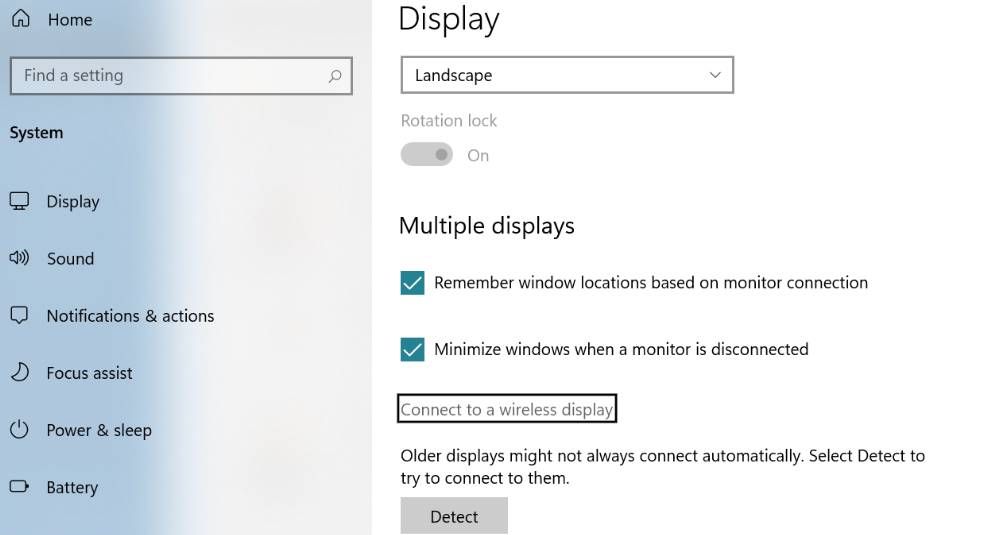
If you watch movies with your family, make presentations to your team, or collaborate with any group of people, chances are you’ll need to share your screen. Typically, you’d do this by mirroring or casting your screen.
Although these technologies have a common focus, they are pretty different. So what’s the difference between screen casting and screen mirroring?
What Is Screen Casting?
Screen casting involves sharing your device’s screen—phone, tablet, or computer—over a wired or wireless network connection, like Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
With screencasting, you can transmit specific content—like your ideas, a video, or a presentation—or apps to another smart device, such as a television or a projector. After casting, the receiving device will manage or control what you have cast.
As a result, you’ll be able to use the sending device for other functions asides from what is being cast. For instance, if you’re transmitting a presentation and you receive a message, you can reply and even engage in a conversation. Meanwhile, anyone accessing the receiving device can pause, play, or rewind the presentation.
What Hardware Do You Need for a Screencast?
Screen casting is ideal for remote collaborations, where you want to view content or collaborate with many people. It typically requires the following:
- A smart device, such as a computer, tablet, or smartphone, that supports casting,
- A compatible device for receiving and viewing content,
- A reliable network connection to ensure smooth screen casting,
- You might need to install an application or software to aid casting, but in most cases, compatible devices and apps have an in-built Cast feature that you can enable through the Settings page.
How to Screencast in 4-Steps
The process of casting your screen may vary depending on your devices, but it usually involves the following:
- Ensure the transmitting and receiving devices have turned on the required network connection.
-
On the device transmitting, navigate to the specific app or media you want to project and select the Cast feature.
-
Toggle the Cast option to enable your device to scan for available devices.
- Once the transmitting device locates and connects with the second device, the information you’re transmitting will be displayed on the receiving device.
Pros and Cons of Screen Casting
While screen casting is beneficial, it also has downsides. Here are some benefits and downsides of casting your screen:
- Screen casting is an excellent tool for collaboration and interaction, as others can control or manage what is projected.
- It offers excellent flexibility. You can switch off the screen of the transmitting device or perform other activities, like browsing the internet or responding to messages, while casting.
- With screencasting, you only display what is required. Unnecessary information, like settings and notifications, remains hidden.
- However, screencasting is highly reliant on a stable network connection. If your network connection is shaky, the quality of what you’re displaying may be low.
What Is Screen Mirroring?
Screen mirroring, also known as display mirroring or wireless display on Windows 11, allows you to mirror (duplicate) your device’s entire screen to another device using a peer-to-peer connection. Essentially, the two devices connect via a direct wireless connection created by in-built wireless display technology, such as Miracast and AirPlay.
When you mirror your screen, you transmit presentations, ideas, multimedia content, and everything displayed on your device to another smart device. However, only the sending device can manage or control the content, unlike screen casting. Also, you’ll be unable to use the sending device while transmitting data to perform other functions, like replying to messages.
When Should You Use Screen Mirroring?
Screen mirroring is ideal for situations where you simply want to display content with a group of people. It typically requires the following:
- A device with built-in wireless display technology that supports screen mirroring and can send data,
- A second device that also supports screen mirroring and can receive, display, and play data,
- If the receiving device isn’t compatible, some wireless display technologies use adapters that you can connect to the sending device via USB and plug into the receiving device via HDMI.
- You'll most likely not need Wi-Fi or another network connection, as any device supporting screen mirroring will have an in-built wireless display technology to foster the required P2P connection.
How to Screen Mirror in 4-Steps
Like screencasting, the steps for mirroring your screen vary based on your device. But you’ll typically need to do the following:
- Turn on both devices and create a direct connection between the two devices.
-
You’ll likely do this by launching the Screen Mirroring or Wireless Display feature, typically found in the Display or Settings tab, on the sending device.
- You can connect to the receiving device once it pops up. Note that you’ll have to connect the two devices using an adapter or dongle if required before the receiving device shows up on the list of available devices.
- Once your devices are connected, everything displayed on the sending device will also show on the screen of the receiving device.
Pros and Cons of Screen Mirroring
Like screen casting, mirroring your screen has benefits and downsides:
- Screen mirroring allows for a better visual experience, as it is not reliant on a network connection. So you’ll be able to display videos, presentations, and other content seamlessly and smoothly.
- With screen mirroring, you’ll manage the transmitted data. It’s best for uninterrupted screen sharing, like movie shows and team training.
- However, you can’t control what you’ll share. As you’ll be mirroring your screen, unnecessary bits like settings and notifications will also be displayed.
- Also, the receiving device’s inability to control the data can be a downside if you want others to manage the displayed content.
- In cases where adapters or dongles aren’t stable, the mirroring can be shaky and unpleasant.
- In addition, since the sending device fully controls the transmitted data, you cannot perform other functions on it.
Screen Casting vs. Mirroring: Which Is Best?
Both screencasting and screen mirroring have benefits, as they are built for different scenarios and user preferences. Whether to cast or mirror your screen depends on your unique needs and the context in which you’ll share your screen.