NVIDIA is known to release a new-generation graphics card architecture every two years. In 2018, it released the Turing chip for the GTX 16-series and RTX 20-series GPUs. Then, in 2020, it introduced the Ampere chips for the RTX 3000 GPU.
And as expected, during the NVIDIA GPU Technology Conference in September 2022, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang finally announced the Ada Lovelace microarchitecture that will power the 3rd generation of RTX GPUs.
So, what improvements does the Ada Lovelace microarchitecture bring to the RTX 4000 GPU?
1. An All-New Process Node
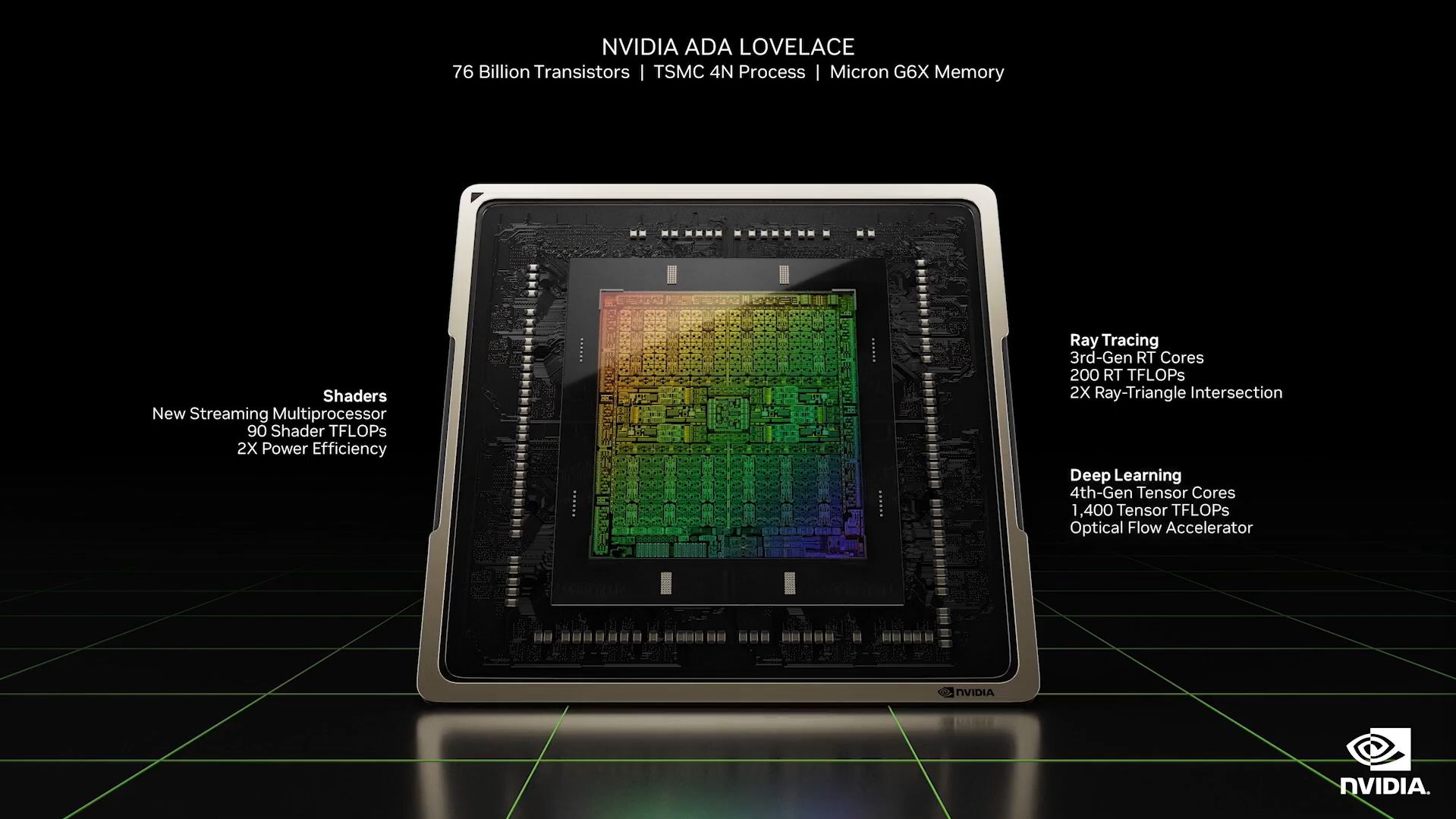
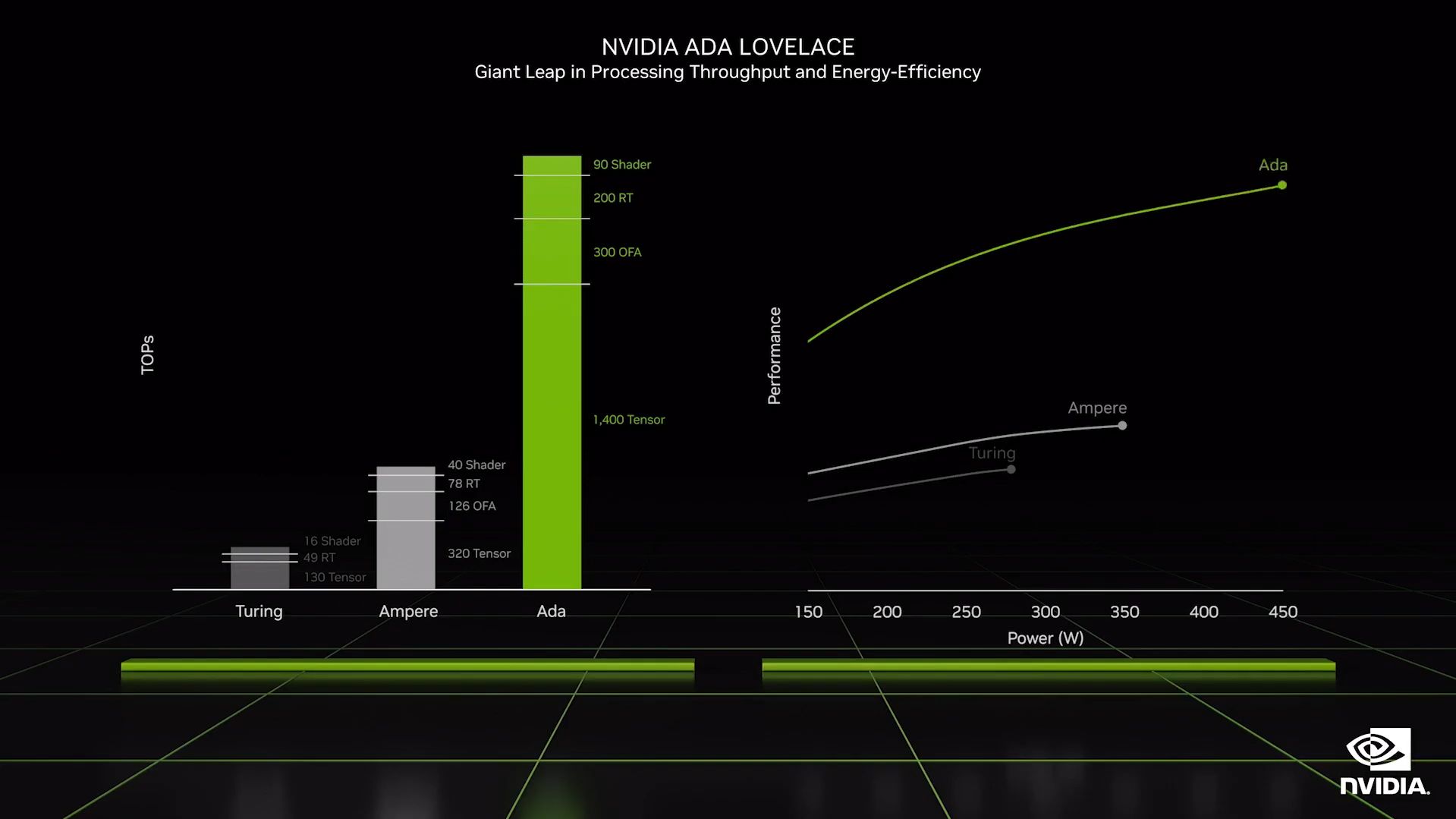
The Ada Lovelace microarchitecture is based on TSMC's 4nm N4 technology, making it half as small as the previous-gen Ampere chip based on Samsung's 8nm process. This smaller nm brought by improvement in the node process allows the RTX 4000 series to deliver more power efficiently.
That means even mid-range variants that NVIDIA will release in the future can compete against top-tier 30-series chips like the 3090 Ti.
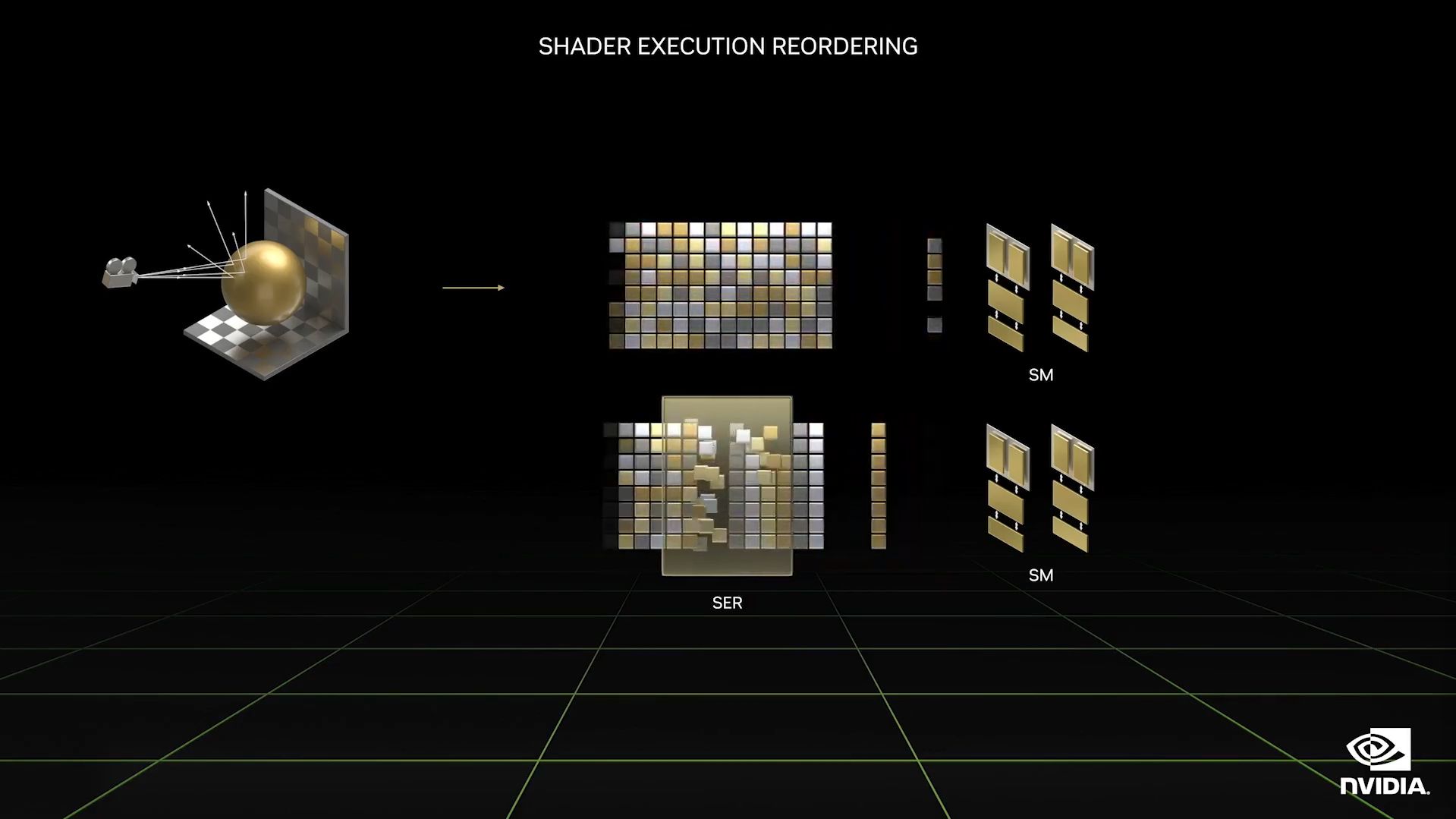
2. Shader Execution Reordering
Because of its parallel structure, a GPU is great at using multiple cores of its processors to handle the same task. However, ray tracing is completely different from rendering scenes. That's because light rays bounce everywhere, requiring different computations for each surface it hits and every direction it goes. This means GPUs are less efficient when it's processing many different shaders.
But with Shader Execution Reordering (SER), the Lovelace chip can reschedule its workload, ensuring that similar shaders are processed together. This allows the streaming multiprocessors to work more efficiently, as they simultaneously work on the same data.
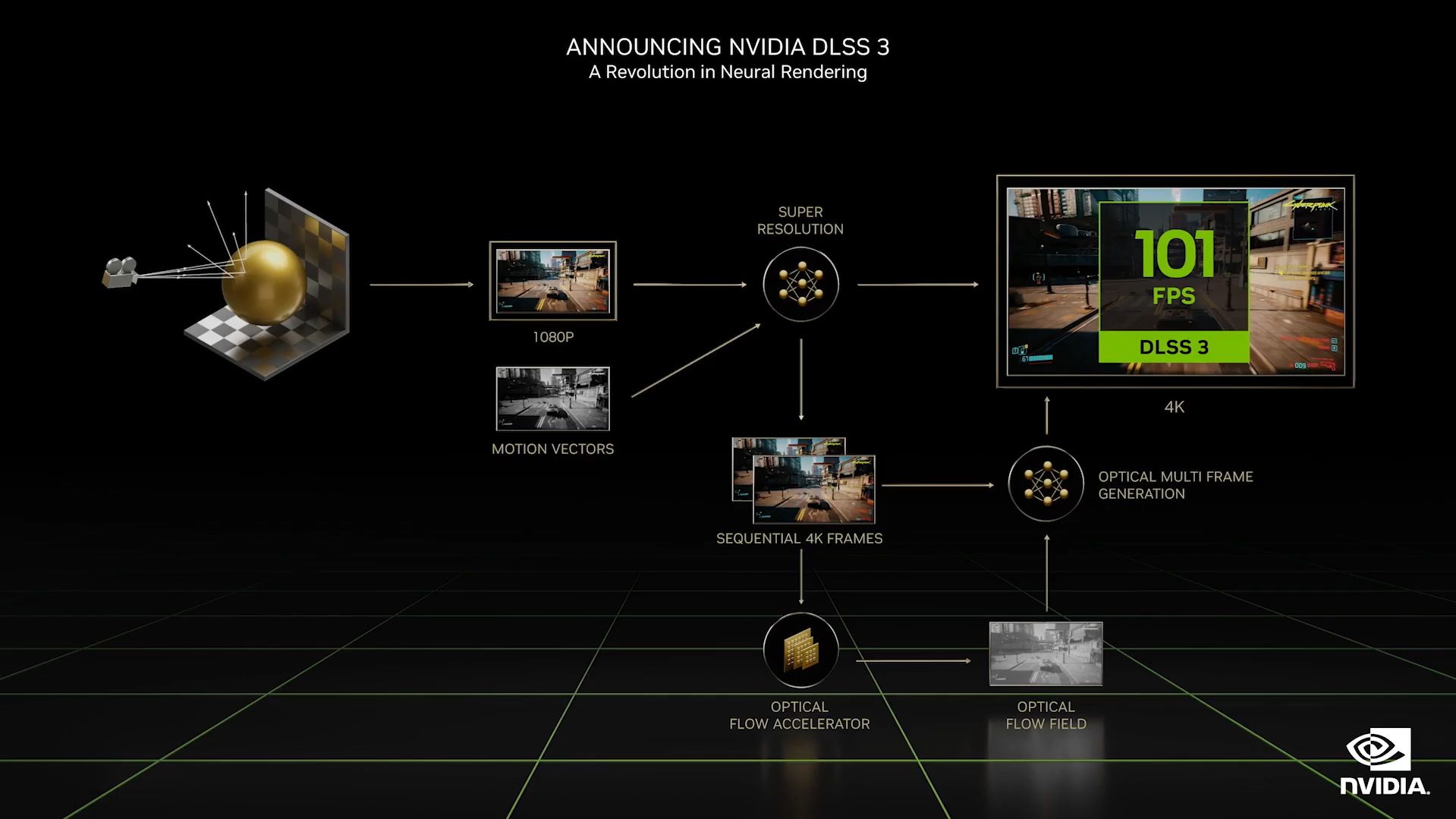
3. DLSS 3.0
RTX is a resource-intensive task, especially if you're working with higher resolutions like 4K and above. That's why NVIDIA developed DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling). DLSS technology uses AI to predict the next pixel, helping reduce the workload on the GPU.
But with the Ada Lovelace architecture's DLSS 3.0, NVIDIA expands the prediction from pixels to frames. This allows the GPU to predict the next frame, even without looking at the image data yet to be rendered. Doing so improves the performance of both GPU- and CPU-heavy games, which Huang claims is up to four times better than brute-force rendering.
4. Tensor Cores
NVIDIA is trying to make it big in the AI computing space, and it shows in its latest-generation chip. The Ada Lovelace microarchitecture uses 4th-generation Tensor Cores, capable of delivering 1,400 Tensor TFLOPs—over four times faster than the 3090 Ti, which only had 320 Tensor TFLOPs.
This new generation of Tensor Cores is probably why DLSS 3.0 performs much better than its previous iterations. It could also be why comparatively lower-model 4000-series chips outperform the top-tier models of the 3000-series GPUs.
5. Improved Power and Efficiency
NVIDIA claims that the Ada chips are two times faster for rasterized games and up to four times faster for ray-traced ones. Furthermore, they say that its latest chips offer more than twice the performance for the same power rating.
And because of these improvements, you can overclock Lovelace GPUs past 3GHz—but this comes at the price of colossal power draw: up to 450 watts for the RTX 4090.
Nevertheless, these improvements could also be why the rumored RTX 4070 is as powerful as the RTX 3090 Ti, and the RTX 4090 delivers twice the power of the 3090 Ti on the same power draw.
The Heart of RTX 4000-Series GPUs
The Ada Lovelace microarchitecture is another leap in GPU power, performance, and efficiency from NVIDIA. And since this chip is the beating heart of the RTX 4000-series consumer GPUs, we expect these incoming cards to deliver outstanding performance.
However, these are just theoretical claims until we get our hands on the RTX 4090 on October 12, 2022, and the RTX 4080 the following month. So, we're holding our breath and waiting to see actual benchmarks when retail units hit store shelves.