At CES 2019, Nvidia announced its software-based version of G-Sync that extended VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) support for Nvidia GPUs on AMD FreeSync monitors. However, initial impressions were a tad bit underwhelming as the company validated only a handful of FreeSync panels that can run G-Sync to its full extent, without resorting to any major compatibility issues.
Now comes the question: is it possible to activate Nvidia's Adaptive-Sync technology on a FreeSync display that hasn't been certified as G-Sync Compatible? Let's find out!
How Nvidia G-Sync Works on AMD FreeSync Monitors
To maintain exclusivity of its proprietary Adaptive-Sync solution, Nvidia's G-Sync technology has been categorized across three different tiers: G-Sync, G-Sync Compatible, and G-Sync Ultimate. While both G-Sync and G-Sync Ultimate monitors feature a dedicated module to drive VRR, G-Sync Compatible monitors are essentially FreeSync panels that have been validated by Nvidia to run G-Sync through its rigorous testing methodology.
|
Trait |
G-Sync Ultimate |
G-Sync |
G-Sync Compatible |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Validated for Artifact-Free Experience |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Certified with 300+ Image Quality Tests |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Certified for "Likelike HDR" (~1000 nits Brightness with HDR) |
Yes |
No |
No |
|
Variable Overdrive Support |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Ultra-Low Motion Blur & Overclocking Support |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
In case you're wondering, Nvidia's G-Sync Compatibility program, which was introduced back in 2019, aims to certify a wide range of FreeSync monitors based on specific parameters. For starters, every G-Sync Compatible monitor should be able to deliver a baseline VRR experience without incurring any visual artifacts such as pulsing, flickering, blanking, or ghosting.
Furthermore, the retroactive program also validates whether a FreeSync display can operate across a VRR range of at least 2.4:1. Such calculations are performed by dividing the maximum refresh rate of a monitor to its minimum refresh rate within the VRR range.
For instance, if your FreeSync monitor supports a wide VRR range of 48-144Hz, which is greater than Nvidia's recommended value of 2.4, G-Sync functionality should be enabled right out-of-the-box. However, if the minimum VRR range went up to 75Hz, which does not comply with Nvidia's VRR threshold, the display loses an official "G-Sync Compatible" certification.
As of November 2022, Nvidia has validated over 150 FreeSync monitors that can run G-Sync at an adequate VRR range. For more information, check out Nvidia's official list of FreeSync monitors that have been certified as G-Sync Compatible.
Although official G-Sync Compatibility has its perks on quite a few occasions, it is possible to drive Nvidia's Adaptive-Sync solution on most non-certified FreeSync monitors, provided that you possess the right set of hardware. Since both FreeSync and G-Sync technologies support VESA's (Video Electronics Standards Association) Adaptive-Sync protocol, any limitations that you might face are based solely on the manufacturing standards.
Nvidia G-Sync on AMD FreeSync Monitors: Setup and Compatibility
Unlike AMD's FreeSync implementation, which works on both HDMI and DisplayPort (over USB Type-C as well), Nvidia's proprietary Adaptive-Sync solution seems somewhat limited in terms of connectivity. For G-Sync to work on a FreeSync display, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Connection Options: DisplayPort 1.2 (or higher) for AMD FreeSync monitors. HDMI 2.0/2.1 support for G-Sync Compatible TVs and BFGD (Big Format Gaming Displays).
- Supported Graphics Cards: Nvidia GeForce GTX 10/16-Series and RTX 20/30/40-Series GPUs.
- Driver Support: GeForce Game Ready Driver Version 417.71 (or newer).
- Operating System: Windows 10/11 (64-bit)
To enable G-Sync functionality on a FreeSync monitor that lacks Nvidia's official certification, follow the walkthrough below.
First, download and Install the latest GeForce Game Ready Drivers from Nvidia's official Driver Downloads page. Alternatively, it is possible to update your GPU drivers by using Nvidia's own software suite: GeForce Experience.
After installing the latest GPU drivers, restart your PC and check whether FreeSync (Basic or Extended) has been enabled from the monitor's OSD (On-Screen Display).
For G-Sync Compatible monitors, G-Sync should be enabled by default when FreeSync has been activated from the monitor's OSD. However, if you are using a non-certified FreeSync display, you might need to change additional settings inside the Nvidia Control Panel. Right-click on the desktop and select NVIDIA Control Panel from the drop-down menu.
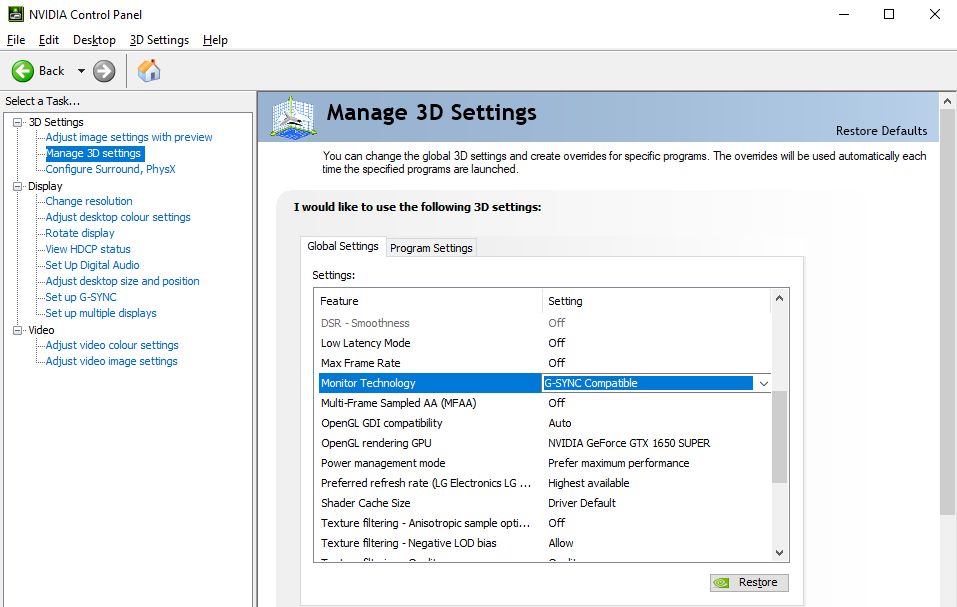
Inside the NVIDIA Control Panel, go to Manage 3D settings and look for Monitor Technology under the Global Settings tab. Set G-SYNC Compatible as the preferred option.
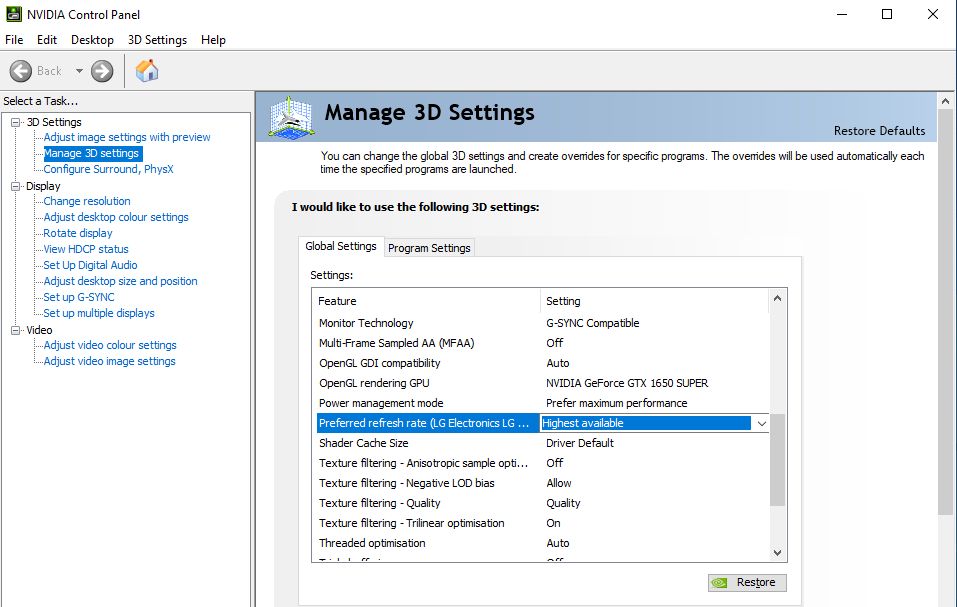
On an additional note, check whether Preferred refresh rate has been set to Highest available. Doing so allows your FreeSync monitor to take advantage of its maximum refresh rate.
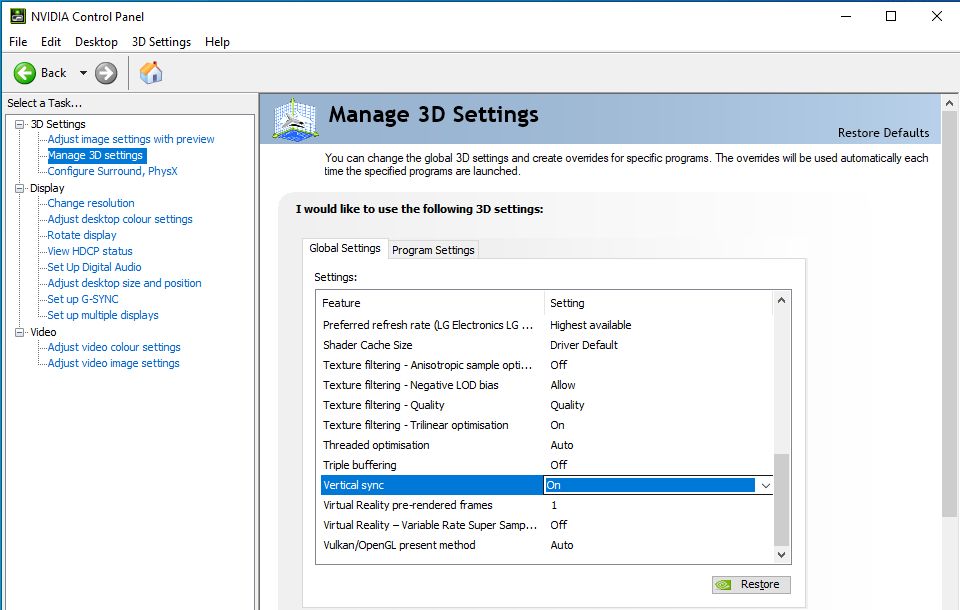
For an optimal G-Sync experience, we recommend using V-Sync along with G-Sync to eliminate screen tearing when the frame rate goes above the VRR range. Under Global Settings, scroll down to the bottom of the list and set Vertical sync to On. Click on Apply to save your changes.
(Note: When playing a game, ensure that in-game V-Sync has been disabled. Doing so allows V-Sync to work in tandem with G-Sync at the driver level.)
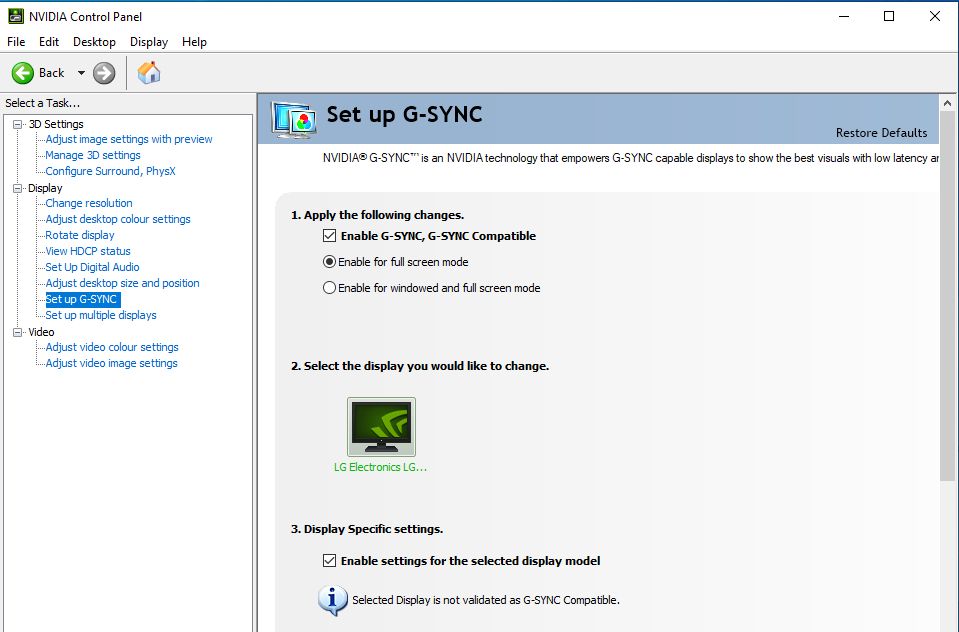
After modifying these settings, click on Set up G-SYNC under the Display tab. In case you're using multiple monitors, select your primary display and click on the checkbox, right next to Enable G-SYNC, G-SYNC Compatible.
Since most non-certified FreeSync monitors suffer from major flickering issues when running G-Sync in windowed mode, it is advisable to enable G-Sync functionality exclusively for full screen mode. When you're done making these changes, click on the checkbox next to Enable settings for the selected display model and then on Apply to save your preferences.
That's it! G-Sync should now be enabled on your FreeSync monitor.
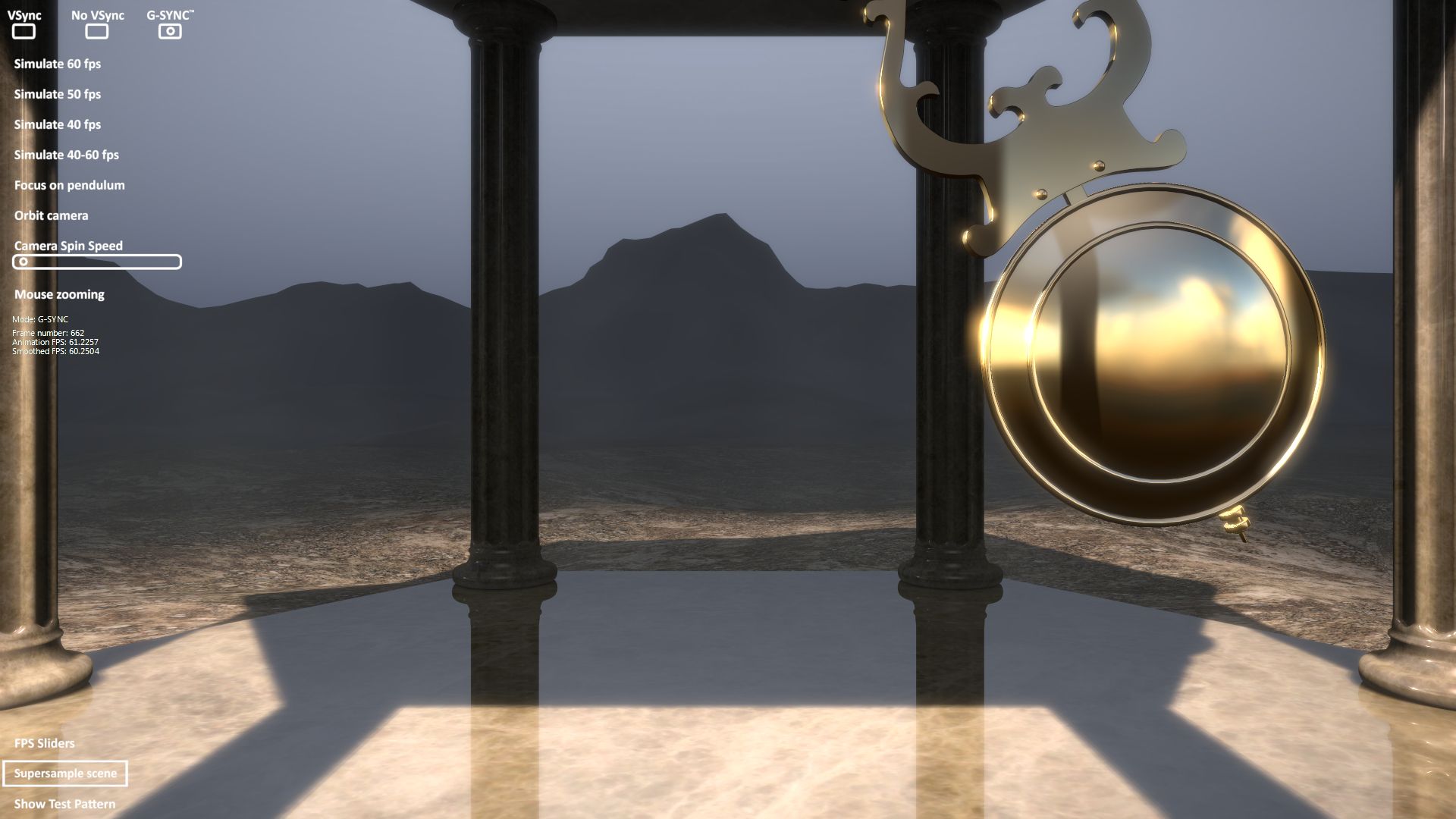
To test whether G-Sync is working properly on your FreeSync display, download and install Nvidia's G-SYNC Pendulum demo, a handy tool that can help demonstrate the benefits of Adaptive-Sync technology. Consider switching between No Vsync and G-SYNC to better understand the purpose of G-Sync in synchronizing your monitor's refresh rate with the frame rate of your GPU.
Now, one of the major concerns for PC gamers when using V-Sync alongside G-Sync is the introduction of input lag. Not only does it contribute to additional system latency but also affects the overall experience by a significant margin.
To reduce any V-Sync level input lag while gaming on a FreeSync display, set the maximum frame rate to three frames below the monitor's refresh rate. For a 144Hz monitor, an FPS cap of 141 should be good enough for consistent frame pacing across the board.
If your game doesn't include an internal FPS limiter, try using an external frame rate limiter such as RTSS (Rivatuner Statistics Server) or Nvidia's Max Frame Rate option inside the Control Panel.
Get a Smooth, Tear-Free Gaming Experience With Nvidia G-Sync
Despite Nvidia's claims about a suboptimal gaming experience when running G-Sync on non-certified FreeSync panels, we found little to no difference between both variants. Besides exclusive features such as ULMB (Ultra Low Motion Blur) and Variable Overdrive support, Nvidia GPUs tend to provide a similar VRR experience as AMD GPUs on most FreeSync monitors.
Instead of going for a premium G-Sync monitor, you can save a large portion of your budget by opting for a FreeSync (Premium/Premium Pro) display that will deliver the best of both worlds.

.jpg)