Excel and Power BI are two very popular tools. They both offer a wide range of analytical and visualization tools to help you create dashboards and reports. Microsoft Excel is great for analyzing data and making it more understandable for day-to-day operations.
Power BI, however, is specifically designed to make data more intelligible, valuable, and actionable by connecting it with other enterprise information, letting you discover insights quickly. In this guide, we'll take a look at how the two applications differ from each other and offer recommendations for using them.
The Key Differences Between Excel and Power BI
Excel is a spreadsheet application that offers powerful functions for data manipulation, analysis, and presentation. You can create and modify spreadsheets, use formulas and functions, create charts and graphs, and import data from other sources.
Power BI is a business intelligence tool that helps you analyze metrics and quickly build visually appealing, interactive reports and dashboards. It's designed to help organizations make decisions more efficiently through real-time insights into data.
You can connect all of your data sources like CRM systems and databases in one place and create visualizations like charts, gauges, and maps. We'll take a closer look at some of their differences in the sections below. To get started, you'll need to sign up or download the applications.
Download: Microsoft Excel for Android | iOS | Web
Download: Power BI for Android | iOS | Web
1. Data Connections and Integration Capabilities
When it comes to Excel, you can import files from several types of data sources—files, databases and webpages—as well as other sources. Both Excel and Power BI use Power Query to extract and fetch data.
To import a file into Excel, click the Data tab on the ribbon and use the Get data drop-down menu to select one of the available choices.
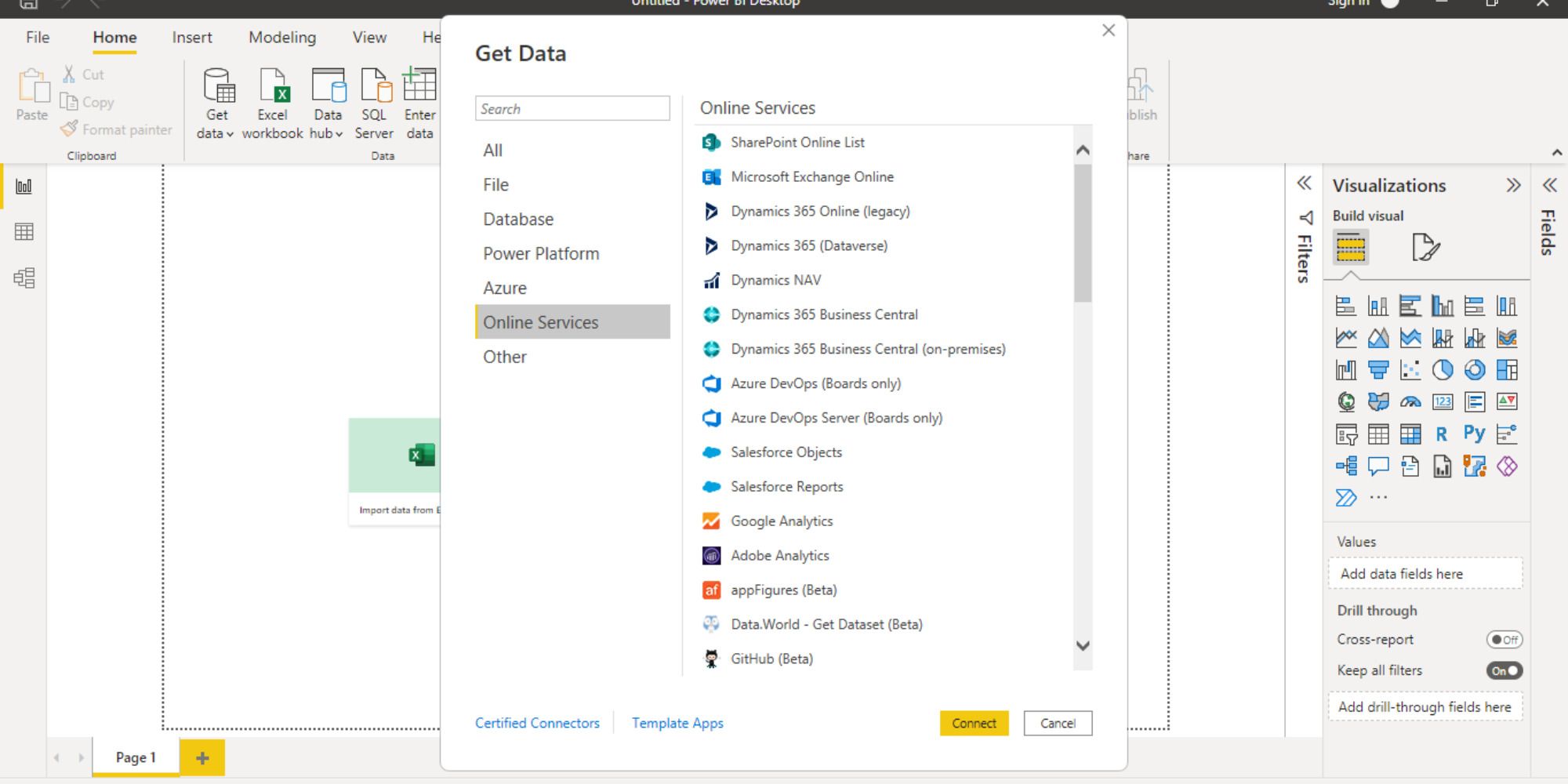
Power BI has an easy-to-use interface for data integration and analysis. You can import data into Power BI from a variety of online and offline sources including cloud services, databases such as SQL and Azure, as well as simple text files. The application helps you transform any kind of data into valuable business intelligence in a fraction of the time.
To import data into Power BI, click on Get data > Get data from another source. Simply select the platform you wish to import data from, and click Connect. Sign in with your credentials (wherever required) to extract data from an external source.
Additionally, you can import visualization templates that are available on its marketplace, and use the ones that are freely available. Excel does not have this ability. Instead, it mostly provides only static charts. All said and done, Power BI is the clear winner in terms of the sheer number of data sources it can connect to.
Winner: Power BI
2. Reporting Features: Dashboards and Interactivity
While Excel does have a robust set of tools for analyzing data, including pivot tables, Power BI offers more advanced charting and reporting options.
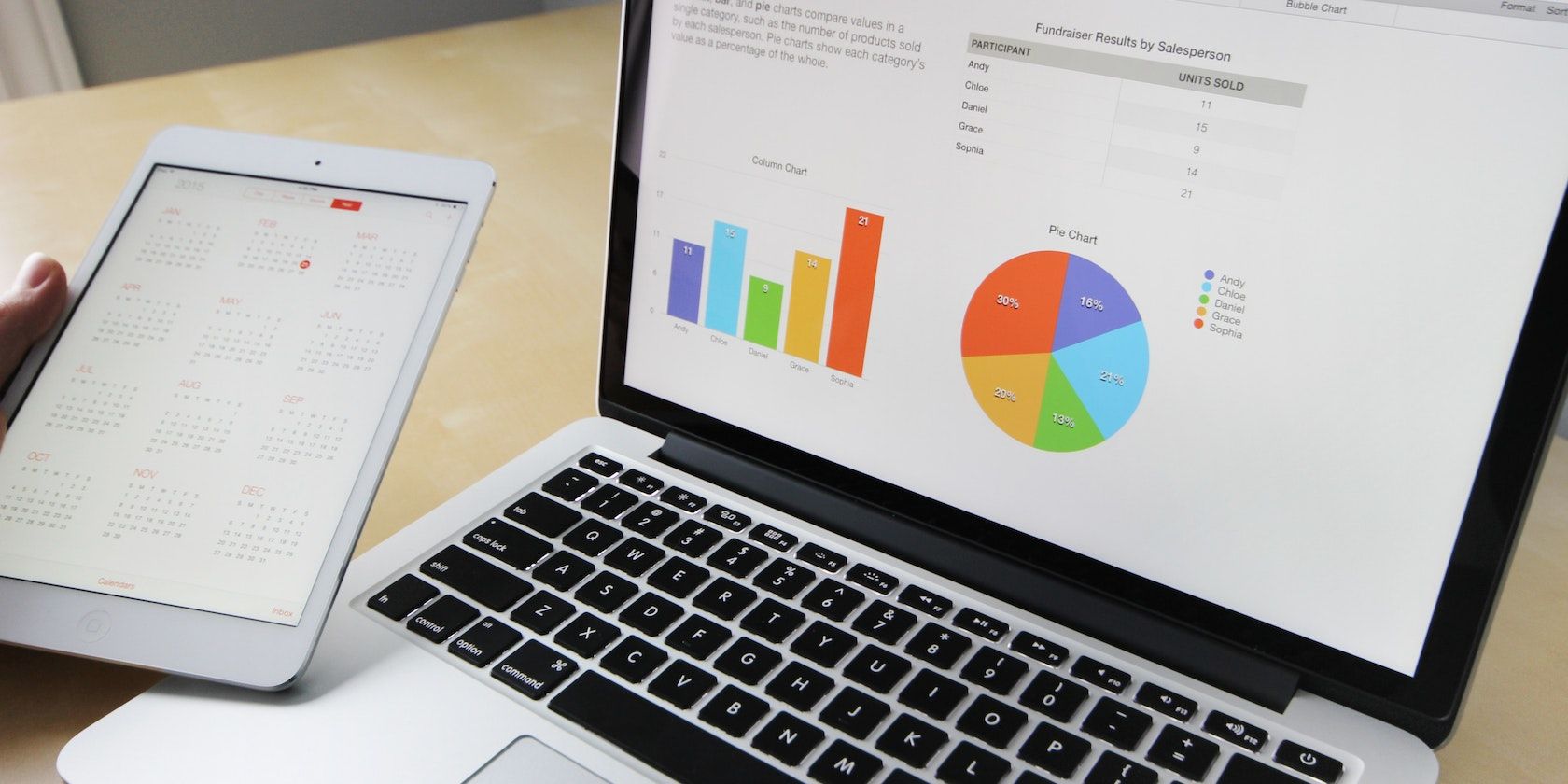
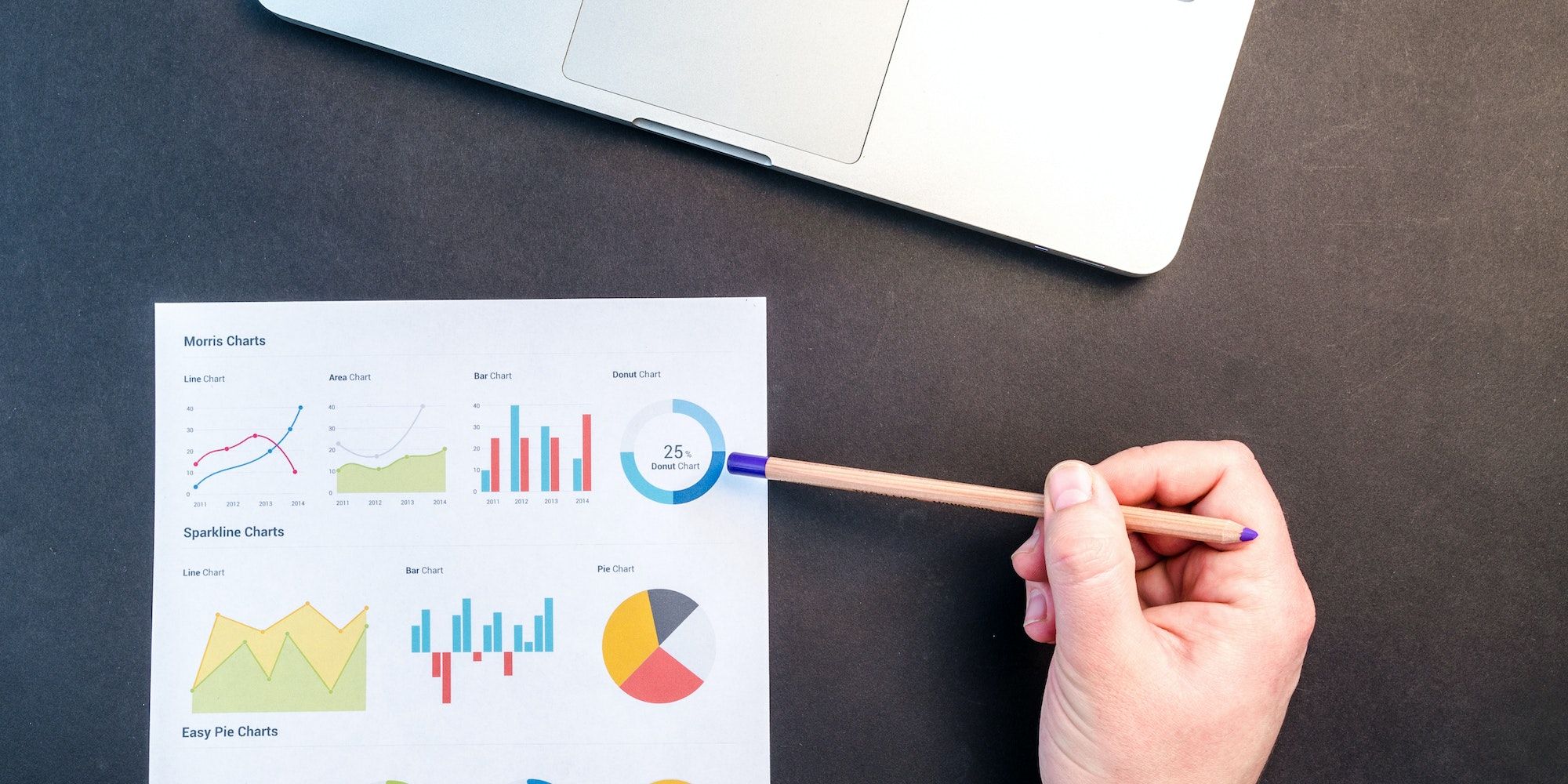
In Excel, you can choose from different types of charts, such as line graphs, pie charts, bar charts, stacked column charts, and PivotTable reports (which allow you to sort through different pieces of data). You can also create your charts using Power Pivot or Power View (these functions have been removed from the latest versions of Excel or Microsoft 365), to display data in different ways.
Power BI reports can be used to generate meaningful insights from your data, help you understand your business or organizational metrics, and make data-driven decisions. You can share those insights with your team and collaborate with them in making decisions. Some of its salient features are:
- Table-like visualizations using R, Python, and other tools.
- Dashboard tiles that you can move around and add more information to.
- The ability to filter, sort, and analyze your data quickly through unique filters that allow you to visualize trends across multiple dimensions.
While you can set up interactive dashboards in Excel, its visualization functions may be somewhat limited. In Power BI, you can also find a variety of filters and slicers for adding interactivity: cross-drill filters, manual filters, drill-through filters, and more.
Winner: Power BI
3. Automation and Customization Capabilities
Excel and Power BI both have a lot of features that make them great for data analysis. But they also have some differences, especially when it comes to dashboard customization and automation settings.
To open up customization options in Excel, simply click on the Home tab. Right-click and choose Customize the Ribbon. Then, you can choose the commands you want to display and add them to the ribbon.
Power BI helps you customize your dashboard by providing easy-to-find settings to the right of your screen. Just click on Visualizations. From there, you can change things like chart types or font sizes or add interactive elements.
When it comes to automation, Power BI allows you to set up custom workflows via Power Automate that are designed to make it easy for you to implement complex tasks. Excel has a built-in tool called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) which allows you to run macros (short programs) within their workbooks. These macros can be used for various purposes, including automating complex tasks.
Excel certainly has a slight edge when it comes to the plethora of customization options available to work with.
Winner: Microsoft Excel
4. Data Modeling and Language Dependencies
Excel is all about the simplicity of organizing and analyzing data sets, whereas Power BI is fine-tuned to handle data from different sources while allowing the creation of complex models.
Microsoft Excel is based on the MDX (Multidimensional Expressions) language, which is used to query and manipulate multidimensional databases. Power BI is based on a functional language called DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions.
Excel provides a wide range of data preparation methods—sorting data, removing duplicate entries from a list of values, merging multiple tables, and much more. You can also use Excel's advanced filters and validation methods to select a specific subset of your raw data based on the criteria that you specify.
Power BI, on the other hand, offers more features, based on its broad focus on data ingestion and analysis, and storage capabilities. It can be used with any type of data source, including structured and unstructured formats.
As we noted above, it gives you the ability to quickly create reports using visualizations and integrations with third-party applications. You can sort your data, build relationships between various data points, and use that information to build predictive models that will help you predict future outcomes.
Winner: Power BI
5. Collaboration Features
Microsoft Excel makes it easy to collaborate on projects by allowing you to send files through email, OneDrive, and other online services to your team members.
You can track changes using notes and comments in Power BI and Excel. These collaboration tools are built-in so that teams can work together on projects.
Power BI can help you create datasets. However, you'll need to upgrade to a Pro version (starting at $10/user/month) to share and collaborate on reports. There's also a Premium version available starting at $20/user/month.
To share your files, open your workspace, and click on the file you wish to share. Once it opens, tap Share and type in the email address of your team member(s). You can collaborate in real time using the chat feature in Microsoft Teams as well.
Winner: Microsoft Excel
6. Cross-Platform Availability
If you're looking for a free tool to help you with your day-to-day tasks, such as timesheets, or tracking your sales and inventory, look no further than Excel. It's the most popular spreadsheet application, after all.
If you're looking for a paid alternative, Power BI is a great option. It has a free version inside Microsoft Fabric which gives you access to a lot of features. However, if you need more advanced functionality or if your data includes complex formulas and functions, then Power BI Pro or Power BI Plus is worth the investment.
Excel is available on desktop and mobile devices. For Power BI, there are both free (as part of Fabric) and paid options available. However, you can only access the advanced features of Power BI if you upgrade to Pro or Plus.
Winner: Microsoft Excel
Excel vs. Power BI: Which One Do You Need?
If you're looking for a tool that will let your organization analyze and visualize your data in real-time, Power BI is probably your best choice. The flexibility, ease of use, and ability to create complex visualizations all set it apart from Excel. On the other hand, if you want an easy-to-use tool that lets you create charts quickly and easily, Excel may be more appropriate.



-(1).jpg)
-(3).jpg)


