High central processing unit (CPU) usage can cause multiple issues for your Mac. These include decreased system performance, overheating, and application crashes. The source of the problem can sometimes be obvious—but often, you'll need to dig deeper to find it.
Nonetheless, you can resolve most macOS high CPU usage problems by following the correct troubleshooting procedure. Let’s take a look at the best steps to identify and remedy the issue.
1. Update Software and Restart Your Mac
"Have you tried turning it off and on again?"
The classic IT Crowd line is funny because it’s true. Sometimes, the simplest solution is the right one.
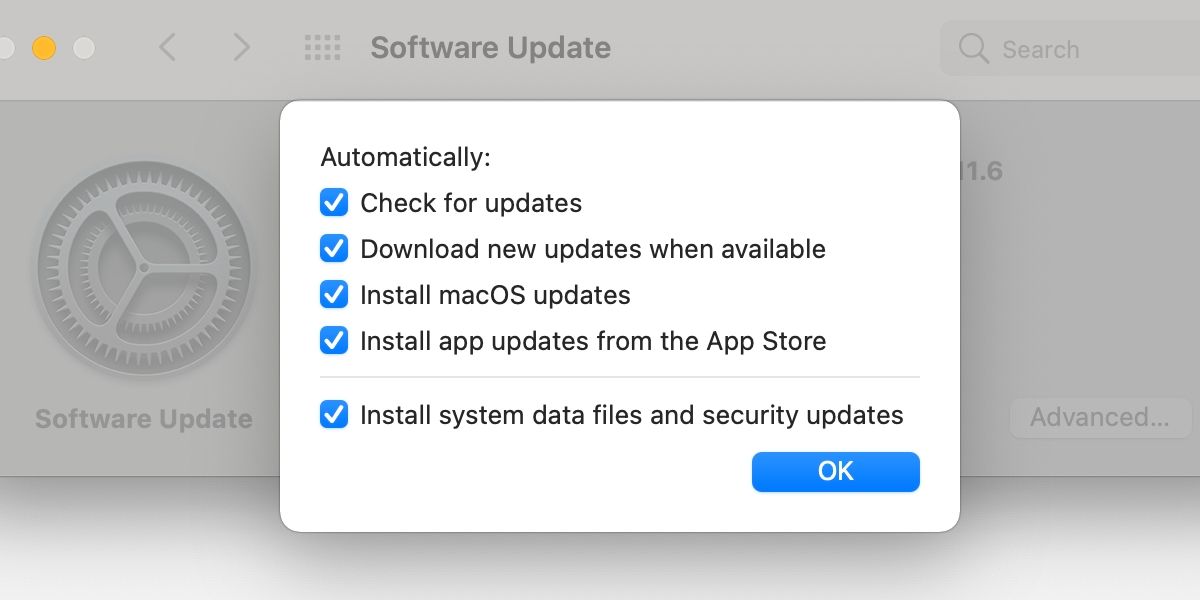
Before rebooting your Mac, you should check for available software updates. Often, updating your system and applications is the quick fix. Also, if you don’t have data restrictions, you should ensure you’ve enabled automatic updates in macOS. That way, you know you’re always running the freshest software.
To update software, follow these steps:
- Open System Preferences > Software Update.
- Accept any available updates when prompted.
- Ensure automatically keep my Mac up-to-date is ticked if applicable.
- Click Advanced for more specific update settings and change if needed.
To check for app updates, follow these steps:
- Launch Applications > App Store.
- Select Updates from the side menu.
- Update all relevant apps.
Whether you installed updates or not, don’t forget to restart your Mac.
2. Use Activity Monitor to Identify the Source of High CPU Usage
If updating and rebooting doesn’t solve the issue, it’s time to launch an investigation. Fortunately, macOS’s built-in Activity Monitor makes identifying the source of your problems easy.
To identify the cause of high CPU usage, follow these steps:
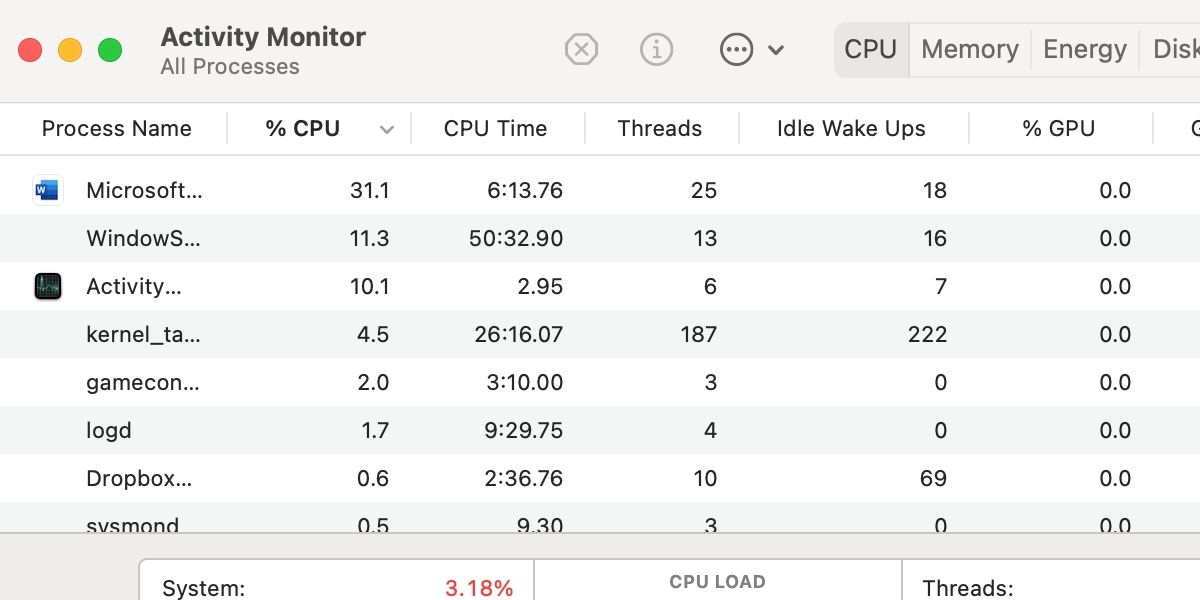
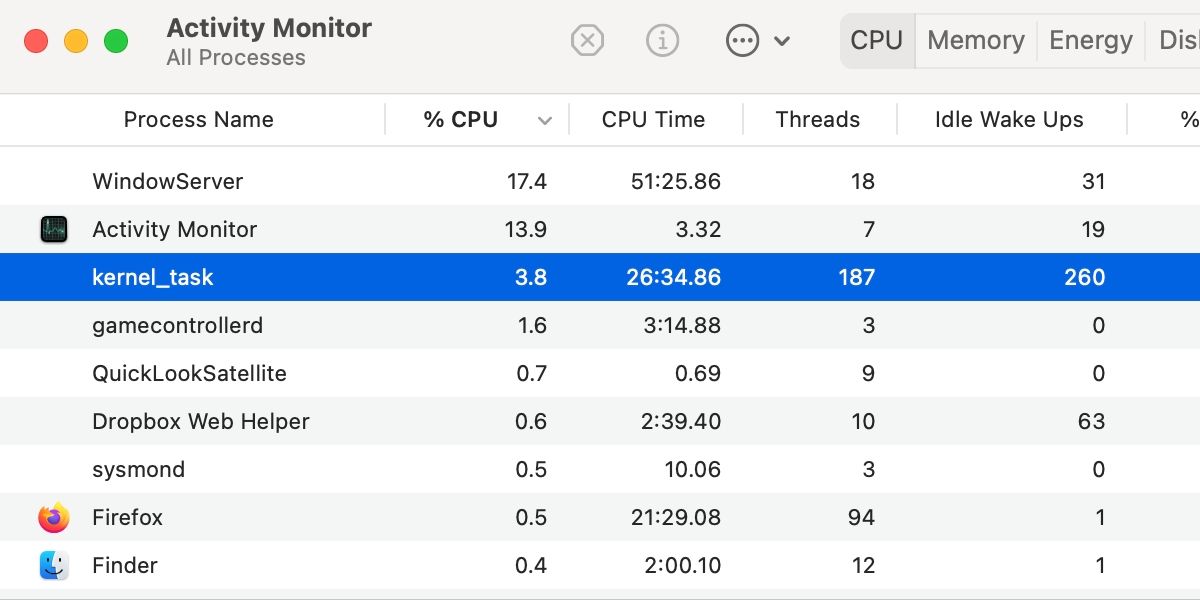
- Launch Applications > Utilities > Activity Monitor.
- Ensure % CPU is selected in the control bar and set to descending order. That means the arrow should be pointing down.
- Examine the list. The process with the highest CPU usage will take the top spot.
Getting to know Activity Monitor is a worthwhile endeavor, as the app can help identify multiple issues that may arise in macOS—including low battery life and excessive data use.
Now that you’ve identified the culprit behind your high CPU usage, you can fix the problem.
3. Update, Reconfigure, or Reinstall the Problem App
If your high CPU usage gremlin is a specific app, you can take several steps to solve the issue. If, however, kernel_task or another macOS process appears to be causing the problem, you should continue to the next section of the article.
First, you should double-check for any application updates, as this can be the quickest way to resolve an issue. If your software is up-to-date, you should examine the problem app for configuration issues or rogue extensions, add-ons, and plugins. You also have the option to contact the developer for guidance on how to troubleshoot the application.
If the problem persists, you may need to reinstall the app. Naturally, you should always back up important data before removing anything from the system. Some applications come with their own uninstallers, which you should use when available, but you can remove most apps by dragging them to the Bin and hitting Empty.
Once removed, you’re free to reinstall the application from the App Store, developer’s website, or another source.
4. Resolve High CPU Usage for Kernel_Task
When processes cause your CPU to overheat, kernel_task steps in to calm things down. Therefore, kernel_task is more of a scapegoat than it is the component causing the issue. Through Activity Monitor, you may be able to identify the real culprit, but if not, you can resolve most kernel_task high CPU usage issues with the right approach.
To troubleshoot kernel_task high CPU usage, follow these steps:
- Remove unnecessary peripherals.
- Reset SMC and PRAM.
- Remove Adobe Flash if present.
- Test in safe mode and remove third-party launch items, launch daemons, and kernel extensions if applicable.
- Check for hardware issues—see the next section of the article.
- Back up and reinstall the operating system (OS) if all else fails.
Ideally, you'll want to try the simplest solutions first and avoid any drastic measures. However, sometimes a complete system erase and reinstall is necessary to resolve stubborn problems. But first, you should check for obvious hardware issues.
5. Identify Hardware Issues That Could Cause High CPU Usage
A quick way to identify any obvious hardware issues is to run Apple Diagnostics. To do so on an Intel Mac, follow these steps:
- Start your Mac.
- Immediately press and hold the D key on the keyboard.
- Release the key when a progress bar appears.
- Follow the prompts.
To run Apple Diagnostics on an Apple Silicon Mac, follow these steps:
- Start your Mac and continue to hold the Power button.
- Release Power when the startup options screen appears.
- Press Cmd + D.
Apple Diagnostics will identify obvious problems; however, more subtle causes may require additional investigation. A good way to confirm a software or hardware issue is to test from the recovery partition, which is independent of the main operating system.
To boot to recovery on an Intel Mac, follow these steps:
- Start your Mac.
- Immediately press and hold Cmd + R.
To boot to recovery on an Apple Silicon Mac, follow these steps:
- Start your Mac and continue to hold the Power button.
- Release Power when the startup options screen appears.
- Select Options.
- Click Continue.
If the issue persists in recovery mode, you may have a hardware issue and should have your Mac diagnosed by an Apple Store or service provider. If, however, the issue doesn’t occur when booted to the recovery partition, you’re likely dealing with a software issue—which you can resolve with further troubleshooting or a full system reinstall.
Fixing High CPU Usage in macOS Means Identifying the Cause
Whenever problems in macOS arise, you should first update software and restart your device. If these simple steps resolve the issue, you’ll have saved yourself a lot of time and effort.
If a reboot doesn’t remedy the situation, you can start to dig deeper for solutions. Activity Monitor is useful for identifying the causes of high CPU usage, and in more serious cases, you might need to look for hardware issues using Apple Diagnostics.
You may have noticed that many of the high CPU usage troubleshooting steps involve isolation. Isolating an issue should always be your initial goal. You’ll save time by avoiding unnecessary troubleshooting steps, and you’ll also ensure that you don’t do anything drastic without good reason.