Display manufacturers like Samsung and LG have been in steep competition for many years. These companies make the best displays regarding color accuracy, dynamic range, color depth, and more. Their research and development resulted in many cutting-edge technologies, like OLED, QLED, and QNED.
So, to get the ultimate TV viewing experience, you need a TV rocking any of these technologies. But what's the difference between OLED, QLED, and QNED? And which one should you get for your specific setup?
So, let's go in-depth on these technologies and see which display is best for your application.
What Is OLED?
Although OLED technology was created in the '80s, OLED TV displays became popular only after LG released its 55-inch EM9700 display in 2013.
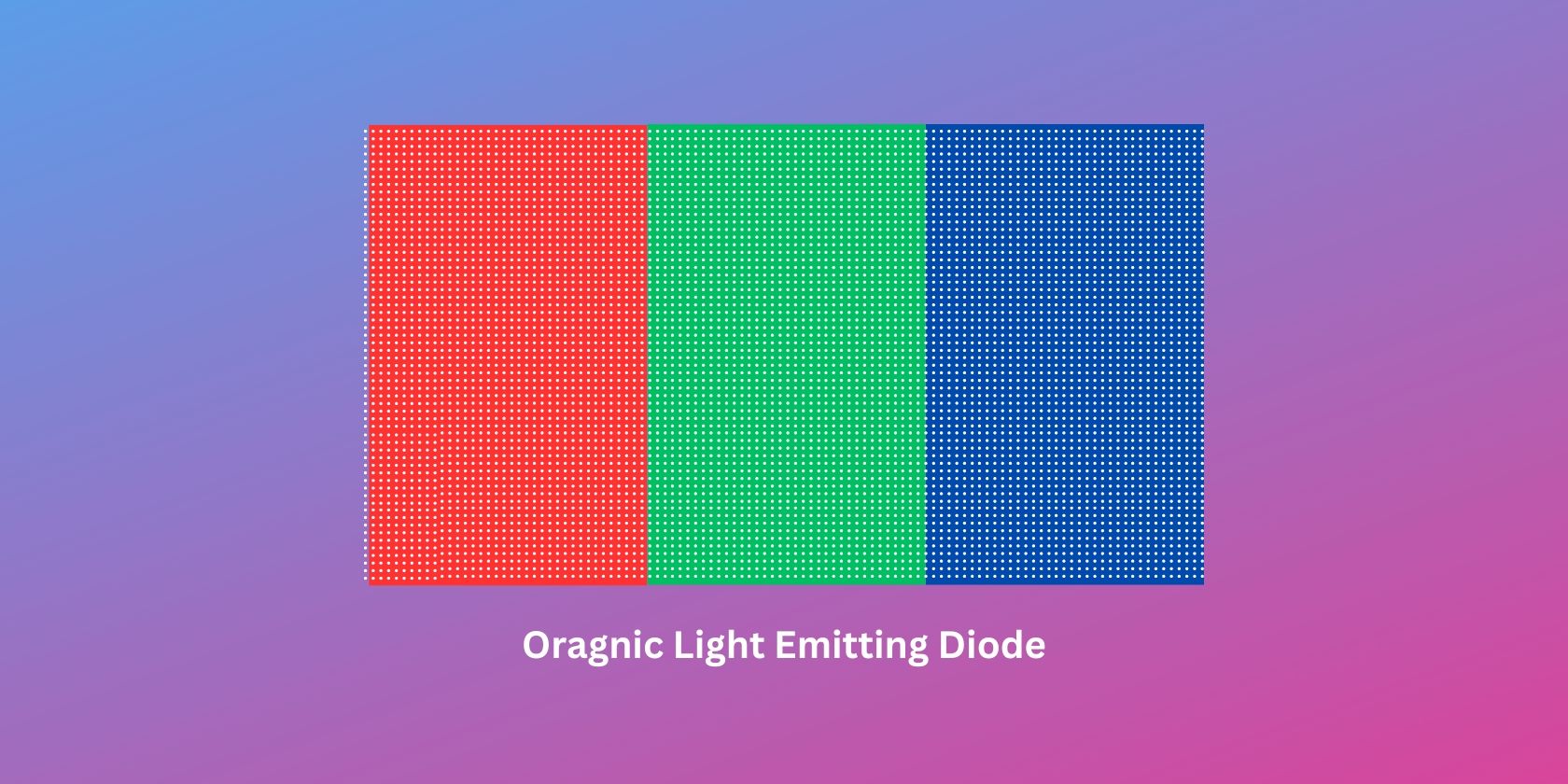
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode, where each pixel emits its own light. This removes the need for a backlight, allowing OLED displays to have the deepest blacks and technically infinite contrast ratios, helping them deliver unparalleled high dynamic range (HDR).
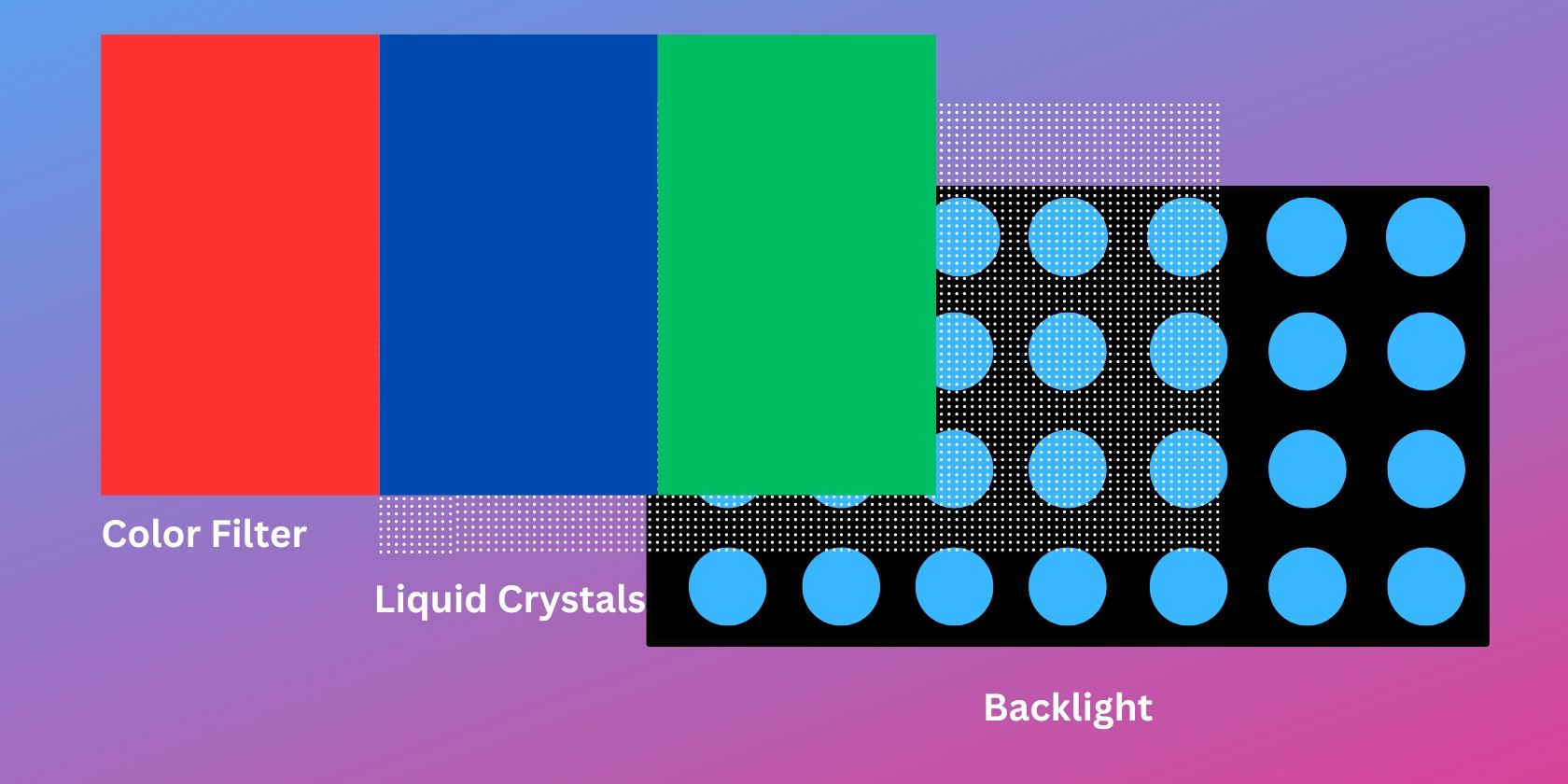
To let you have a better understanding, this is how a regular full-array LCD works:
As shown in the image above, a regular LCD screen has three main layers: a backlight, a liquid crystal panel, and a color filter. The display uses the backlight as a light source. The light is then variably dimmed and manipulated by the liquid crystal panel to create a grayscale image. This grayscale image then passes through the color filter layer, resulting in the final colored image you see on your screen.
On the other hand, OLED displays only use a single-layer panel. Although this panel consists of sublayers, including the substrate, an anode, an organic layer, a cathode, and an encapsulation layer, it comes as a single unit, allowing OLED displays to come in extremely thin form factors.
Furthermore, as OLED screens are controlled per pixel—from their brightness to their color—you don't need any other layer to shape the images you see on the screen. With these properties, OLED displays are known to have the smallest subpixels and the highest dynamic range. They're also usually the most color-accurate panels in the market.
However, OLED displays are also known to have poor brightness, typically ranging from 500 to 1,500 nits of brightness. In contrast, QLED and QNED displays can go much brighter at 1,000 to 4,000 nits.
What Is QLED?
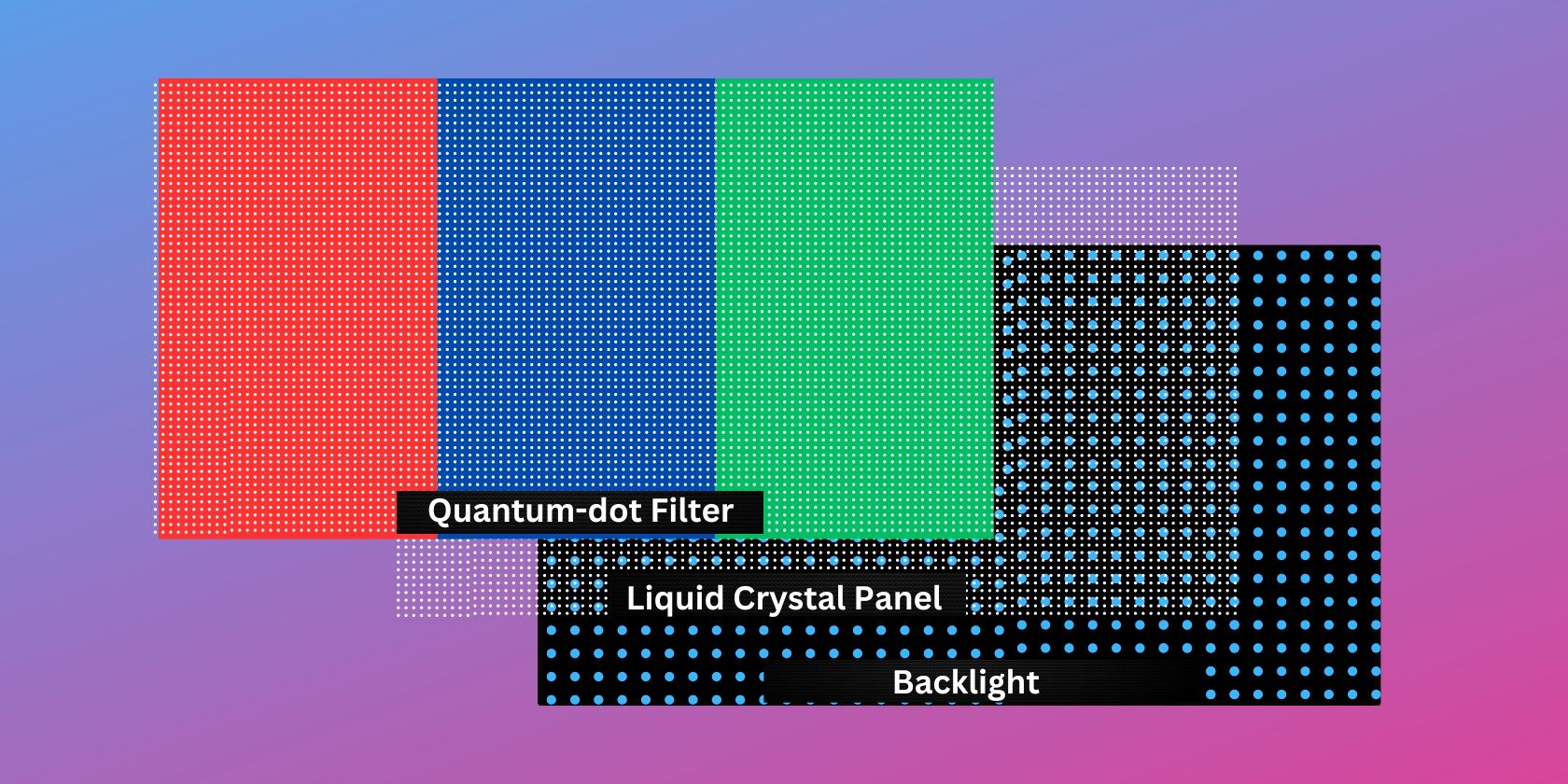
QLED stands for quantum dot LED. This type of display uses quantum-dot technology to replace the typical color filter in traditional LCDs. This newer filter uses quantum dots to absorb blue light. It can emit redder reds, greener greens, and bluer blues, which provides several advantages over traditional LCDs, such as a wider color gamut, higher brightness levels, and better color accuracy.
In addition, newer QLED displays are equipped with mini LED backlight technology, which minimizes screen blooming while providing higher dynamic range due to its better local dimming capabilities.
What Is QNED?
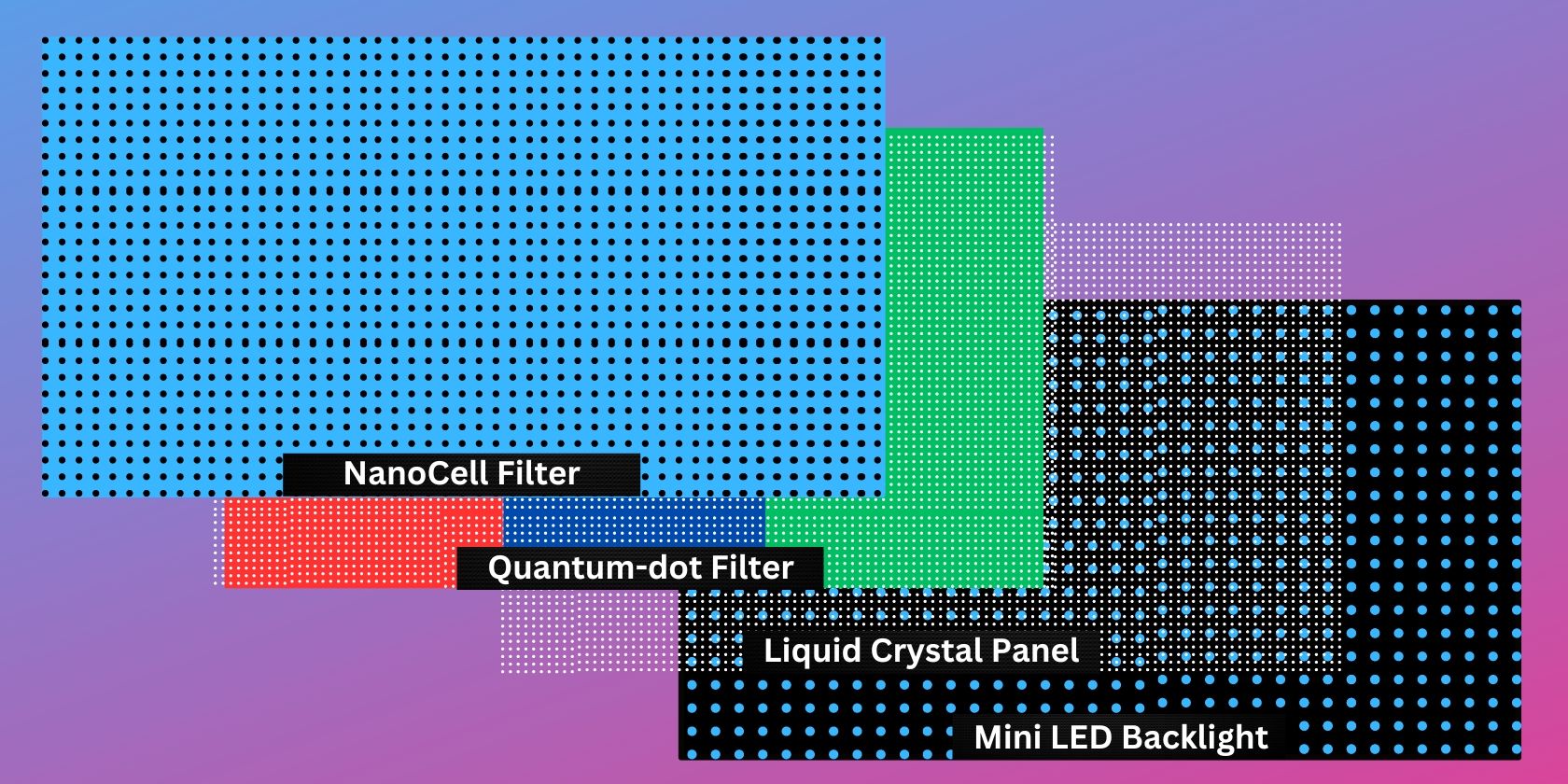
In response to Samsung's QLED and other high-end displays, LG released its screen technology, QNED. QNED, also known as Quantum Nano-Emitting Diode, combines Quantum-dot, mini LED backlight, and LG's NanoCell technology to provide purer colors and a wider color gamut with little blooming even at high levels of brightness.
QNED works just like QLED, which uses mini LED technology. However, QNED adds another layer in front of the quantum-dot filter, called NanoCElls. This layer uses nanoparticles to absorb unwanted light emitted from the Quantum Dot layer, reducing color distortions. QNED displays also often use AI ThinQ to optimize their settings and sound quality based on the viewed content.
Comparing OLED, QLED, and QNED
OLED, QLED, and QNED are the best display technologies currently available. They all provide a high dynamic range, wide color gamut, and high brightness levels and can display true HDR content. Although all are capable devices, their technological differences affect their performance depending on their environment, which is something you should consider when getting a new TV.
Here is a table of the typical specification of QLED, QLED, and QNED displays:
|
OLED |
QLED |
QNED |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
HDR Capable |
YES |
YES |
YES |
|
Viewing Angle |
178° |
160° |
160° |
|
Dimming Technology |
Pixel Level |
Direct Full Array |
Mini LED |
|
Peak Brightness |
400–1,500 nits |
1,000–4,000 nits |
1,000–4,000 nits |
|
Delta E Color Accuracy (lower is better) |
2–1 |
2 |
2 |
|
Dynamic Range |
1,000,000,000:1 |
1,000,000,000:1 |
1,000,000,000:1 |
|
Power Consumption |
50–200 Watts |
100–400 Watts |
100–400 Watts |
As you can see from the table above, OLED excels in viewing angles, power consumption, and even color accuracy on some displays. Many of these advantages are largely in part of an OLED display's pixel-level dimming technology, which allows it to emit colors and turn off individual pixels in completely dark parts of an image. However, OLED screens are also susceptible to burn-in problems.
And although OLEDs have around the same dynamic range as QLED and QNED on paper, this is only due to the max brightness available on these displays. Practically speaking, as long as the room isn't glaringly bright, you should have a better dynamic range with OLEDs over QLED and QNED.
Unlike OLED, QLED displays can output higher brightness levels and aren't as susceptible to screen burn-in. QLED's color accuracy isn't far off from OLED either, as it uses Quantum-dots to accurately portray redder reds, bluer blues, and greener greens.
The downside to using QLED displays is that they are more susceptible to screen blooming due to their LED backlight. This is even more of a problem with older QLED devices since they are likely not equipped with modern mini LEDs, which are becoming a standard for high-end displays.
QNED, the latest type of display, can employ the newest display technologies such as Quantum-dot, mini LED backlight, and NanoCell filters, providing higher dynamic range and color purity than QLED displays with little to no screen blooming.
Which Display Is Right for You?
Although OLED, QLED, and QNED can all provide crystal clear, color-accurate images, when it comes to choosing the best display technology for you, the decision ultimately depends on your specific needs and preferences.
Get an OLED display if you plan to build a home theater setup where you can control the lights and stop reflections from bouncing all over the room. The dynamic range from an OLED panel is the best in the market.
If you plan to use the display in a living room with ambient light from windows and doors, getting a QNED TV should work better than an OLED screen since it can output higher brightness. Also, the viewing angles on QNED displays are better than OLED and QLED, which is great if you watch with the family, where everyone is viewing it from different angles.
In contrast, you may want to go QLED if you're into gaming, where only one or two people will be in front of the display. QLED displays handle motion better than OLEDs since most QLEDs offer variable refresh rates (VRR) and low input lag. Also, QLED TVs are generally less expensive and readily available in most markets, unlike QNED displays.
OLED, QLED, and QNED Are All Awesome Displays
Now that you know the difference between OLED, QLED, and QNED, you should know what to get when looking for a new display. As for those who have already bought one of these displays and are wondering if they made a good purchase, all three technologies provide a similar level of performance, and many of their differences are only visible in certain conditions.
So, if you have already purchased one of the displays we discussed, there is not much else you are missing out on.