While Debian is stable by default, it gets this stability by relying on older versions of software packages. There are times when you might want newer software. Fortunately, it's easy to switch from Debian Stable to Testing to get the latest versions of software on your system.
What Is Debian Testing?
Debian Testing is just a version of Debian that's on a different track than the stable version. It's less stable than "Unstable." This means that you shouldn't run into as many problems as you might with Unstable.
According to Debian's FAQ, Testing is frozen for the next stable Debian release. Ubuntu uses Debian Testing as a basis for the LTS (Long-Term Support) versions of their distro.
Software updates come more frequently on Debian Testing than on Stable. In contrast to how Windows updates tend to come once a month, Debian Testing updates are available to download when they're ready. If you run "apt update" once a day on Testing, you can often find new packages available.
Why Use Debian Testing?
There are various reasons why you might want Debian Testing. The main advantage is newer software. If you're running it on a desktop, and especially if you're a developer, you'll have newer versions of apps and languages.
How to Switch to Debian Testing
To use Debian Testing, you don't need to go through an entire OS installation process. You can easily convert your existing Debian Stable installation to Testing in a few simple steps.
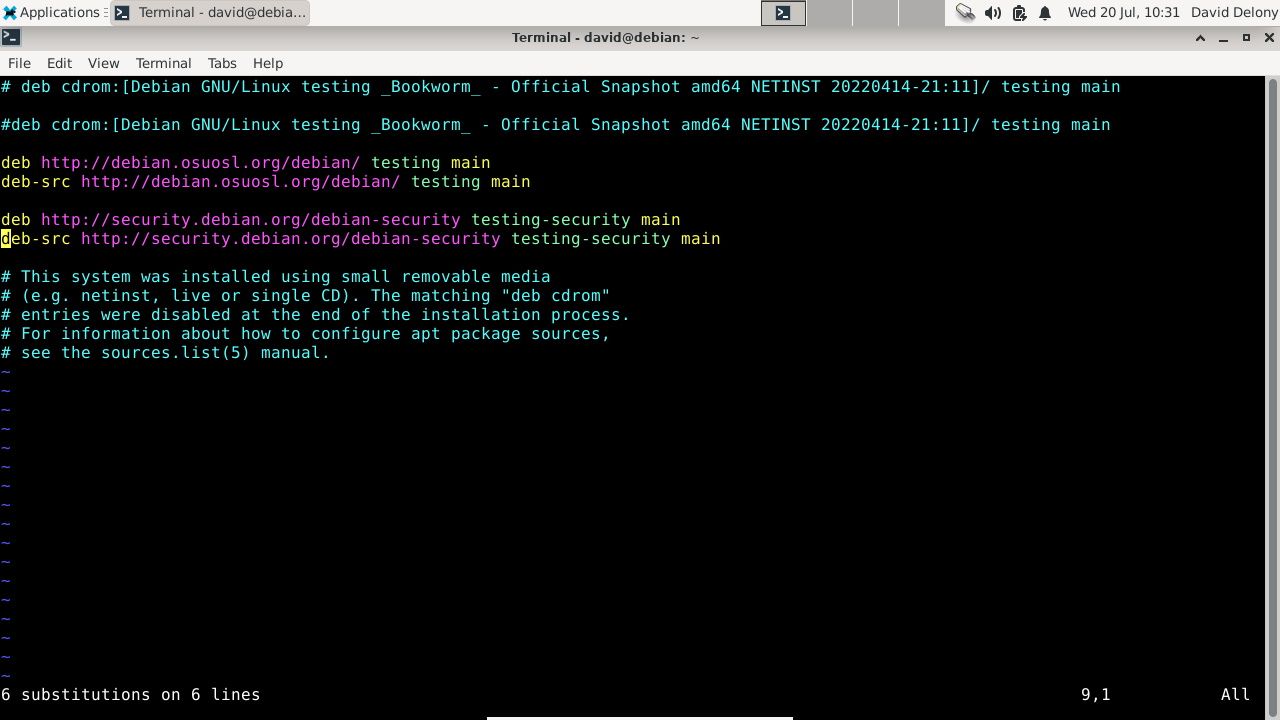
Step 1: Edit the sources.list File
To switch to Debian Testing, all you have to do is edit the /etc/apt/sources.list file as root. Change the references to the stable version ("Bullseye" as of July 2022) to "testing". You can search and replace the words with either sed or AWK to do this quickly.
Keep a backup copy of the original file in case you make a mistake.
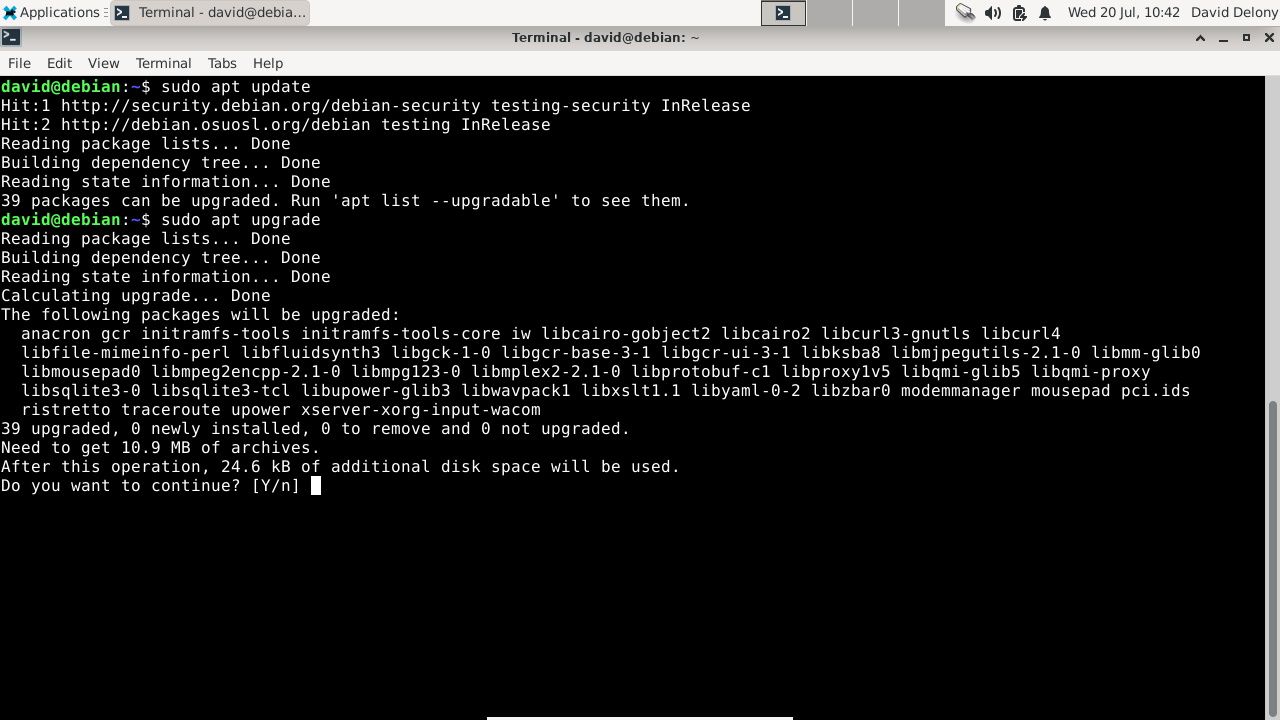
Step 2: Upgrading Your Packages
Now that you've switched your APT repository, the next step is to upgrade your packages. It's the same as upgrading your Debian packages normally using the apt command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Since you're effectively replacing your OS, it may take a while to download and install the new packages. When it's finished, you can reboot into your new Debian Testing system. To check that you've upgraded to Debian Testing, examine the contents of the /etc/debian_version file.
Upgrading to Debian Testing Is Quick and Easy
Now that you've seen how easy it is to change from Debian Stable to Testing, why not take advantage of it and have newer software? Or perhaps you might want to consider a rolling-release distro?