Nvidia's RTX 40-Series has been the topic of much controversy since its launch. From high prices to potential scalping problems to confusing names, Nvidia has had to jump multiple hoops just to get these cards on the market.
However, the problem that's arguably the most annoying is the power draw issues affecting these behemoth GPUs. Monstrous power demands are why some people are questioning the 40-Series GPUs, the new ATX 3.0 PSU standard, and whether you really need to upgrade your PSU to run the new Nvidia GPUs.
Do Nvidia's RTX 40-Series GPUs Draw More Power?
First up, Nvidia's RTX 40-Series GPUs don't consume as much power as you think. So while you might see high TGP (Total Graphics Power) numbers on these GPUs, they perform relatively efficiently as compared to their last-generation counterparts.
For example, when tested on 22 games at 4K, 1440p and 1080p, the RTX 4080 consumed less power on average, coming in at 251 watts as compared to the previous generation's RTX 3080, which was drawing 320 watts—its maximum rated TGP. Keep in mind that both cards are rated at a 320W TGP.
The difference wasn't as notable when the GPUs were idle or playing video, but the RTX 4080 still consumed less power than the 3080. Even in 4K, the 3080's maximum power draw was 297W when running Control in the aforementioned test run by Nvidia.
So despite what you might hear, Nvidia has attempted to optimize these GPUs and lower the power draw.
You'll also get similar results when comparing the RTX 4090 with the RTX 3090. While both cards are rated at the same TDP of 450W, the 4090 performs significantly better at a similar power draw, if not less.
What Is ATX 3.0?
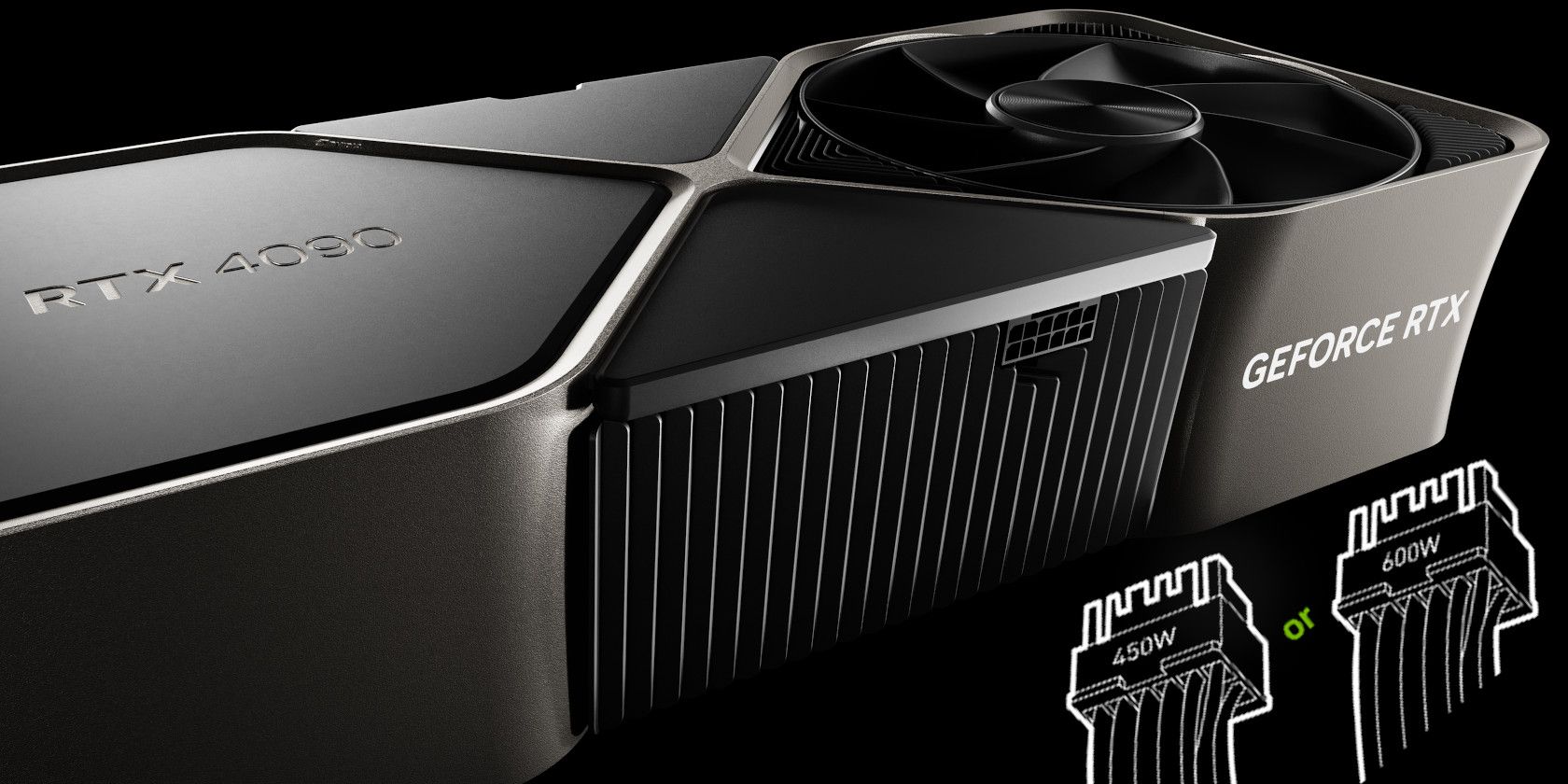
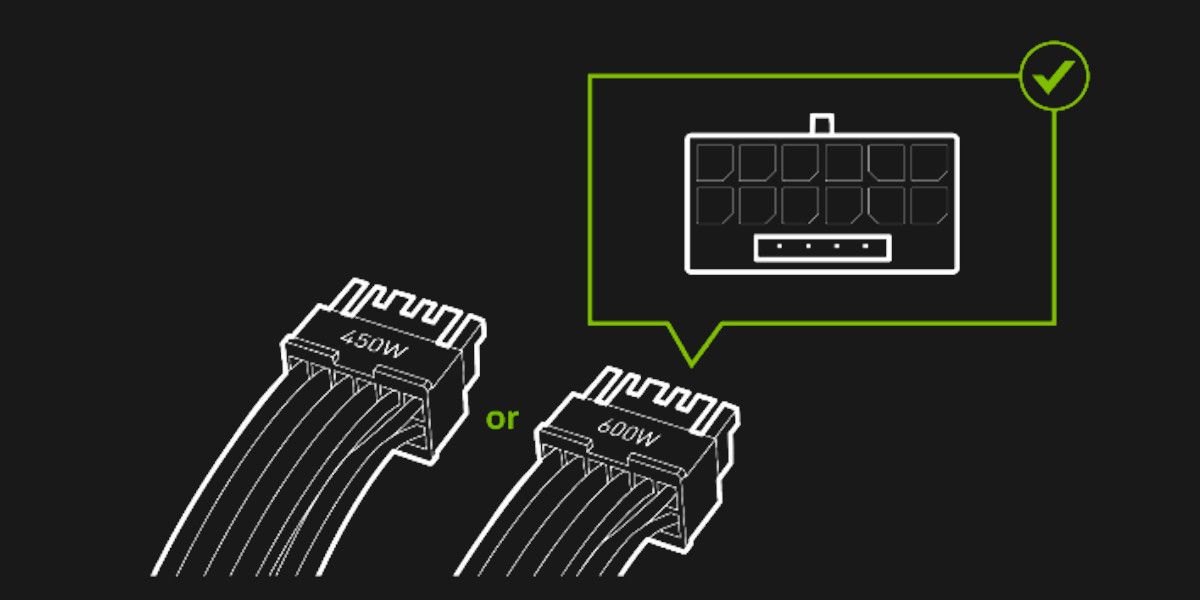
ATX 3.0 is the new specification standard for Power Supply Units (PSUs). The new design adds a new PCIe 5.0 12VHPWR connector with 12 + 4 pins alongside the usual six or eight-pin connection to supply GPUs with up to 600W of power.
While that might not sound like a lot, this new addition allows ATX 3.0 PSUs to handle power spikes of up to 1,800W, although only for about 100 microseconds. However, those 100 microseconds might just be enough to save your $1,500 GPU from turning into a paperweight.
Additionally, this new connector also carries signals indicating its power capabilities to PCIe-connected devices. This enables power limitations to be set on components using PCIe, including GPUs and SSDs.
The RTX 40-Series cards have suffered power spikes periodically, but new ATX 3.0 PSUs can handle those spikes instead of just giving up and bricking expensive parts inside your PC. Knowing how much power your PC needs is crucial to having a stable machine that makes the most out of its hardware.
Other notable changes in the ATX 3.0 specification include:
- It can handle GPU excursions (power spikes) three times the card's power rating.
- The 12V rail can go as high as 12.2V allowing for lower voltage drops.
- Up to 60% efficiency on a 10W load, or 70% efficiency for 2% load of max rated capacity.
- Faster system wake up and power on signal.
ATX 3.0 is the first time PSUs have seen a major change since 2003, at least in terms of ATX standards. The GPU power spike problem is one of the most common GPU issues and has finally been officially recognized by Intel and PCI-SIG alike.
Do You Need to Upgrade to ATX 3.0?
As long as your PSU meets Nvidia's minimum power recommendations for the RTX 40-Series, your existing PSU will work just fine with the new GPUs. While the cards have five slots, they come with a power adapter to make them compatible with existing six or eight-pin PSUs.
The PSU recommendations for RTX 40-Series cards are as follows, according to Nvidia:
- RTX 4090 (450W TGP): 850W minimum
- RTX 4080 (320W TGP): 750W minimum
- RTX 4070 Ti (285W TGP): 700W minimum
The most power-hungry GPU in the 30-Series was the 3090 Ti, which required a minimum 850W PSU. As you can see, the 4090 has the same minimum PSU power requirement, except you get more performance per watt.
In case your power supply isn't up to the mark, or if you're looking for signs to upgrade your PSU, we strongly recommend you get a new and preferably ATX 3.0 compatible one. It's never a bad idea to dish out extra cash on your PSU to protect your other components.
Besides, leaving a healthy amount of headroom on your PSU will give you peace of mind and room for overclocking. However, you'll likely hit a CPU or memory bottleneck before you're able to get the GPU to its limits.
That said, if the specifications listed above didn't change your mind, another reason you might want to upgrade your PSU is fewer cables. The 40-Series GPUs use the PCIe Gen 5 connector that allows you to power the GPUs with just one cable. So when accounting for the total cable management you'll have to deal with, this becomes an important factor.
Debunking Power Adapter Myths
Finally, if you're concerned about the power adapters provided with the GPUs to adapt them to ATX 2.0 or other PSUs, don't be. Nvidia has confirmed that the adapters carry active internal circuitry that translates the 8-pin plug status to the correct sideband signals according to the ATX 3.0 (or PCIe Gen 5) specifications.
The 30-cycle lifetime on the new PCIe Gen 5 connectors is also nothing to worry about. It has basically remained the same for over two decades and hasn't changed with PCIe Gen 5, either.
Another fun fact about these connectors is that the internal circuitry can detect the number of connectors plugged in, meaning if you're connecting four connectors instead of the usual three, it'll allow the RTX 4090 to draw more power up to 600W.
Power Efficiency Improvements in Nvidia's RTX 40-Series GPUs
The Ada Lovelace architecture that the 40-Series GPUs are based on brings major performance and power efficiency improvements. As a result, these GPUs perform better than their predecessors while using far less power. The power requirements were ramped up, but they weren't as big as compared to the performance enhancements.
While 30-Series GPUs were limited in terms of boost clock speed by their overall power consumption, on 40-Series GPUs maximum clock speeds or voltage limits are being hit first. This allows Nvidia to further tune the cards and lower power levels for better efficiency.
At the end of the day, power efficiency enhancements do matter when it comes to your PC's overall performance. Not to mention a slightly cheaper electricity bill.