As climate change becomes more apparent, we should monitor and limit our carbon footprint.
Blockchains can consume enormous amounts of energy—depending on the type of consensus algorithm used—and this puts a strain on the environment. The proof of capacity (PoC) consensus algorithm combines the benefits of other algorithm options without the high energy consumption. So it looks like we are on to the greenest consensus algorithm yet.
What Is Proof of Capacity?
PoC, also known as proof of space, is a type of consensus in which you demonstrate an interest in a service by offering memory space to the service providers. This model allows you, as a miner, to exchange your free disk spaces for cryptocurrency over a decentralized network. It offers a quid pro quo service, so the more space you have, the more likely you will claim the mining reward.
PoC employs less energy consumption than other models because it uses just your free memory size to verify blocks. It is no wonder the mechanism is backed as a greener alternative to earlier consensus mechanism algorithms, such as proof of work (PoW).
How Does the Proof of Capacity Algorithm Work?
Imagine going for a computer-based test with a list of possible answers on a hard drive. The larger your hard drive, the more answers you can store. And the more answers available, the more likely you'll obtain the correct ones necessary to ace the test. These test questions are similar to the data hashing problems PoC miners solve, while the answers are the plots to be stored on the hard drives.
The block times in proof of capacity are short—only about four minutes per block, unlike ten minutes per block for bitcoin. This means the solutions for the complex mining problems must be "plotted" beforehand to meet up with the time.
Block rewards are the end goal of dealing with blockchains, and the PoC algorithm employs two steps for this: plotting and mining.
Hard Drive Plotting
Every blockchain miner seeks a nonce—a unique encrypted four-byte number used to verify the information embedded in a block that is only used once (nonce stands for "numbered used once"). All possible nonce values are compiled on the hard drive via plotting, even before mining starts properly.
Each plotted nonce has 8,192 hashes, starting from 0 to 8,191. All 8,192 hashes are paired into scoops, which are instrumental in the mining that will be done later. These nonces are created by nodes repeatedly hashing data; this is the only energy-consuming part of this consensus mechanism. It requires very little energy (about 4 watts) compared to other proof algorithm mechanisms.
Block Mining
In the mining aspect of the PoC mechanism, the scoops are used to compute a deadline value, which is the maximum time that must pass before another block is produced. The shorter the deadline, the more likely it is for a block to be forged and for the node to claim the reward.
For example, you come up with a deadline value of 20 seconds. You get to forge the block and claim the reward if no other participant can beat your 20 seconds deadline.
Block mining requires no energy consumption, making the PoC mechanism much greener than other consensus mechanism algorithm alternatives.
5 Advantages of Proof of Capacity Over Other Mining Methods
Proof of capacity is currently gaining much traction because it combines the best features of earlier consensus algorithm models while remaining eco-friendly.
1. Low Energy Consumption
With the PoC consensus algorithm, energy consumption can be lowered by up to 96%. Using this model is a step in the right direction in pursuing greener, cleaner mining and computing practices.
2. Low-Maintenance and Affordable
There is no need for expensive gadgets when using the proof of capacity mechanism. Any regular hard drive will work, and you won't have to worry about upgrading the hard drive periodically. It is as easy as mining from the storage of your Android phone.
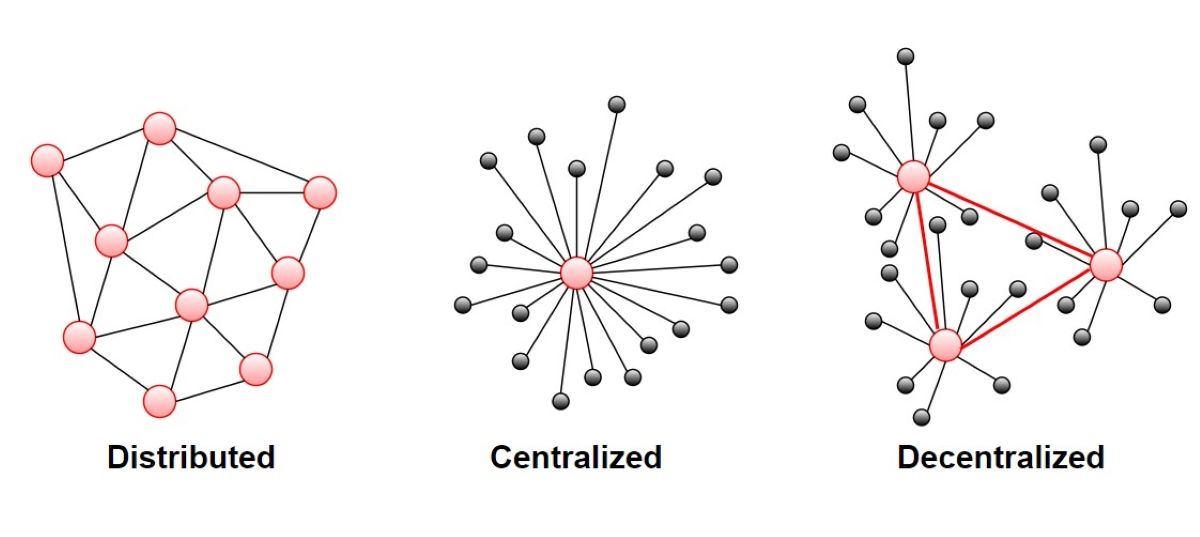
3. Decentralized Network
Since largely everyone has some form of hard drive, PoC is highly decentralized. This is a notable edge over the PoW algorithm model.
4. Shorter Mining Time
Using the PoC algorithm, you can whip up a block in under four minutes, whereas you can spend ten minutes using the PoW algorithm.
5. Reusable Space
If you want to pursue other interests, you can easily clear all mining data cached on your hard drive and reuse it for other things. The storage remains yours to use.
4 Limitations of Proof of Capacity
With all the benefits of the PoC algorithm, it has a few drawbacks compared to other consensus mechanism algorithm alternatives.
1. Less Secure
With the increase in mining comes an increase in mining malware. A space-dependent algorithm like PoC is susceptible to malware as much space is used, most of which isn't monitored for strange files.
In addition, the abundant free space in drives used to cache hashing data makes it even more difficult to detect malware.
2. Favors Space Hoarders
The proof of capacity algorithm favors those with larger disk spaces. More storage space is required as more miners are added to the network. People can easily start purchasing humongous drives to mine a large chunk of the cryptocurrency. This makes mining a lot more difficult if you have smaller drive sizes.
3. Limited Reach
Only a few developers use the PoC algorithm, unlike the PoW consensus algorithm.
4. Technical Issues
Technical issues as regards PoC algorithms can take several forms. For example, if a node drops out of a network, it can take quite some time to reconstruct the plot files, and in a race against time, that's disadvantageous.
Proof of Capacity vs. Proof of Work & Proof of Stake
Proof of capacity algorithms use storage space on hard drives as a resource to be mined or validated in exchange for network tokens over a decentralized network. This provides the benefits of PoW and proof of stake (PoS) models without the downsides of either approach.
PoW consensus algorithms are slow and require tremendous computational power—like application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). PoS algorithms suffer from high centralization risks and the need for participants to provide deposits upfront.
Although less popular than the PoW and PoS consensus algorithms, PoC removes the problem of cryptocurrency stockpiling in PoS and greatly reduces the high computation energy used in PoW.
Which Cryptocurrencies Use Proof of Capacity?
Although relatively new, the proof of capacity algorithm is already being applied and modified:
Burst
Before being rebranded as Signum in 2021, Burst pioneered the proof of capacity mechanism. This involved using affordable, regular hard drives utilizing energy as low as 4 watts on average. Burst's energy consumption was more sustainable than Bitcoin, using specialized ASICs that can consume an average of 1400 watts.
Burst, now called Signum, has transitioned into the proof of commitment (POC+) consensus algorithm, an advanced level of the PoC model. Signum can be used for crowdsourcing, payments, crypto contracts, and encrypted messaging.
SpaceMint
The proof of space mechanism used for mining the proposed SpaceMint crypto employs a non-interactive format. As a result, the participants here must create a hard-to-pebble graph, a highly interconnected vertex used in computing hashes. This sets it apart from other uses of the proof of capacity algorithm.
Chia Network
The Chia network is one of the most popular proof of capacity (PoC) algorithm applications. Chia is a blockchain-based platform designed to make decentralized and distributed storage more secure, reliable, and cost-effective. Chia has implemented the PoC algorithm to create a distributed network of storage devices, known as farms, that store and secure data. In fact, Chia caused a worldwide increase in storage prices at launch!
However, Chia has been met with controversy due to its potential to wreak havoc on hard drives. It works by generating plots of data on the drive that takes up a large amount of space, which could potentially cause serious damage to the hardware if it is not monitored and maintained properly. This has led some users to question the network's security and its PoC model's sustainability.
Despite this, other existing PoC applications do not seem to have had any issues related to hard drive damage. For example, while Burstcoin does use hard drives to store data, it does not generate large plots of data that could potentially cause damage to hardware. As such, it appears that PoC is still a viable consensus algorithm that can be implemented without damaging hard drives.
The Future of Blockchain Is Green
The computing and crypto world has begun to realize the importance of being environmentally conscious. With the advent of the proof of capacity consensus mechanism algorithm, we can be assured of an easier, faster, and greener means of mining—possibly the greenest yet.