Bell Labs' Unix source code inspired the creation of Berkeley Software Distribution, commonly known as BSD. Ever since, BSD has spawned a long list of distros that empowered open-source computing back in the 90s.
Despite being similar to the more general-purpose Linux, Unix commands a demographic of its own. Today, BSD systems are operating under the hood of modern computing and have even inspired the codebase for premium desktop and non-desktop platforms.
So, which BSD distros are standing the test of time? The following seven distro options will give you an inkling into this question.
1. FreeBSD
FreeBSD dates back to 1993; however, in 2002, the distro was reconfigured to meet the new millennium's computing needs.
FreeBSD is a 4.4BSD-Lite release and packs enhancements from the Lite2 release. It gives you access to a repository containing a staggering 20,000 packages for various use cases.
Currently, at version 12.3, FreeBSD is meant explicitly for computing on i386, amd64, IA-64, ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, ppc64, PC-98, and UltraSPARC platforms.
FreeBSD finds its use in the modern age for embedded platform computing. Ideally, it is also used in networking and server deployment, storage, security, and more.
Download: FreeBSD
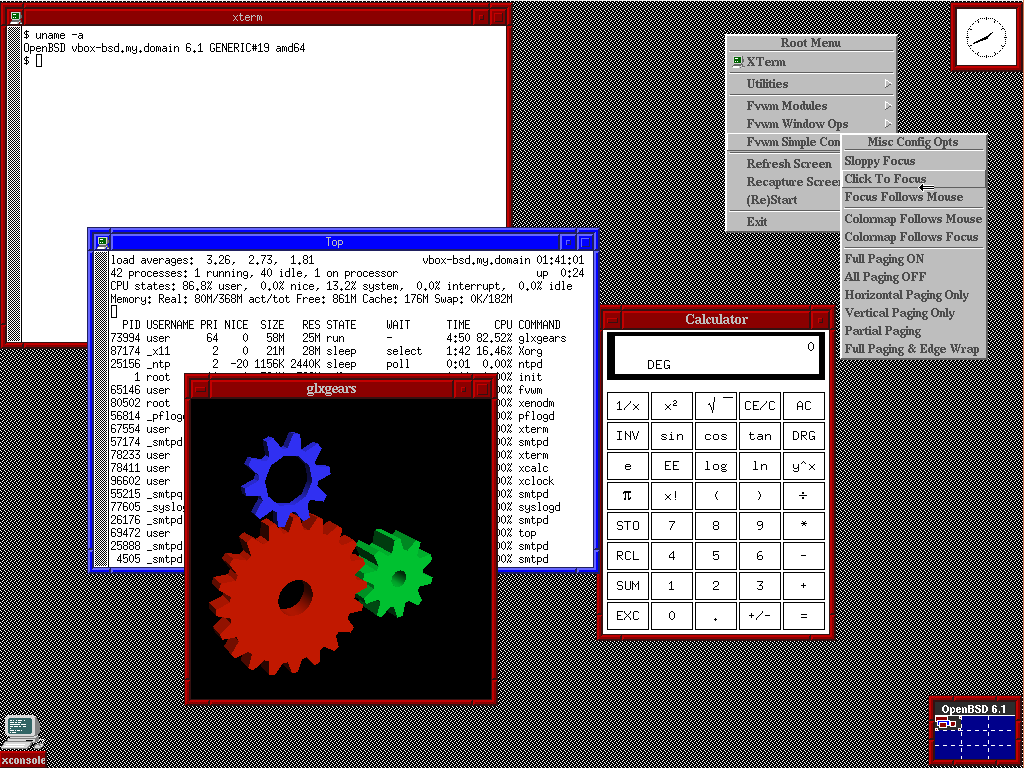
2. OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a developer-centric platform that gives Unix users a community-improved, open-source OS solution.
OpenBSD’s latest version, 7.0, is ideal for processor architectures such as i386, alpha, landisk, loongson, luna88k, OCTEON, PowerPC, PowerPC64, RISC64, sgi, socppc, SPARC, SPARC64, x86_64, Zaurus, and many more.
The diverse architecture support shows that OpenBSD promotes portable advanced computing and engineering. It finds use in cybersecurity, encryption, cryptography, and end-to-end server engineering.
Many OpenBSD codebases are used to extend Windows and macOS functionalities, and the developers highly stress using its codebase components for different development forms.
Download: OpenBSD
3. NetBSD
NetBSD is an open-source, Unix-like, portable operating system that powers everything from servers to embedded platforms and video gaming consoles.
This open-source distro runs under the hood of consoles, including the likes of SEGA Dreamcast. Like FreeBSD, NetBSD also finds practicality in systems engineering and embedded systems.
Developers rely on NetBSD's cross-compiling framework to create custom OSes using components from other systems.
NetBSD supports amd64 and i386 devices like 64-bit x86-family machines or 32-bit x86-family generic machines with AMD or Intel CPUs. It also caters to ARM systems such as the Raspberry Pi, PINE64, ODROID, and ServerReady.
Download: NetBSD
4. DragonFly BSD
DragonFly BSD is an OS based on Unix source and API code. The distro floated to prominence with its standout features, including the HAMMER filesystem, which supports in-built mirroring and historic accessibility.
DragonFly packs a powerful kernel with efficient SMP mechanisms for delivering high-performance and server-side transactional computing.
DragonFly BSD’s extensive VFS, user, process, threading, and storage subsystems user support is unparalleled. Embracing the BSD ethic, DragonFly directly gives users access to many applications in binary and source form.
Through community participation, the distro has reached version 6.0.1 at the time of this writing.
Download: DragonFly BSD
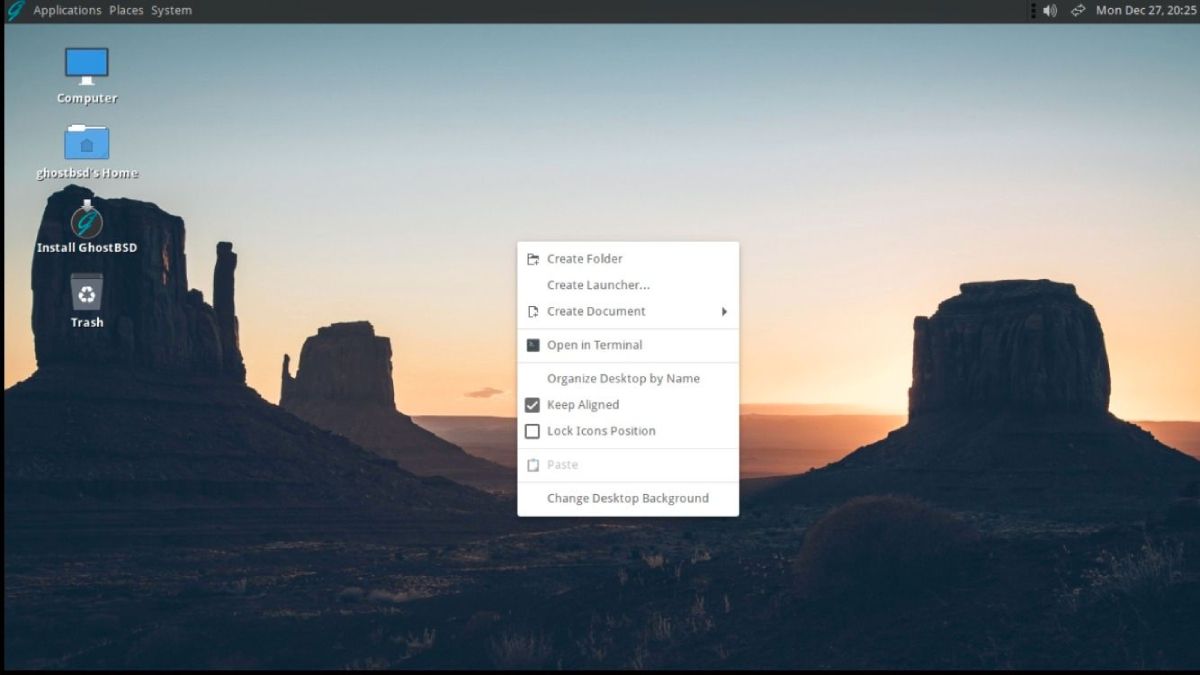
5. GhostBSD
Users searching for a more user-friendly Unix-based OS should feel right at home with GhostBSD. The distro is built and powered by FreeBSD, and it incorporates some excellent components from the now-defunct TrueOS.
As a distribution, GhostBSD gives you the power of a Unix-like kernel, but with standard MATE packages.
The GTK-aided desktop environments (KDE, GNOME, etc.) welcome users to a neat user interface. Post-installation, you can rest assured you will be spoilt for choices with the pre-installed apps and software.
GhostBSD assures advanced Unix-specific computing needs and more general-purpose office and home computing requirements alike.
The distro comes equipped with slow-rolling releases, which make it different from some of the other well-known names within the BSD gamut. Despite this fact, there is no limitation in terms of stability or release cycles.
Even if you are a novice or beginner in the world of BSD, rest assured, you will find the distro rather easy to use, as compared to some of its counterparts.
Download: GhostBSD
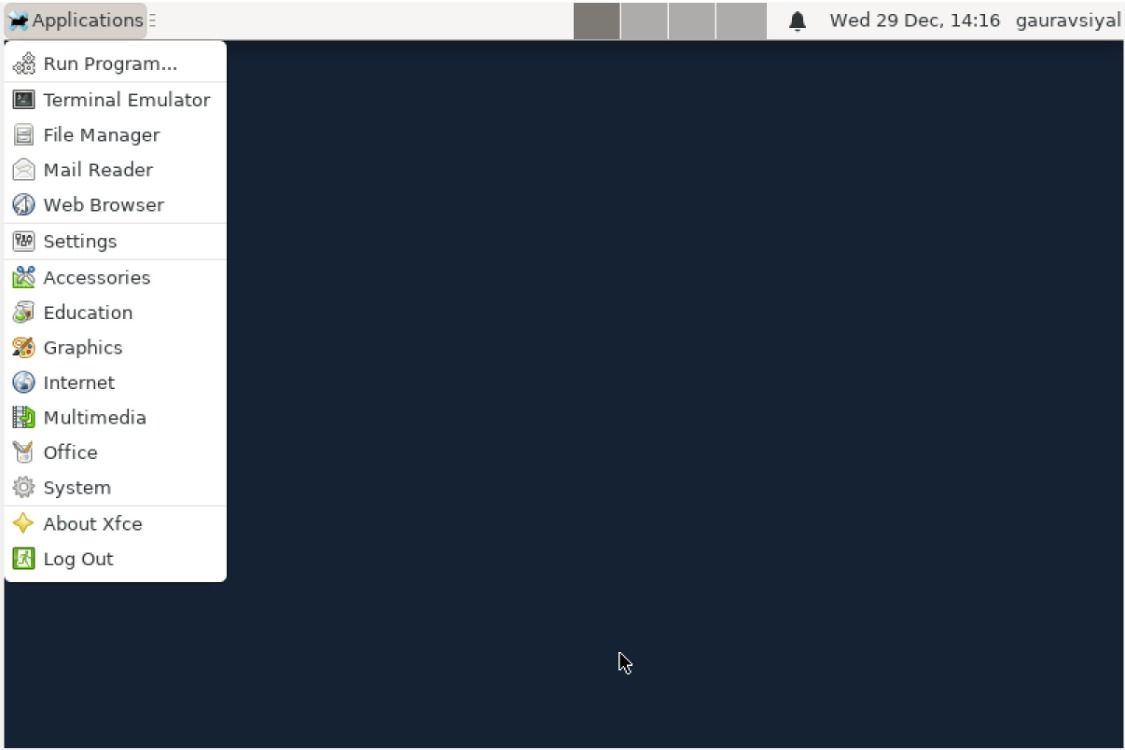
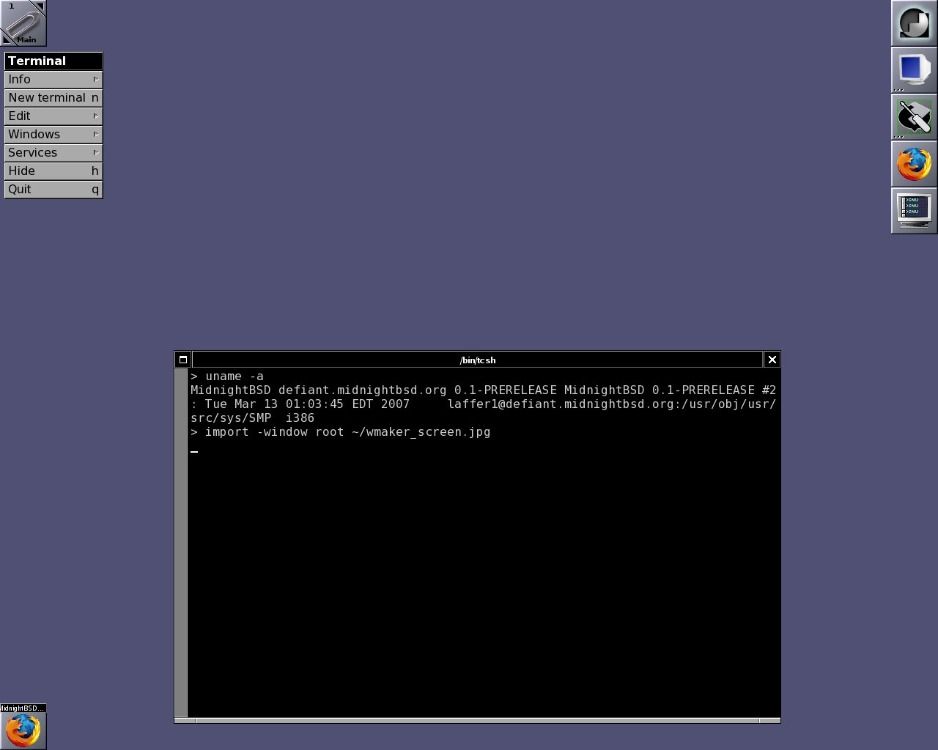
6. MidnightBSD
FreeBSD has given users a myriad of paid and open-source OSes, one of which is MidnightBSD. MidnightBSD features a ready-to-use desktop with open-source software like X.org and GCC, published under GNU step licenses. The familiar Xfce default environment and application setup allow BSD newcomers to dive into the OS for immediate use.
Users can expect a highly optimized desktop environment, which continues to be unintimidating to Unix-system novices. Tasking through MidnightBSD for security, file management, scheduling, etc., is a breeze with its swift user interface. Users can also expect a range of development and server deployment tools for network engineering.
In recent times, MidnightBSD has also integrated features from DragonFly and OpenBSD. MidnightBSD gives users the chance to run the OS on highly customized system configurations and ports. It even synchronizes with newer FreeBSD versions.
Download: MidnightBSD
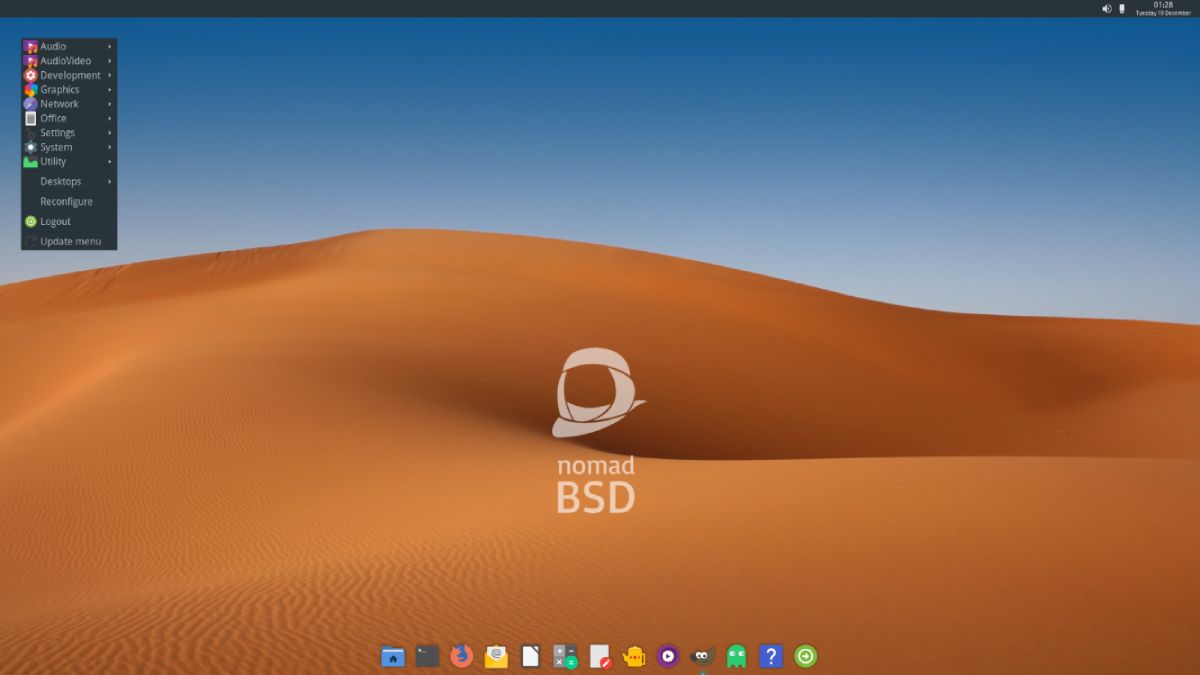
7. NomadBSD
You can’t negate Linux’s role when thinking about open-source operating systems. In its many distro avatars, Linux offers resourceful OS solutions for various use cases.
However, BSD has constantly challenged Linux’s supremacy as an open-source alternative. NomadBSD is a dark horse, proving to be a worthy addition to the list of alternatives.
NomadBSD is a live, portable Unix-like distro that you can install on flash drives and use repetitively for system repair and data recovery. This not only applies to Unix and Linux systems but to Windows and macOS as well.
The FreeBSD-based codebase allows NomadBSD to immediately detect hardware as soon as you plug it in. You can readily use it for software testing as well.
Download: NomadBSD
Choosing the Best Open-Source BSD Distribution
BSD systems won over users with their powerful kernel, functional system software ecosystem, and permissive licensing (best solution for advanced engineering workstations).
Each of these operating systems is the best within the current generation of open-source Unix-inspired OSes. Given their excellent feature sets and open-source license, they are always a steal, regardless of what purpose you have in mind for them.