If you've been to the cinema, you've probably watched a movie using a projector. Or maybe you use it at home to catch up on movies and play video games.
Ever wondered how your projector works? What's more, did you know that there are different types of projectors with different pixels and clarity? If you know how a projector works and the specs to look out for, it'll be easier to choose a suitable projector for your needs.
How Does a Projector Work?
You know how you can cut up a small hole and put a flashlight inside it to reflect light on a wall that mimics the shape of the hole? A projector works similarly, but instead of the light going through an open hole, it goes through a lens, and an inverted image is magnified on the wall.
The real difference comes down to the type of projector technology used to create the image, and there are numerous types of projectors.
Types of Projectors
Cathode Ray Tube Projector
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) projectors, also known as gun projectors, are the oldest type of screen projectors. They use the same technology you would find in CRT televisions.
More succinctly, CRT projectors generate images using a light magnifying lens and three high-brightness cathode ray tubes arranged like horizontal traffic lights—but with red, green, and blue colors. The lights are then merged on a phosphor-coated surface to create an image.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Projectors
LCD projectors are engineered with three panels made of glass and liquid crystal. They're also designed with three regular mirrors and two dichroic mirrors. When you want to watch a movie using an LCD projector, white light is passed through the dichroic mirrors and split into three colors: red, green, and blue.
The red, green, and blue lights are reflected into three separate LCD panels and reconverted to create a single vibrant image projected on the big screen.
Digital Light Processing (DLP) Projectors
DLP projectors can process an image with up to 35 million colors—this is more advanced than the human eye. To pull it off, DLP projectors are designed with Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) chips made of millions of micromirrors. The higher the number of micromirrors in the chip, the higher the pixels.
However, white light is first split into red, blue, and green light via a color wheel and reflected onto the tiny mirrors in the chip. Then, in a microsecond, the tiny mirrors blend the colors depending on the video source data and pass it through a lens that projects the image to the screen.
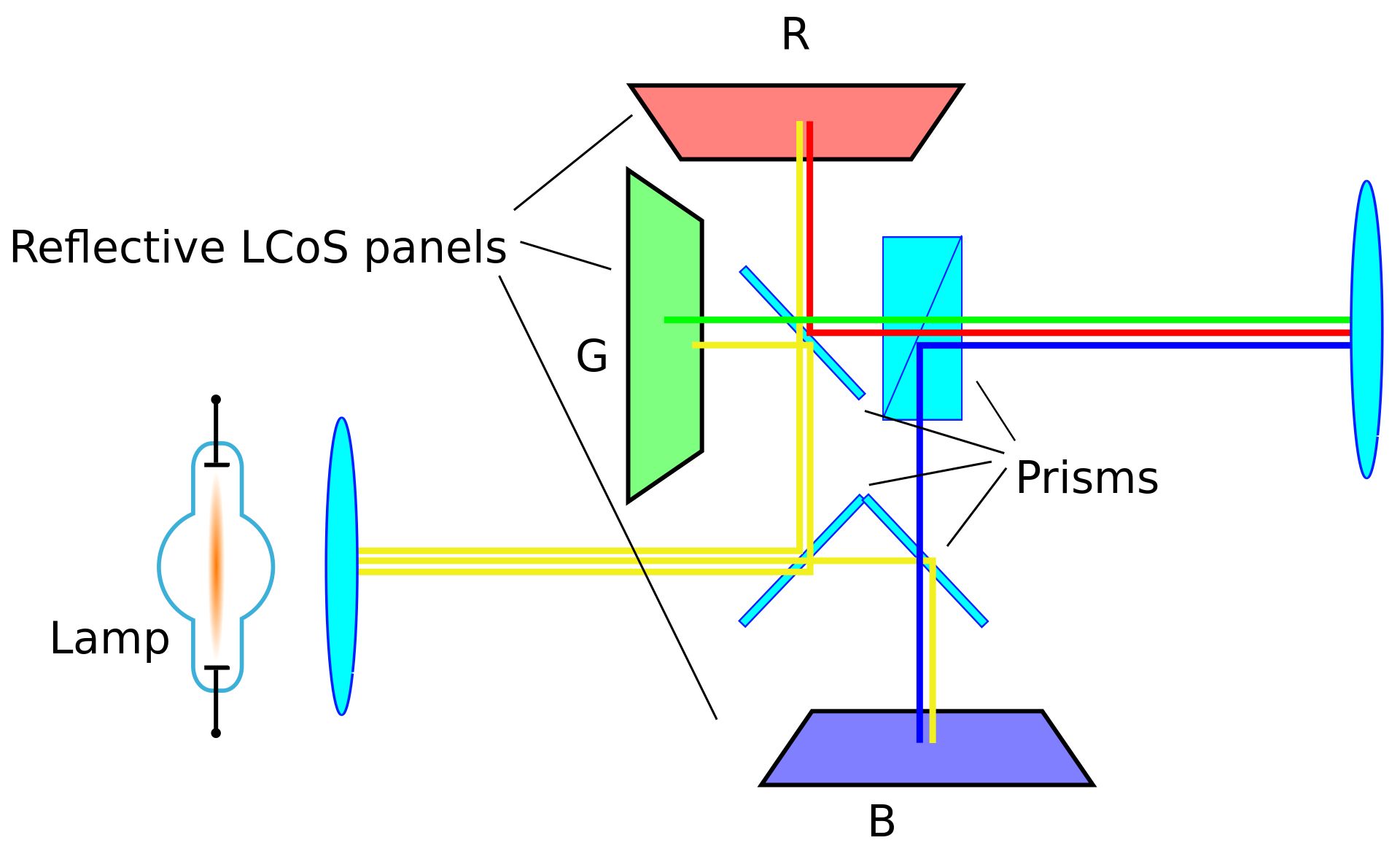
Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCOS Projector)
LCoS projectors are the latest type of projectors on the market. They're basically a fusion of LCD and DLP projectors. However, instead of using mirrors like DLP projectors, LCoS projectors are designed with silicon.
How does it work? A beam of light is split into red, blue, and green using dichroic mirrors and passed through different filters before reaching a microdevice. The filtered lights are then merged through a prism and projected onto the screen using a lens.
LED Projectors
Technically, LED projectors can also be a type of LCD or DLP projector. This is because they use light-emitting diodes (LED) to generate the light instead of traditional projector lamps—but they can use LCD or DLP technology to magnify an image on the screen.
Laser Projectors
Like LED projectors, the laser is a type of light-generating technology on a projector, but not image-generating technology. As the name suggests, this type of projector uses a laser as the light source rather than traditional bulbs. Laser projectors can also use DLP, LCD, or LCOS technology.
If you're on the fence between choosing a video projector or a tv screen, there are a few reasons why a projector could be a better option.
Which Is the Best Type of Projector?
Since LCoS combines the best features of LCD and DLP projectors, they're the best type of projectors—especially those that use laser. For example, LCoS projector delivers a clearer video than LCD and DLP projectors. Better yet, projectors with laser technology tend to last longer with less maintenance and power consumption.
However, LCoS projectors are more expensive to purchase and maintain compared to LCD and DLP projectors. Laser light projectors will also cost you more than LED projectors.
Then again, many DLP projectors are just as good as LCoS projectors. So if you're looking for some of the best home theater projectors, DLP projectors are perfect. This is because DLP projectors tend to be smaller and lighter with sharp, high-quality images.
But the biggest disadvantage of DLP projectors is "the rainbow effect"—when you see flashes of split colors on the projector screen. At least 40% of people can notice the "rainbow effect" when watching a movie using a DLP projector, according to Projector Screen. Since it's caused by a genetic trait, you can't avoid the rainbow effect if you're affected, but you can reduce it by purchasing a good-quality projector screen.
Alternatively, you could use an LCD projector if you want excellent color saturation. LCD projectors are also budget-friendly with low energy consumption compared to DLP projectors. However, you have to compromise on portability.
Last but not least, CRT projectors are cheaper and more durable. The only problem is that they're outdated and discontinued by most manufacturers.
Currently, the best projectors can showcase movies and games in 4K resolutions with low lag performance. But, besides looking at the resolutions, there are other ways you could optimize your smart projector.
Projectors Keep On Getting Better
The latest projectors are available with almost all the features you would find on a TV. From HDR, 4k resolution, and high refresh rates, projectors are now competing with TVs in home theater set-ups. But unlike a TV, a projector gives you more freedom since they're more portable and flexible.
Of course, before you make the switch, you should first understand how different projectors work to make the right decision.