CPU sockets might not be high up on your list of criteria for choosing a computer. However, they do have a bearing on cost and performance, so understanding the difference between the two most common forms is useful.
LGA and PGA sockets are the two common forms in question. But what's the difference, and what should you choose?
What Is a CPU Socket?
A CPU socket is the physical connection between your computer's motherboard and the CPU. The CPU can be likened to the engine of a car. And just like a car engine has a bearing on a vehicle's performance, the CPU plays a large part in determining the speed and power of your computer.
Whereas the CPU socket is like the mounting point for the car engine, providing a secure connection between the engine and the car's chassis. The socket allows the CPU to connect to the motherboard, facilitating communication with other components. Then, the motherboard feeds information and power to the other computer hardware.
The genesis of the CPU socket in its modern form can be traced back to the original Intel 286 processor that kick-started the age of the PC. This used a 132-pin PGA socket, from which CPU sockets have changed hugely as computer architecture evolved.
Despite these changes, the PGA socket is still widely used. LGA sockets followed in the mid-nineties.
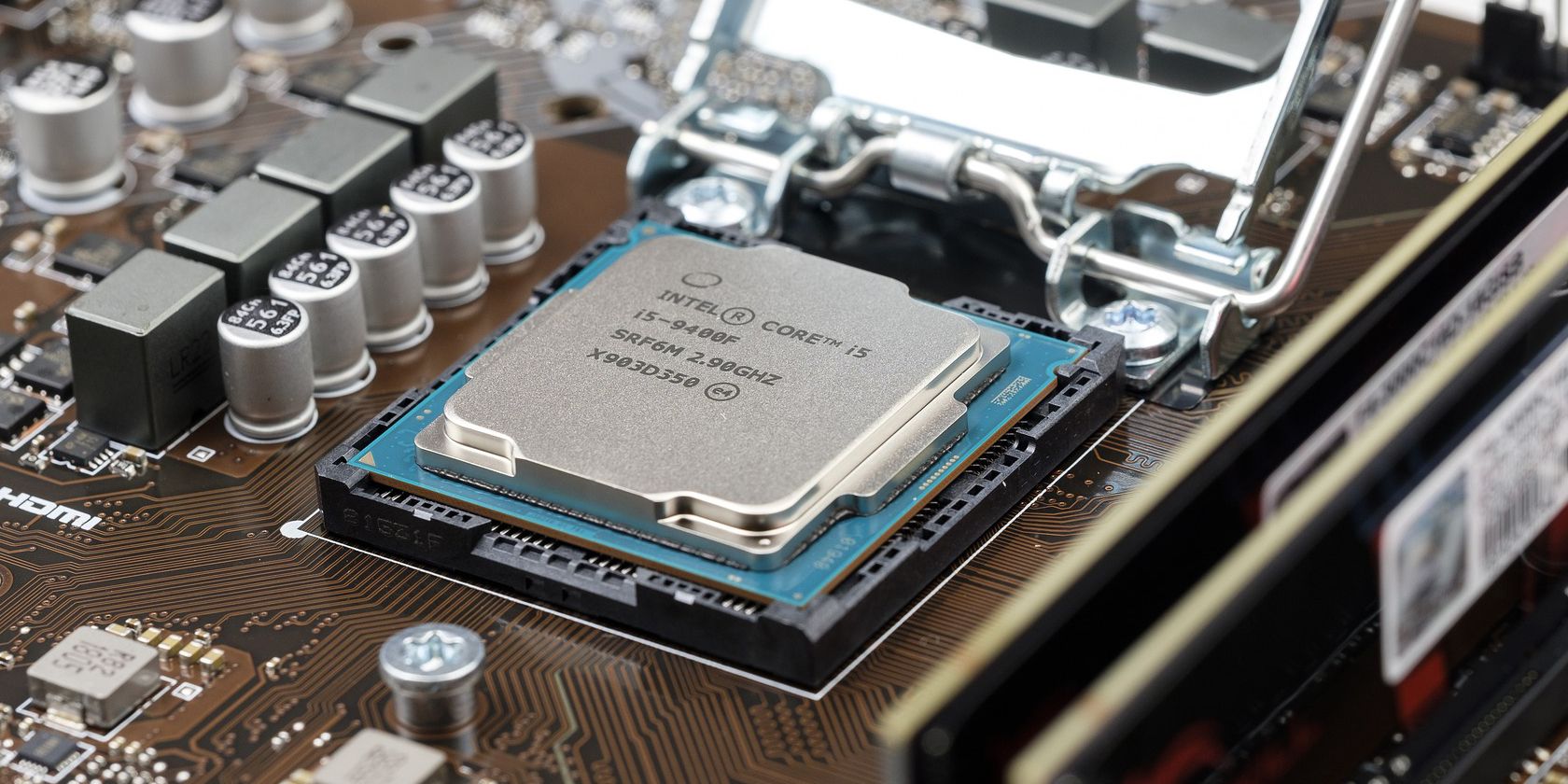
Land Grid Array (LGA) Sockets
LGA sockets are commonly, although not exclusively, associated with Intel processors. This is due to one of the main differences between Intel and AMD motherboards.
With LGA sockets, the pins connecting with the processor are on the motherboard. The processor is designed with corresponding "pads" that make contact with these pins.
The pads are often referred to as lands and are manufactured using gold to maximize conductivity. This type of socket allows for easier and safer installation of the processor. The process is as simple as sitting the processor on top of the slot and using a mechanism to hold it in place.
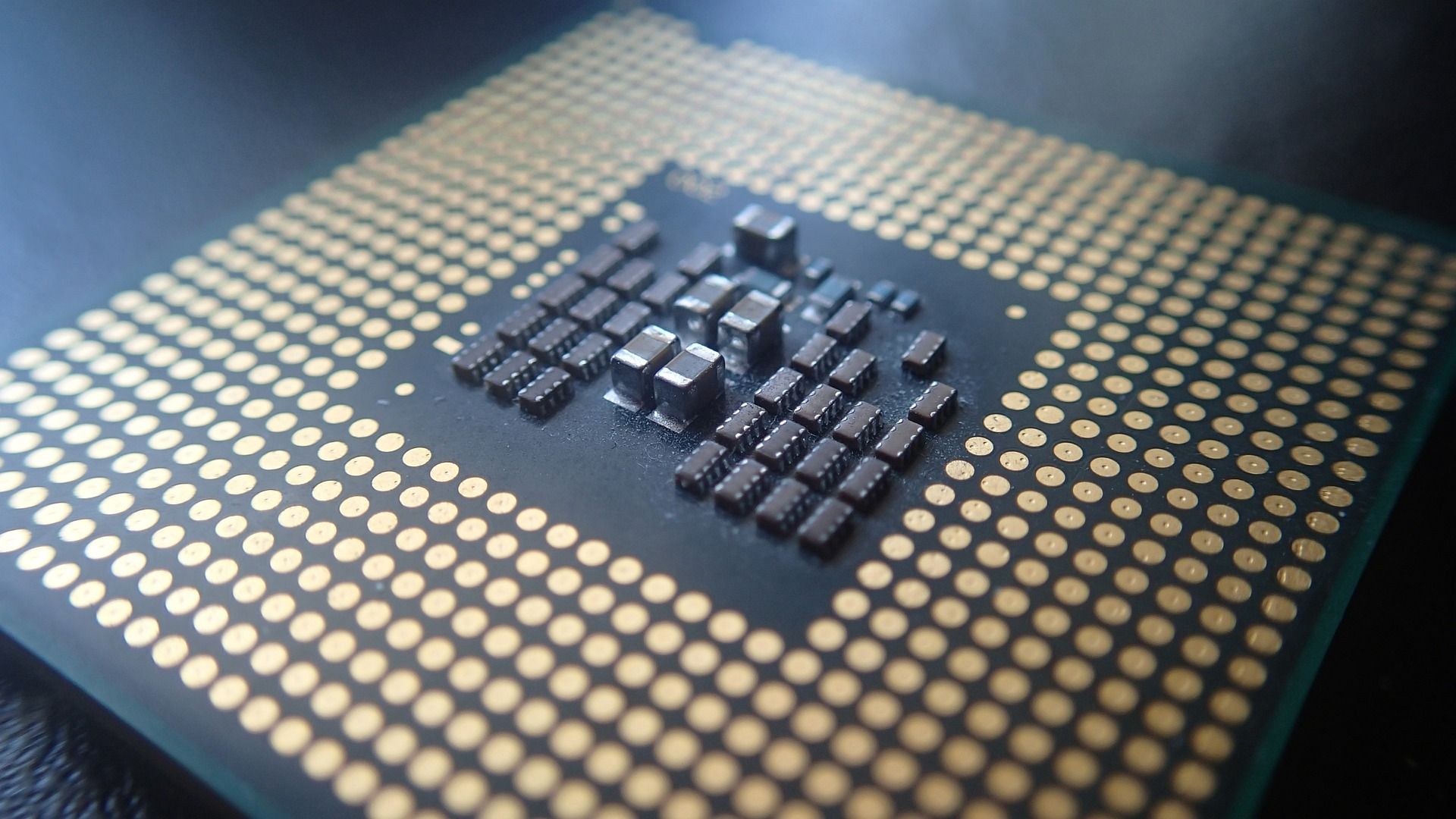
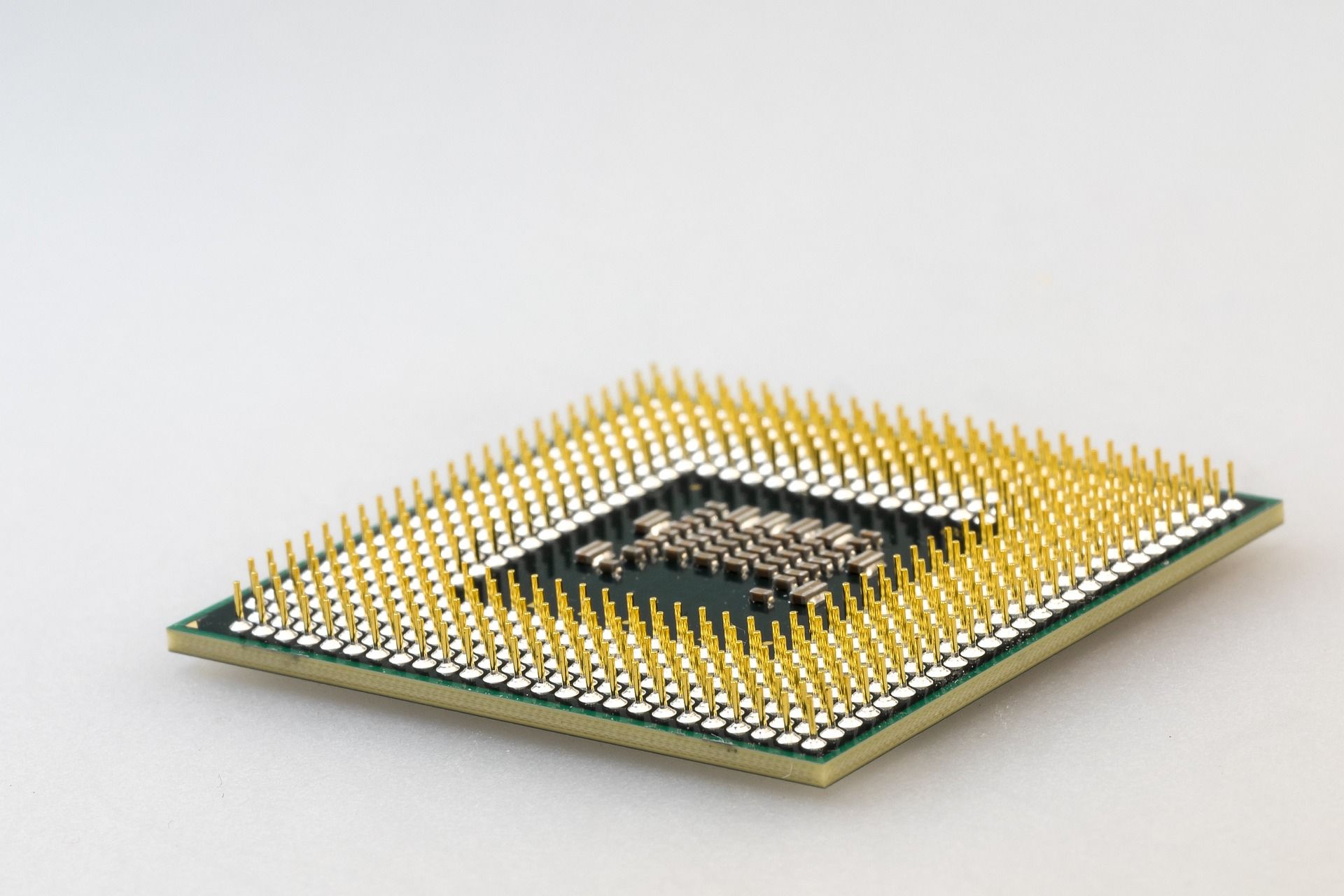
Pin Grid Array (PGA) Sockets
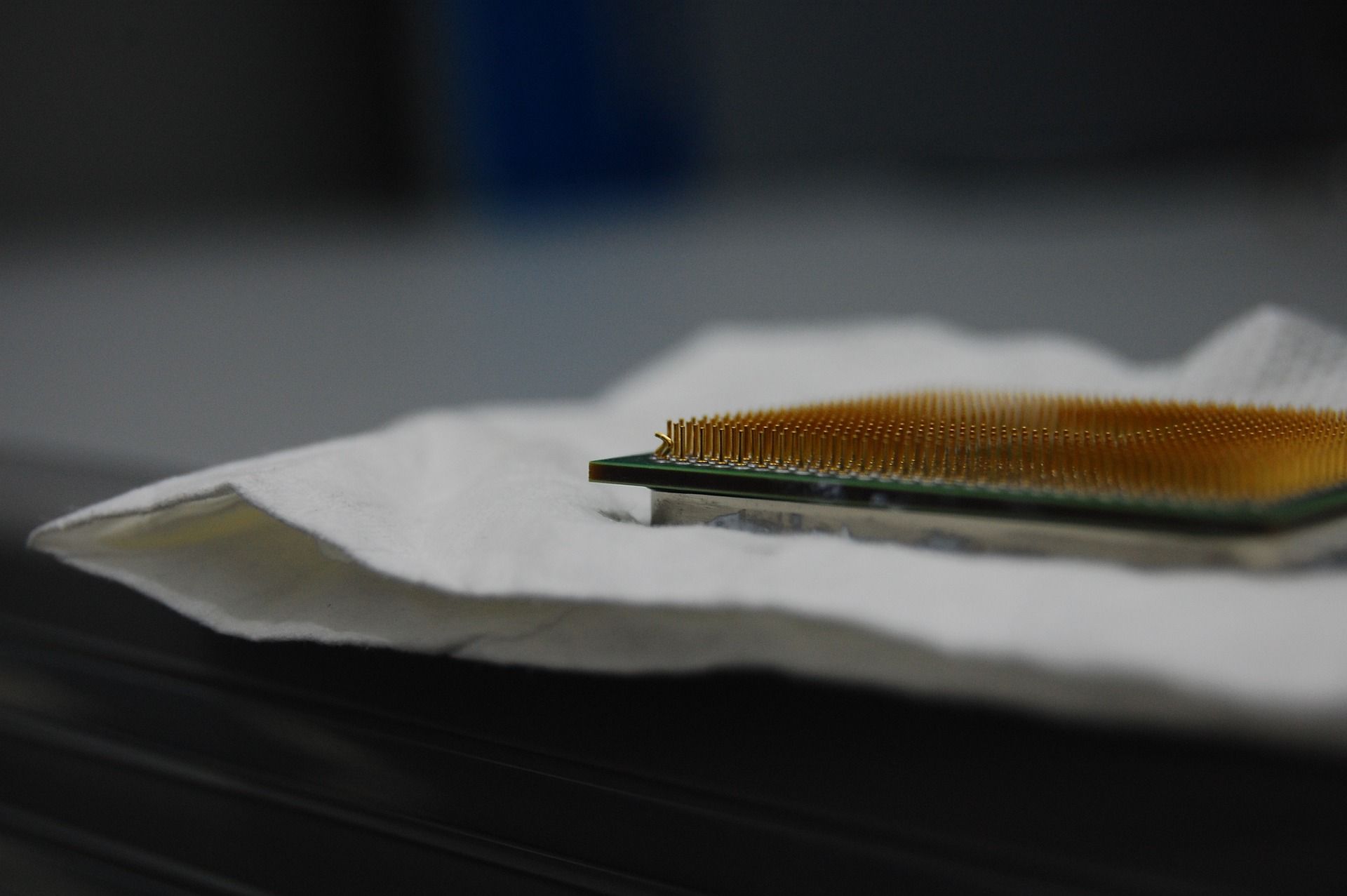
PGA sockets have been used in most AMD computers until the launch of its AM5 socket in 2022. They differ from LGA sockets as the pins are on the processor, not the motherboard. This is more important than you may initially think because it makes them vulnerable during installation. More on this point a little later.
However, if done properly and carefully, they should just drop into the CPU socket. Once seated properly, a locking lever is used to secure the processor. One thing to be careful of is that the locking lever is in the open position before you seat the processor.
Which Is Best: LGA or PGA CPU Socket?
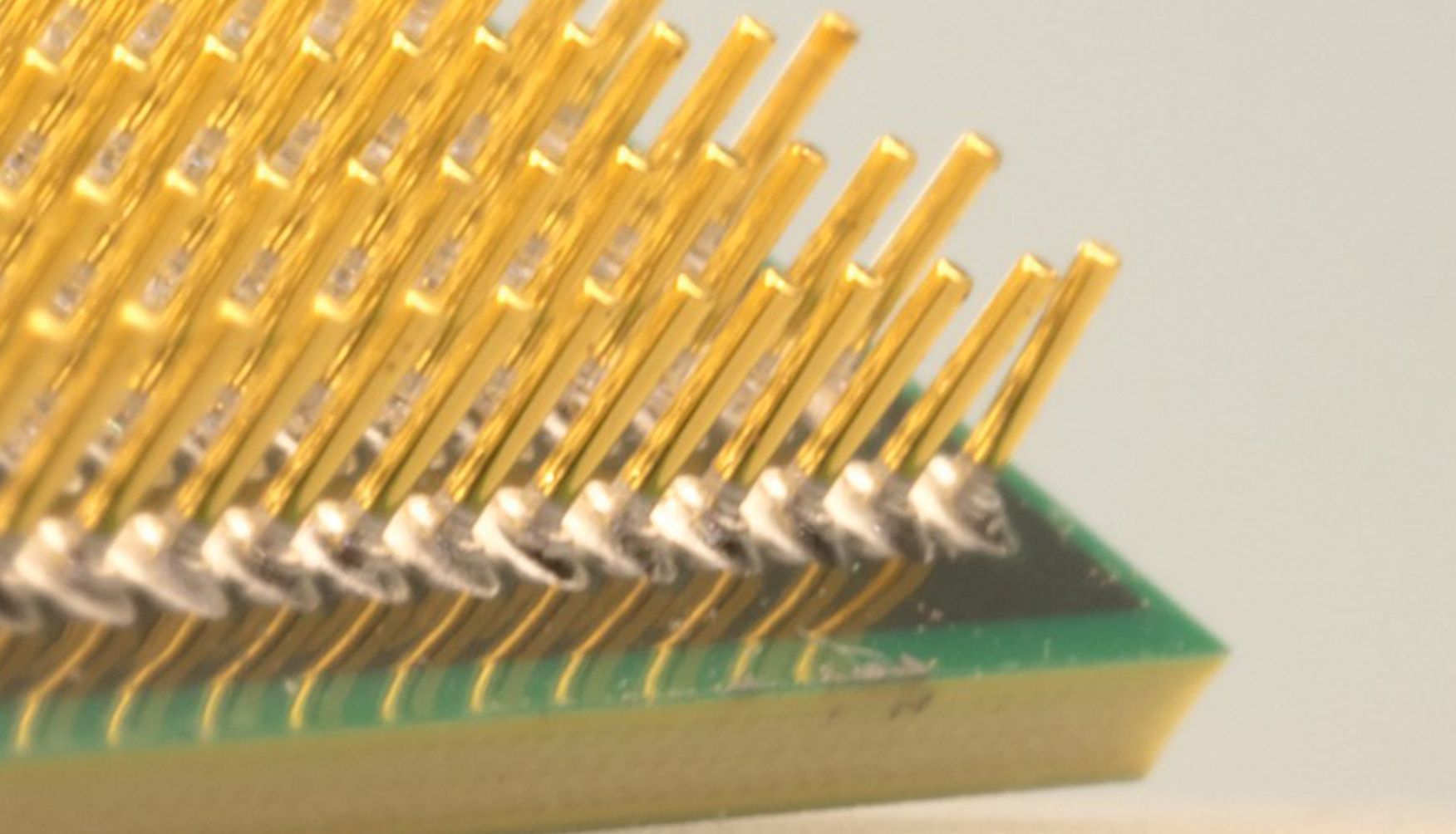
There are pros and cons to both forms. But let's start with an Achilles heel that has always dogged the PGA CPU socket—namely, the fragility of the pins.
I speak from experience here. Having built bespoke PCs commercially for over twenty years, I can testify that it only takes one moment of ham-fistedness to turn an expensive CPU into a useless tangle of bent pins.
The following photo shows a common result of a careless attempt at installation. In this instance, some delicate tweezer work would likely rescue the processor, an exercise I performed a few times. But again, care is needed if you find yourself in this situation, as the pins will easily snap.
If you remember to take extra care with PGA sockets, the installation is quick and simple. So, what other differences can sway your choice? Here are some of the other considerations:
- Electrical Properties: LGA sockets perform better thanks to better contact between the CPU and the socket. This can lower power consumption and improve performance.
- Pin Density: The pin density on LGA sockets tends to be higher. This allows for higher data transfer rates.
- Cost: This is harder to quantify as a high-end PGA will cost more than a low-end LGA, but there are also different manufacturers to consider. But as a rule of thumb, when comparing similar specs, PGA CPUs are cheaper.
- Durability: LGA sockets are more durable. However, to a lesser degree, the pin vulnerability of PGA sockets is switched to the motherboard with the LGA format.
There isn't much to choose between the two. Both formats have proven track records that stretch back decades. But with AMD's move to LGA sockets, PGA CPU sockets may fade out of fashion.
LGA vs. PGA: Is It a Consideration?
If you are just looking for the right PC at the right cost, this is probably not a deal breaker. However, if you want to custom-build a PC or upgrade a motherboard, knowing your CPU sockets is useful information.
Some general advice that I always gave customers was to opt for LGA for high-end gaming PCs. Anything requiring mid-to-low spec, then both choices are fair game.