Brave is an open-source browser based on the Chromium project, but unlike Chrome, which eats up your RAM, Brave offers improved performance and a considerably faster browsing experience. Brave rose to fame as a browser focused on privacy and anonymity.
In June, the company launched the beta version of its own search engine that prioritizes privacy above all else. Here's everything you need to know about Brave's search engine.
The Key Features That Set Brave Search Apart
Brave Search was announced in March when the company acquired Tailcat. Brave Search is the latest offering by the company and slots in nicely in their portfolio of privacy-focused solutions like Brave News and Brave Ads.
Now that Brave Search has launched, we have a pretty clear idea of what sets Brave Search apart from the competition. Let's talk about the main differentiators and key features of Brave Search.
1. Built on an Entirely Different Index
Perhaps the greatest difference between Brave and other search engines like Google is that it uses an independent web index. Once Google discovers a new page on the web, its crawlers understand what the page is about.
It analyzes the content, the images, and the video files, all of which are stored in Google's database. Brave's biggest competitor, DuckDuckGo, does not have its own index. Instead, it derives results from other indexes like Bing.
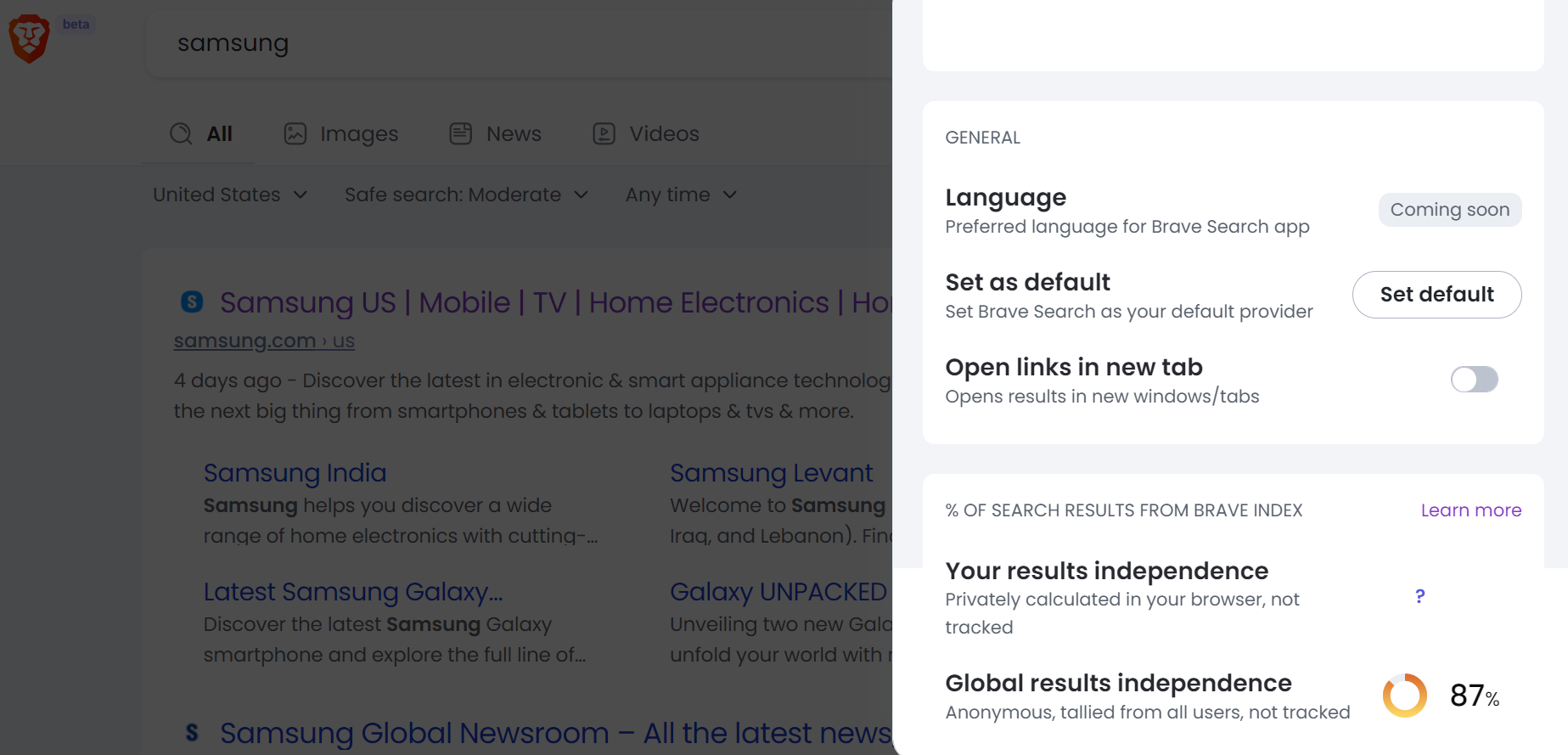
The results you see in Brave Search are those indexed by Brave's own crawlers. However, for certain keywords, where the search engine cannot pull relevant results, they may still pull information from other indexes. This is known as "fallback mixing," and you can always turn it off.
To give users a better understanding of how independent the search results are, the company has added a new metric known as "search results independence," which you can view on the search page.
The company intends to make Brave Search the default search engine as the browser is becoming more popular by the day.
2. A Privacy-First Approach
One of the reasons people have been moving towards search engines like Brave is their privacy-first approach. More and more internet users are seeking alternatives to big tech, and browsers like Brave allow them to manage their digital fingerprint much better.
Companies like Google and Facebook offer their core product for free to customers. They harvest user data and then sell it to third parties, creating digital profiles that help advertisers target a more relevant audience. In fact, Google has been known to pressurize smartphone manufacturers to even hide privacy settings!
Brave Search does not track or profile its users. Instead, it offers a fully anonymous search experience while relying on a community-driven index. The company has been incredibly vocal about its approach to privacy and transparency.
Unlike search engines like Google, which track your clicks, location, devices, and virtually everything you give them permission for, Brave Search doesn't collect any data about its users. Brave Search will be free to use, and the company is working on releasing an ad-supported version soon.
This will use Brave Ads, the company's machine learning adtech platform to deliver ads while rewarding its users with 70% of the revenue. A premium version without ads is also expected eventually.
3. It Uses "Goggles"
The Brave Search Team published a whitepaper (PDF) that highlighted the concept of "Goggles," which is the company's in-house algorithm designed to mitigate biased results. Goggles relies on community-curated open ranking models to reduce biases within the algorithm.
At its core, Goggles are just sets of rules and filters that can be applied to define the pool from which the search engine can pull results. For instance, communities or users can create multiple Goggles, such as:
- Product Reviews with no commercial intent: This would rank review sites that don't contain price comparisons or affiliate links higher. For instance, all e-commerce sites would be removed.
- Tech blogs: This would only show a collection of company or personalized tech blogs that have been suggested by the community.
- Independent media outlets: Smaller media outlets will rank higher than major media businesses based on the location that the user searches for.
More importantly, Goggles will be available to other search engines as well. These anonymized contributions will help improve results over time and make them more relevant.
4. A Refined Search Experience
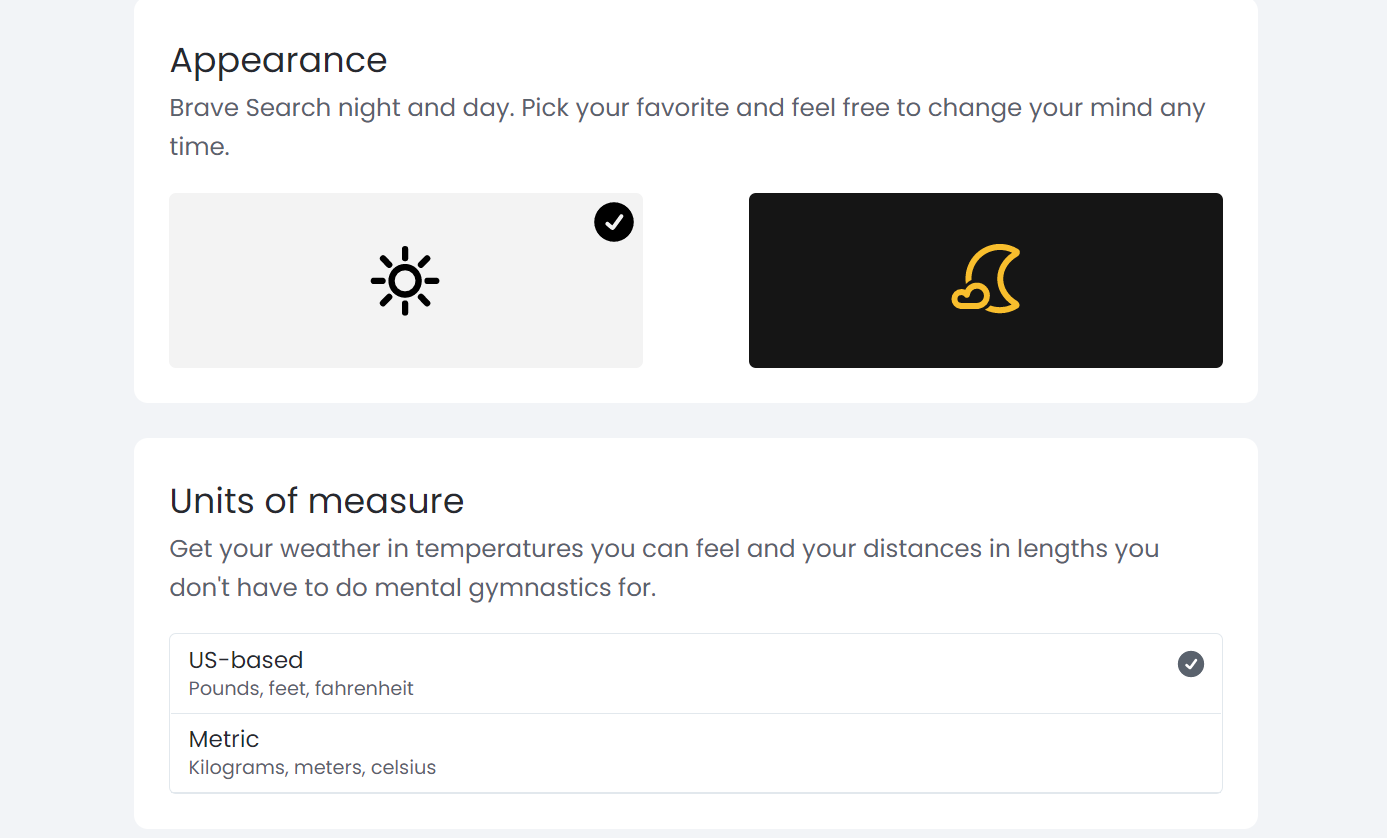
Brave Search also offers a host of other options designed to make your search experience much better. For example, you have a choice of both light and dark mode for search (Google's dark mode feature is still in beta), and you can also select how you'd like units of measurement to be shown.
You can choose either the metric (meters, Celsius, and grams) or the imperial system (feet, Fahrenheit, and pounds). You can also select whether to view open new links in a separate tab or not.
Brave Search does not tap into your location. However, you can enable the "anonymous local search results" option if you want localized search results. The search engine will use your IP address, but instead of broadcasting it, it takes a slightly different approach to show relevant results:
- Brave Search does not pinpoint the IP address; it returns results from a broader, more generic location.
- Brave Search does not store your IP address. It's only used for the query.
- You can set your location manually as well to view relevant results in a specific area.
Privacy Is Becoming Increasingly Important
The world at large is coming to terms with just how much data companies like Google and Facebook collect about them. Brave Search offers an anonymous search experience to users on mobile and computers and syncs seamlessly on all platforms.
Moreover, their Brave Rewards program has been hugely successful and will work with Brave Search, offering users payments in BAT (Basic Attention Token) for opting to view ads on their platform.