You might have heard people telling you to change your DNS if your internet speeds are suffering. Some may even claim that changing the DNS settings may effectively double your internet speeds!
Your DNS settings play an incredibly important role in your browsing speeds. You use the DNS regularly, despite not knowing about it. So let's discuss what DNS is and why your DNS settings affect your internet speeds.
What Is a DNS Server?
DNS is a simple acronym for Domain Name System. Think of it as an enormous directory that records all addresses on the Internet. When you type a URL in your browser, it's translated into an IP address by your browser using DNS records.
Every device that's connected to the Internet has its own IP address. Without DNS servers, you'd have to memorize each IP address to access a specific website. But, thankfully, with DNS records, the hostname is automatically translated into an IP address, and your browser sends a request to the server, which returns the resources that load up your site.
There are both dynamic DNS servers and static DNS servers. The former regularly update DNS records as IP addresses change. There are several free dynamic DNS providers that you can use too.
How Your DNS Server Affects Speeds
To understand how your DNS server affects speeds, it's important to focus on DNS records, the most important of which is the A record, which stands for "address."
The A record maps all domain names to IP addresses. When you access a website, the DNS resolves your query, translates the URL into an IP address, and then points to a server where the website is hosted.
If the latency is high on a DNS server, it may slow down the process of resolving the website's name. This may cause the website to load slower than you'd expect.
By default, the DNS server is selected automatically, though some internet service providers may use a specific DNS server that's geographically close to the user.
But, if the DNS servers are under a heavy traffic load, it'll cause a spike in the name resolution times, thus slowing down browsing performance. Similarly, if the DNS server is situated at a considerable distance from where you're based, it's going to take longer to resolve website queries.
You can change your DNS settings to improve your internet speeds, but it's never a one-size-fits-all solution. Ideally, you'll want to choose a DNS server that's closer to you and has updated records.
Websites on the Internet are spread out across servers, or nodes. Many use a content delivery network (CDN) such as Cloudflare or Google DNS to improve performance and load their sites faster.
The core files are distributed throughout the network, instead of being stored on the same server. This reduces latency and improves the time it takes for your website to load.
For instance, let's assume that you're based in Canada and are downloading a file through a website that uses Cloudflare. If the outdated DNS A records resolve the query to a Canadian server, your speeds will be pretty good.
However, if the DNS resolves your query to a server in the United Kingdom, for instance, you'll notice connection speeds slowing down. Keep in mind that DNS queries don't generally affect download speeds, but they do cause websites to load slower.
How to Find the Best DNS Server
One of the best ways to find the fastest DNS server is to use Namebench. This is a simple utility tool designed by Google that lets you quickly identify tested DNS servers nearer to your location. Here's how it works:
1. Download and Install Namebench
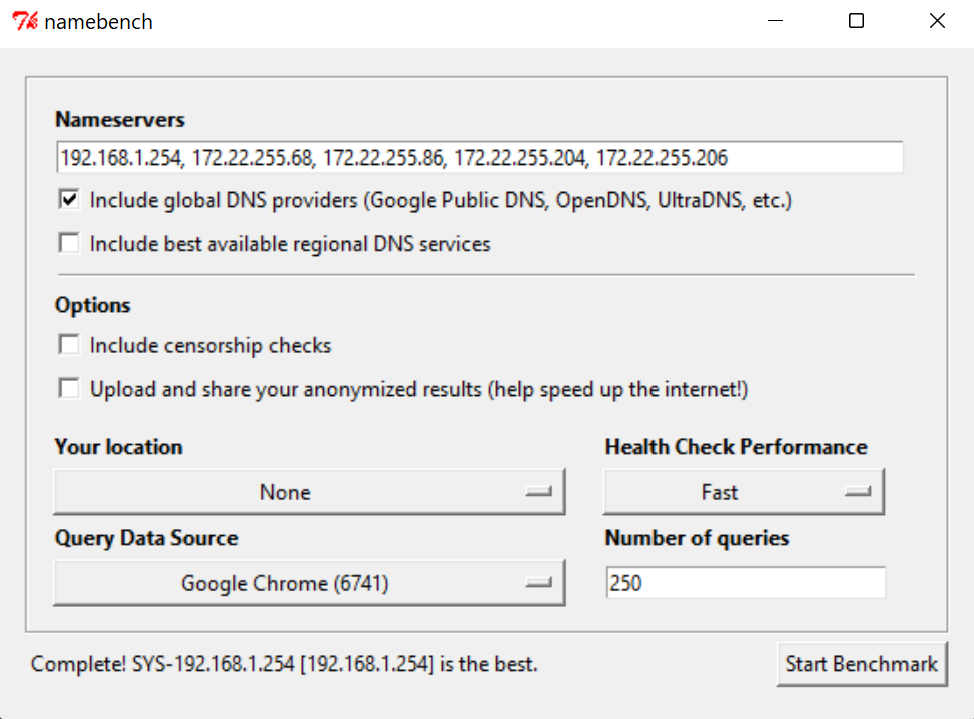
Once you download and install Namebench, you'll have to add in the DNS server that you're using. In most cases, Namebench will automatically detect the nameservers that you're using and fill it out, as shown above.
This is a portable executable, so there's no need to install anything. Just download the application, extract it, and it'll run immediately.
2. Run the Benchmark
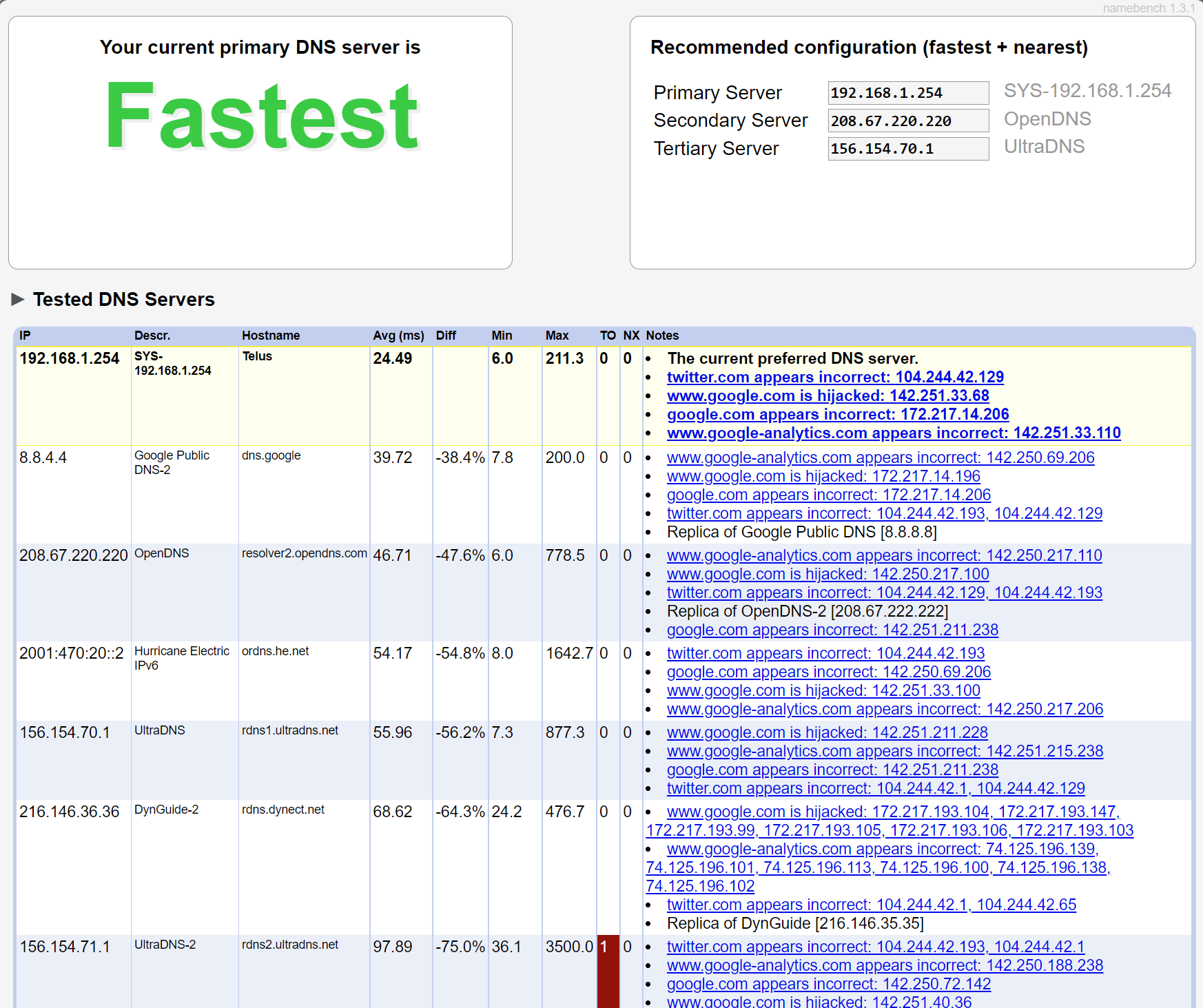
Once you run the benchmark, Namebench will show you the results. These results, shown below, can be a bit hard to interpret, but ideally, you just want to pay attention to the recommendations at the top. Here's how it looks:
If you take a look at the top, it says that the current primary DNS is the fastest, which means there's no reason to change things around. You can also see the recommended configuration on the right, including the primary, secondary, and tertiary server.
Then, Namebench shows you all the DNS servers that it tested, along with the results for each. You can even see the mean response duration and other technical details if you scroll down.
3. Change Your DNS Servers (If Necessary)
Now, if you're connected to a slower DNS server, you can change the DNS server on Windows 11 or macOS. There are several alternative ways to change your DNS settings too on Windows 11.
Keep in mind that you'll have to change the DNS server for all connected devices. So, for instance, if you're connected to the internet using another device, like a PlayStation 5, you may want to change the DNS there too.
Why DNS Servers Affect Your Internet Speeds
Arguably the most important factor is the DNS lookup times, which is when your DNS resolves your query. The slower it is, the longer your website will take to load. Similarly, if the DNS cache was recently flushed, it may take time for new records to be cached.
The DNS will check the browser's cache memory, the operating system's cache, and even send a request to the recursive DNS server (which is provided by your ISP) to resolve the query.
The Bottom Line: Should You Change Your DNS Settings?
It's important to note that changing your DNS settings isn't going to be necessary all the time, as your internet service provider will usually connect you to the fastest-performing DNS server.
But if you're traveling or are connected to a DNS server that's not updated or far away, you may experience slower speeds. Changing the DNS settings will definitely help. In some cases, using a Smart DNS can also help.