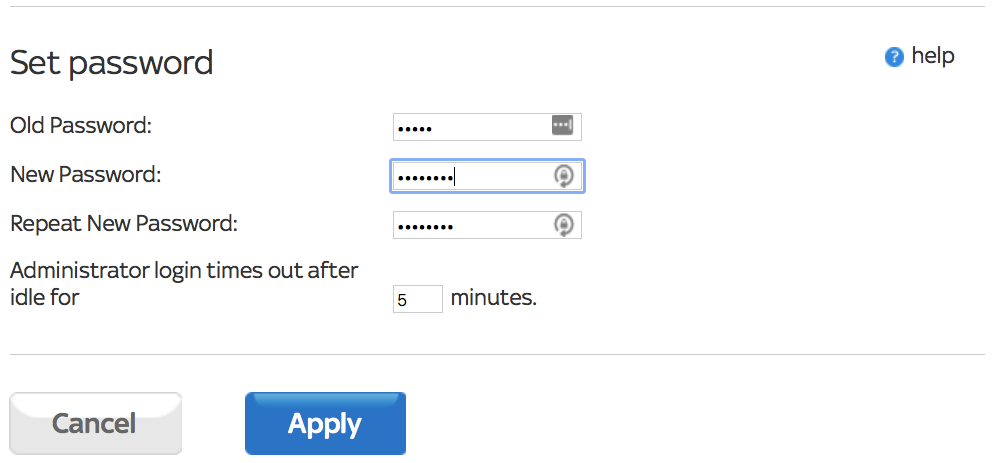
So you should always change the router password. You should change the username, too, if your router allows it, and the SSID as well. You can usually find the SSID in the Wireless section of the admin page and the Maintenance or Administration section's password.
Note that changing the router's admin password won't affect the password you use to connect to the internet. It's simply the password used to access the router settings page.
4. Update the Firmware
With any new piece of hardware, it's always a good idea to check whether there's a firmware update available, and a router is no different. You probably won't get any exciting new features with a router firmware update, but you may get performance and connectivity improvements, and you'll certainly get security patches.
Vulnerabilities are discovered in routers all the time, so for this reason alone, you should always ensure that yours is kept up to date.
It should happen automatically in the future, but since it isn't uncommon for products to ship with older firmware, it's a good idea to force a manual update straight away when you get a brand new router. You'll find the option in the Maintenance, Administration, or other similarly labeled section of the router settings and it may involve downloading a file to your PC. Simply follow the instructions for your particular router model.
5. Set a Wi-Fi Password
Most routers come with basic security settings already in place. It will have a Wi-Fi password, which you need to enter on every device you want to connect to the internet, and you can find it either in the documentation or on a label stuck to the underside of the router itself.
Unlike the router password, the Wi-Fi password is unique to each router, so there's no urgent need to change it. However, it is essential that you double-check the other security settings.
Password protecting your Wi-Fi is important for two reasons:
- It prevents unauthorized users from leeching off your internet, so there's no chance of your neighbor downloading Game of Thrones torrents using your bandwidth.
- It encrypts the connection between your computer and the router, eliminating the risk of the data you send or receive being intercepted by other devices.
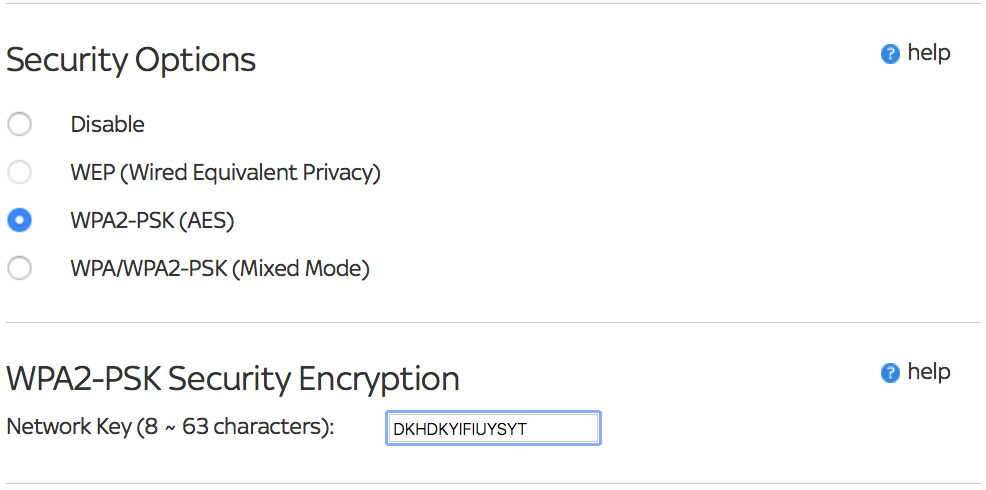
Routers offer a number of different Wi-Fi encryption methods, some more useful than others. Put simply, you should be looking for WPA2 security as the other types are too easy to hack.
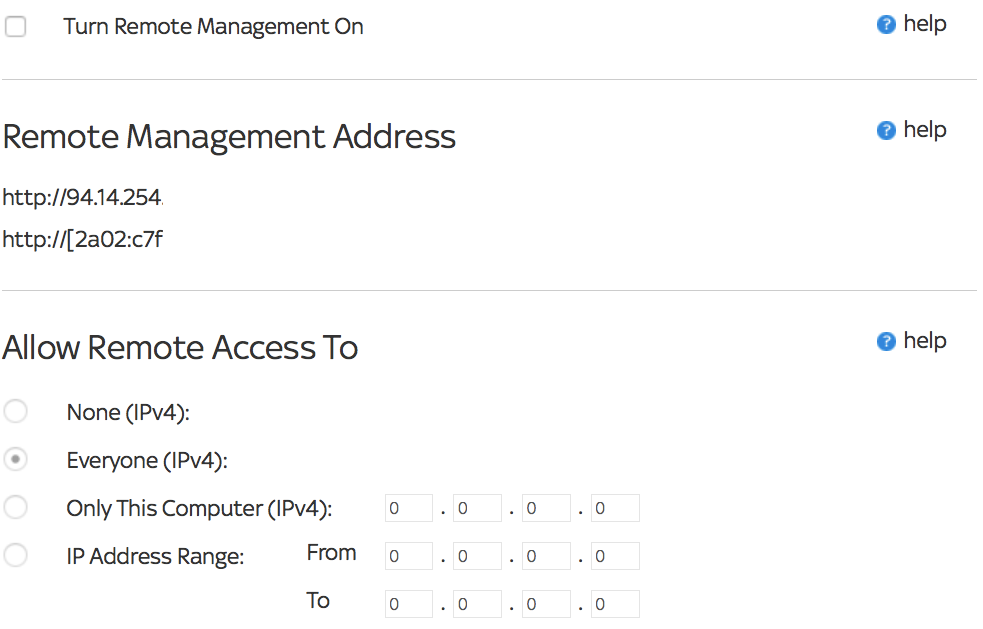
6. Disable Remote Access
Remote Access is a feature that network administrators (or anyone else) can use to log into the router remotely via the internet. It has little practical use for a typical home user and should be disabled by default because it poses a potential security risk.
If you decide that you need to access your router remotely, you must ensure that you change your router's admin password (see #3 in this article) to something very secure.
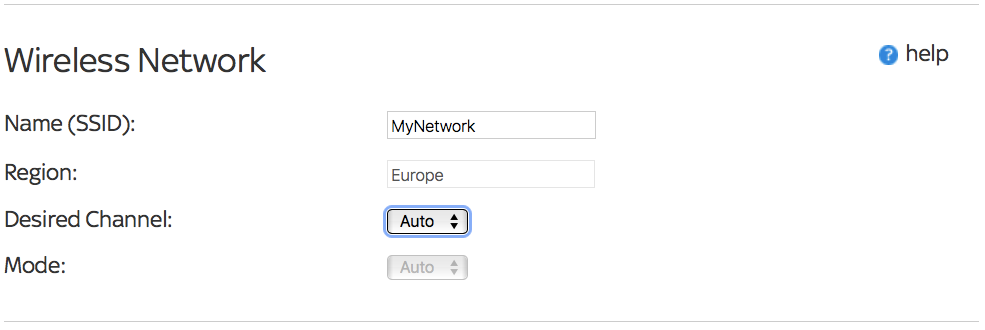
7. Pick the Right Channel and Network Mode
There are two settings you can quickly explore to ensure you get the best speeds from your router from the get-go. These are the channel and the network mode.
Routers broadcast on different channels that cover the entire frequency range for the Wi-Fi protocol standard. If lots of routers in close proximity use the same channel, they will all suffer interference and experience decreased performance.
The default for many 2.4 GHz routers is channel six. Steer clear of this as there's a good chance your neighbors will also be using it. Many modern routers can automatically pick the best channel based on least usage or find the best channel yourself.
The network mode refers to the protocol the router uses to communicate with your devices. Routers support many protocols, with Wi-Fi 6 being the current fastest, followed by 802.11ac as the next best.
Make sure you're using the fastest protocol your router supports. They're mostly backward compatible and will work with your older devices, although they won't benefit from the faster speeds.
With the newer Wi-Fi protocols, you also have the option of using the 5 GHz band. This is much less prone to interference than the older 2.4 GHz band, although it also has a shorter range and is incompatible with devices that were designed before 2014.
8. Enable Parental Controls
If you've got children and you want to restrict access to what they can do or how much time they spend online, then your router can help.
A lot of modern routers ship with Parental Control options built right in. They can prevent access to specific sites, filter particular content, limit the hours where the internet is available and much more. They can also be tailored to specific users so that the controls won't infringe on your own internet use.
You can often manage the parental controls through a companion mobile app that you install on your smartphone. Just don't rely on it as the only way to police internet usage in your home—kids are always likely to find ways to bypass software controls.
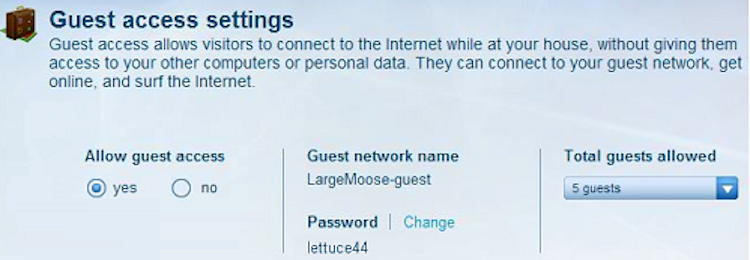
9. Enable or Disable Guest Browsing
It's safe to say that anyone who comes to your house will be asking for the Wi-Fi password within about five minutes of stepping through the door. If your router supports Guest Access, it's a good idea to turn it on—and keep it on—for this very reason.
Guest mode effectively creates a second network with its own SSID and its own password. The options vary between routers, but on the most basic level, changing the Guest password regularly lets you control who has access to your Wi-Fi without the inconvenience of resetting the password on all of your own devices.
Some routers give more control, like being able to restrict the internet speed available to guests. They also vary in how much security they offer. Some are essentially unsecured like public hotspots, while others let you choose how far you want to lock it down.
10. Enable Quality of Service
Quality of Service is a more advanced tool that prioritizes which applications are most important when sharing bandwidth. For example, imagine watching Netflix in 4K and having a large file backed up to the cloud. You want the Netflix video to be stutter-free, and you don't mind if the backup speed suffers, so QoS can be used to prioritize bandwidth to Netflix.
QoS isn't available on every router, but it can fix lag in games and video calls.
What to Do When You Get a New Router
By taking a few minutes to set up your router properly, finding the best position, and then checking that the settings are just right, you can be confident it will give you the best performance and the highest level of security.
And once you've upgraded, don't throw your old router away. There are lots of ways you can still put it to good use.