Year after year, manufacturers strive to bring the best TV to market. Companies like LG, Sony, and Samsung compete against each other in the display space, offering groundbreaking developments in display technologies. This led to the development of various displays—from LCD and LED to QLED and OLED screens.
While we're used to these display types, at CES 2022, Samsung and Sony announced a new display tech: QD-OLED. This new tech combines the advantages of both OLED and QLED, allowing you to get the deepest blacks while getting the brightest, most vibrant colors.
So, what exactly is QD-OLED?
OLED and QLED Limitations
OLED TVs are known for their deep darks and high contrast. That's because each pixel in an OLED display can light up or dim on its own. That means you can get true blacks and high contrast ratios with these screens. However, OLED panels can't produce much brightness because they're susceptible to overheating and burn-in at high brightness levels.
On the other hand, QLED screens use a quantum dot filter to enhance screen color and contrast. It does this by breaking down the white backlight into simple RGB colors. These colors then travel further through the display's layers to create the onscreen image.
While this does deliver higher brightness, and the quantum dot filter improves color accuracy over previous LED technologies, these TVs require a backlight, thus limiting their black levels and contrast ratios.
The Best of Both Worlds
Samsung generally stuck with QLED and LED technologies, while LG focused on OLED displays. On the contrary, Sony offered both OLED and LED TV models. Nevertheless, consumers must either choose between a high-contrast display or a bright TV, but not both.
That's until Samsung announced the new QD-OLED panel. This tech combines quantum dot technology with OLED, allowing the screen to have increased brightness while still retaining deep blacks and increased contrast ratios.
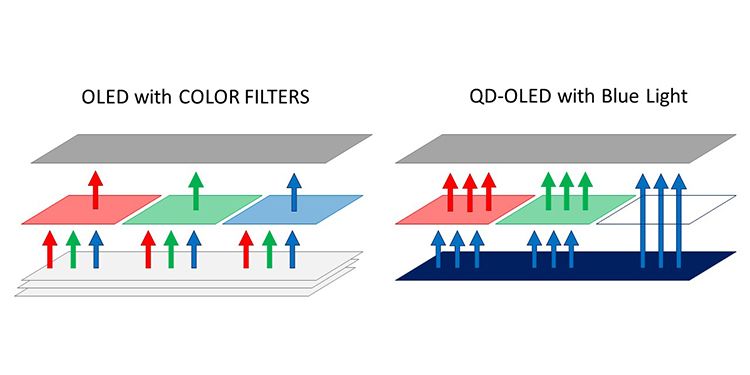
White light is composed of red, green, and blue colors. Regular OLEDs use red, green, and blue subpixels that filter the white pixel. That means a pixel can lose more than 80% of its brightness if it's showing just one color.
But with QD-OLEDs, the base pixel used blue instead of white light. Then, instead of using subpixels for color filtering, they used a quantum dot (QD) layer. This QD layer converts blue light into red and green by shifting its frequency instead of filtering it. This frequency conversion helps retain the light's intensity, allowing the display to have higher nits than traditional OLED devices.
Beyond Brightness
This new technology doesn't just affect the overall brightness of the TV. Because the QD layer converts color, there's less light energy being filtered out, thus enhancing the intensity of each color. For this reason, QD-OLEDs have better reds, greens, and yellows, even when compared to the latest OLED displays.
This enhanced contrast and brightness allow for sharper images and better HDR performance, thus allowing your TV to recreate natural color better than previous technologies.
QD-OLED: The Future of Displays
While Samsung developed this display technology, it's currently available in Sony TVs only. Nevertheless, even though Samsung hasn't made any announcements yet, we also expected to see this screen in their TV lineup. Furthermore, it's also likely to be available for gaming use, with rumors of 34-inch panels being made for both Samsung and Alienware monitors.
Although the QD-OLED offers groundbreaking color for TV screens, it's not a quantum leap in display technology. Instead, it's a fusion of the best technologies from OLED and QLED displays. And while we're excited for what QD-OLED can bring us, we're also looking forward to what LG's answer will be to this challenger to their OLED supremacy.