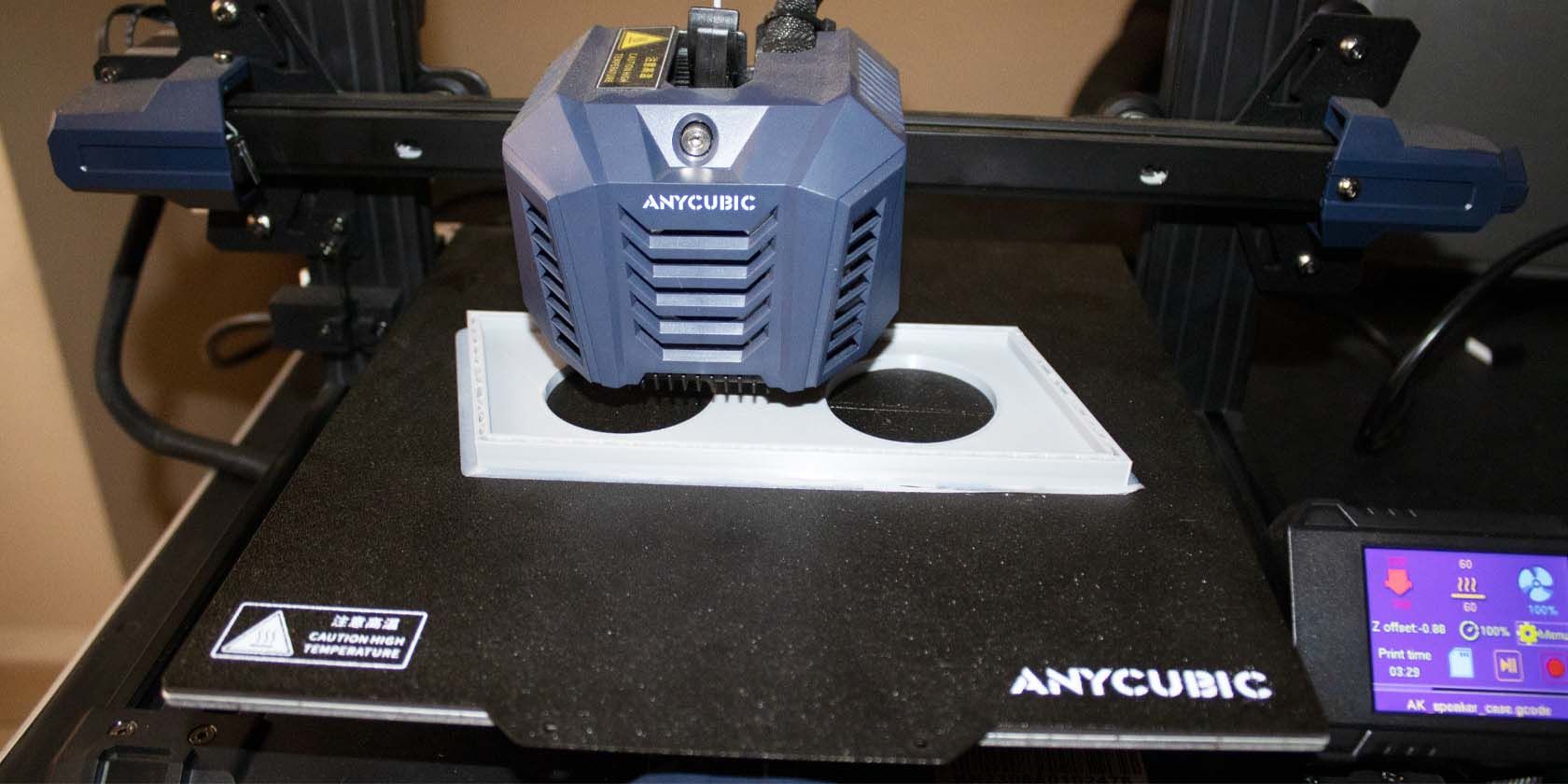
The Anycubic Kobra Neo is a superb, affordable 3D printer for beginners and experienced makers. In addition to being a great entry-level machine, it is straightforward to assemble all of its parts. Unlike similar 3D printers that need building, It can take you less than an hour to get everything up and running.
To set up the Anycubic Kobra Neo, you can follow the steps below.
Anycubic provided the printer used for this demonstration. The company did not pay for or have input into this article.
Step 1: Unboxing the Printer
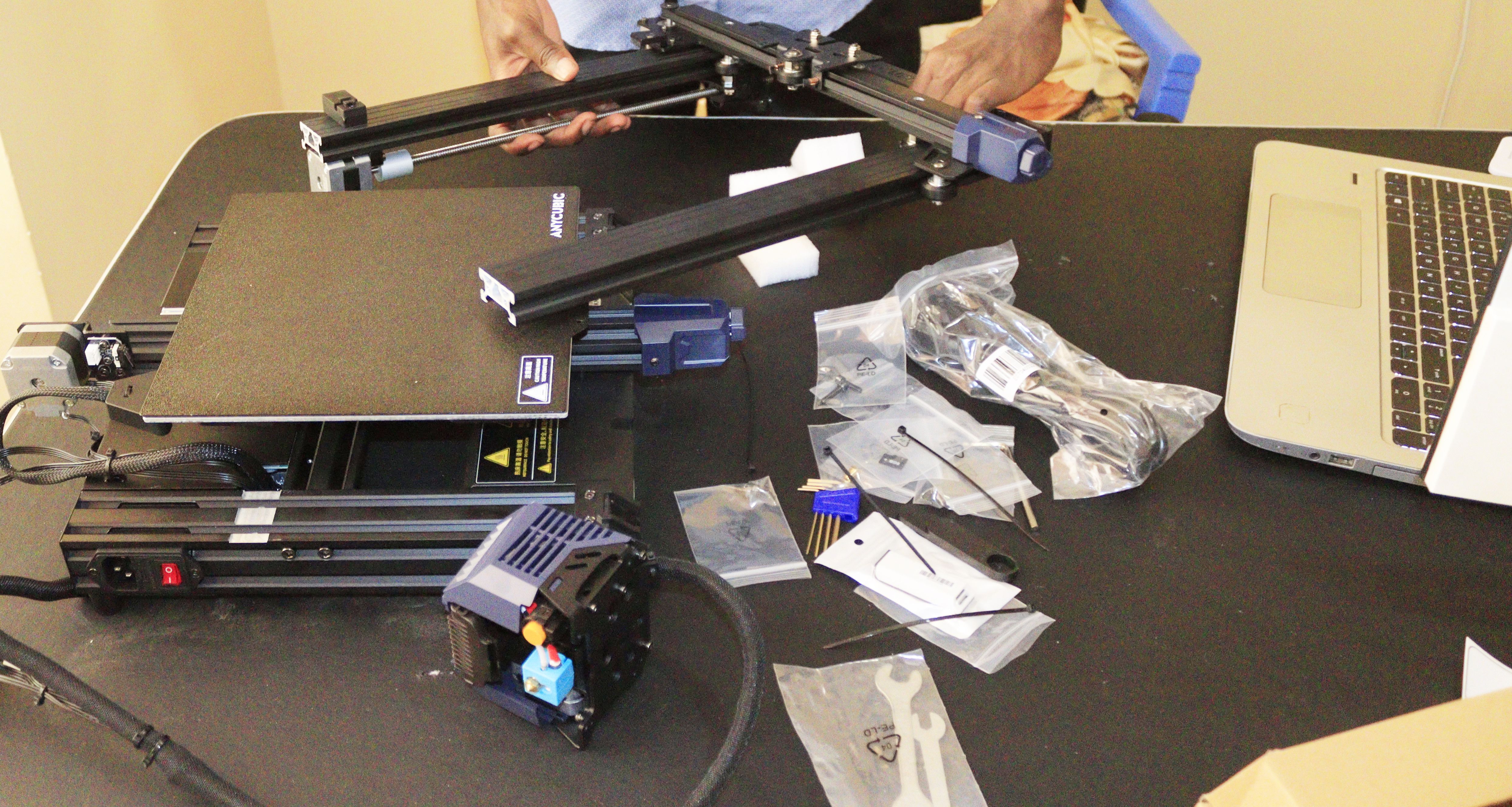
When you open the box, you will see the printer's various components well-packed. There is also a manual that comes taped on top. After carefully opening the box, you can check that all the parts are present. You should have the components listed below:
- Frame
- X-axis limit switch kit
- Printer base
- Print head
- Filament holder
- Screen kit
- Memory car
- Card reader
- Spare nozzle
- Screws
- Tool kit
- A small roll of filament
Once you confirm that all the above components are present, the next step is to remove them from the box and start the installation process. This task is easy as you only need to lift them from their slots and place them on the ground, ready for assembling.
Step 2: Tighten the Screws on the Base
To ensure that your 3D printer is stable, you should tighten the screws on the base. You can use a screwdriver or a wrench to do it.
If a screw is loose, it could cause the entire printer to become unstable and cause damage to your 3D prints. Tightening the screws on the base of your 3D printer can also help prevent any accidental movements that may occur during a print.
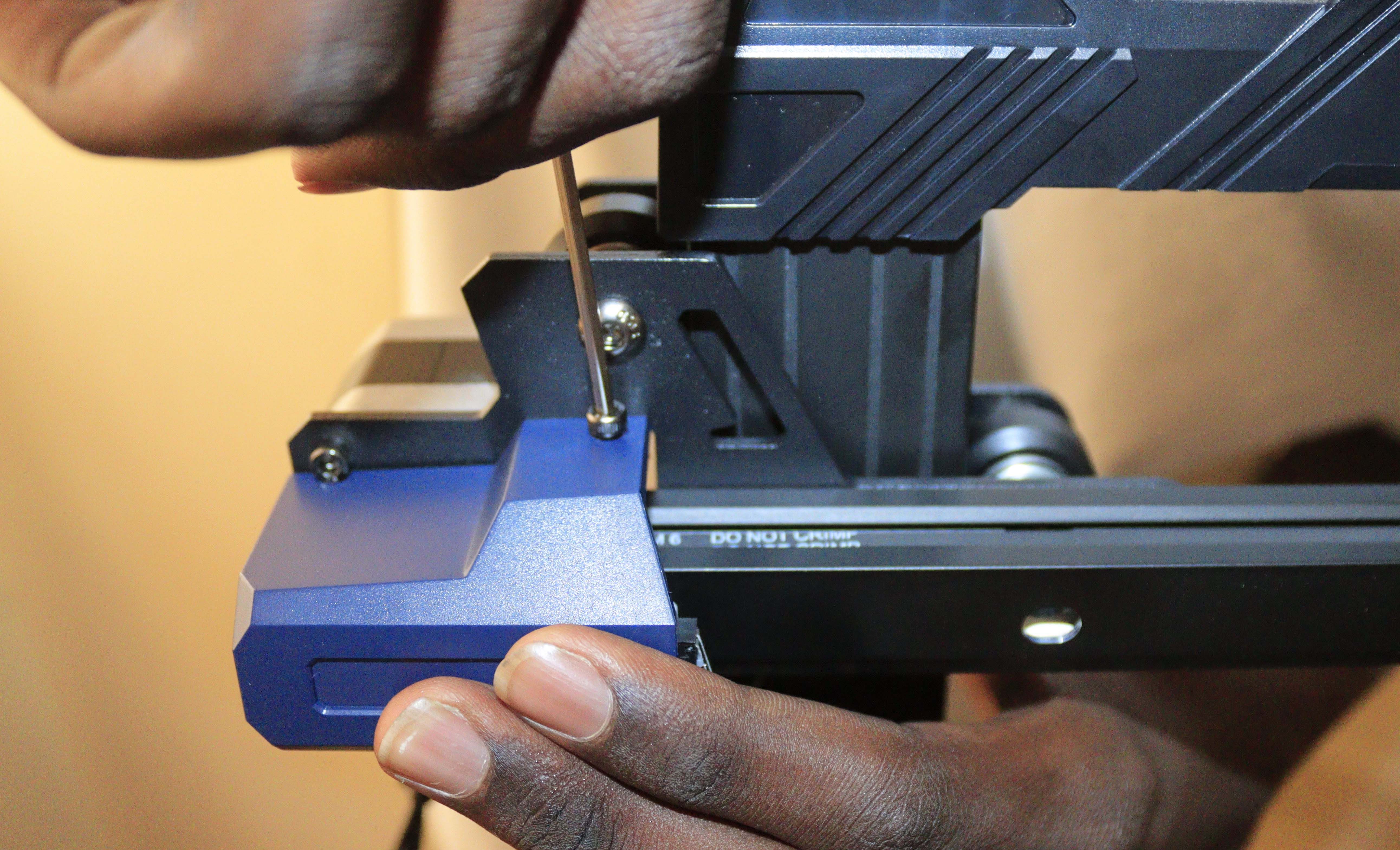
Step 3: Install the Frame
Loosen the screws on both sides of the holes where the frame will fit into the base. Then take the frame and attach it to the base. Ensure that you correctly align the z-axis profile with the groove of the aluminum base. Then, take the screws and use them to secure the frame in place.
Step 4: Install the X-Axis Limit Switch
Start by loosening the screws locked on the bracket of the x-axis.
Don’t remove them entirely—you just need to create space for attaching them to the frame. Next, take the limit switch module and install it to the left bracket of the x-axis, then tighten the screws to secure the switch in place. Remember not to over-tighten, as this could damage the switch.
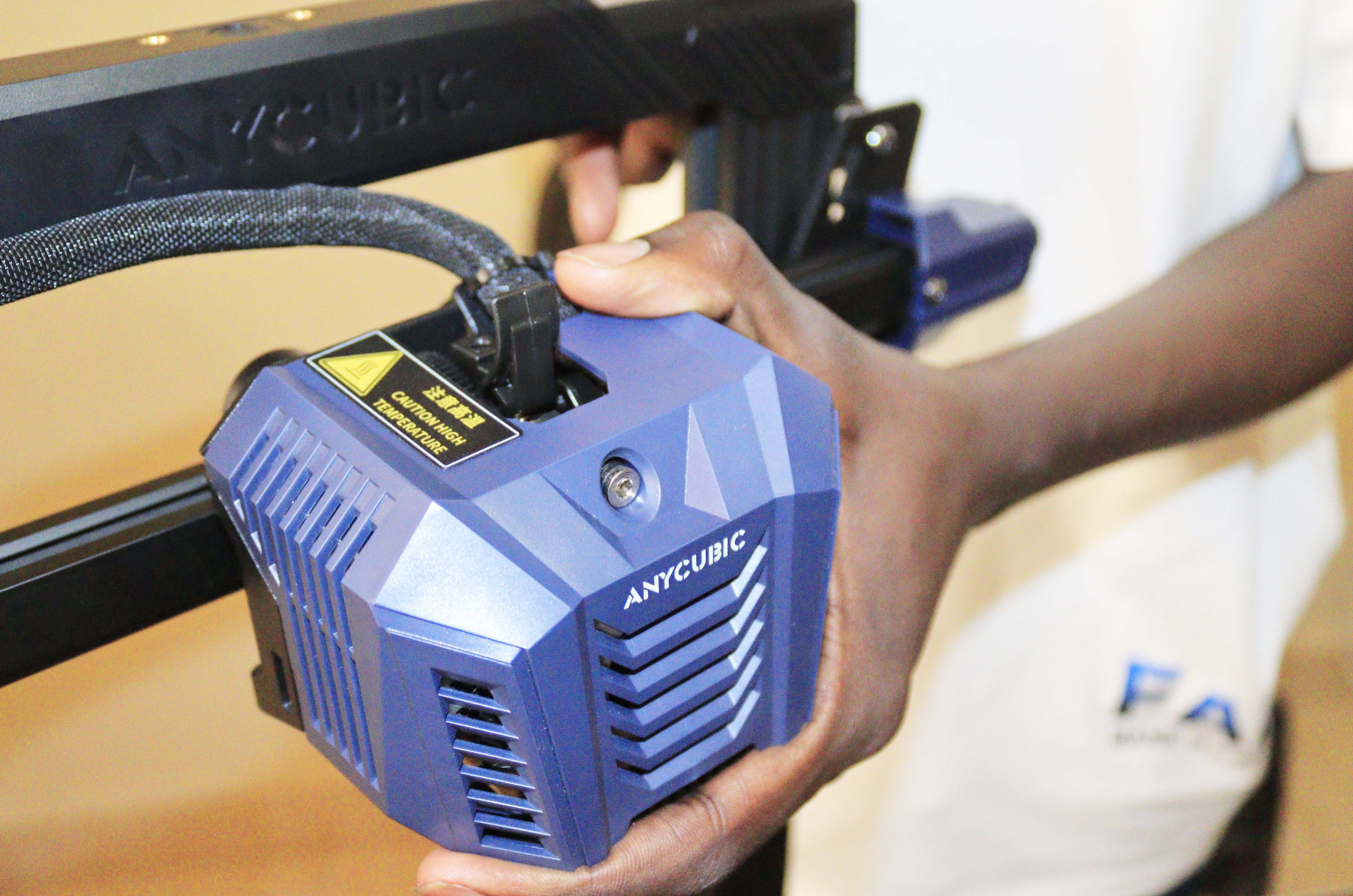
Step 5: Install the Print Head
Start by placing the print head onto the x-axis of the printer. Ensure you place it in the correct orientation.
Then, use the four screws to secure it in place.
Step 6: Install the LCD Touchscreen
To install the screen, take the screws included in the kit and use the screwdriver or wrench to attach it to the front part of the printer's base where there is a screen cable.
Once you tighten the screws, connect the included screen cable to the touchscreen. Be sure to press firmly on the connections to ensure that you secure the cable properly.
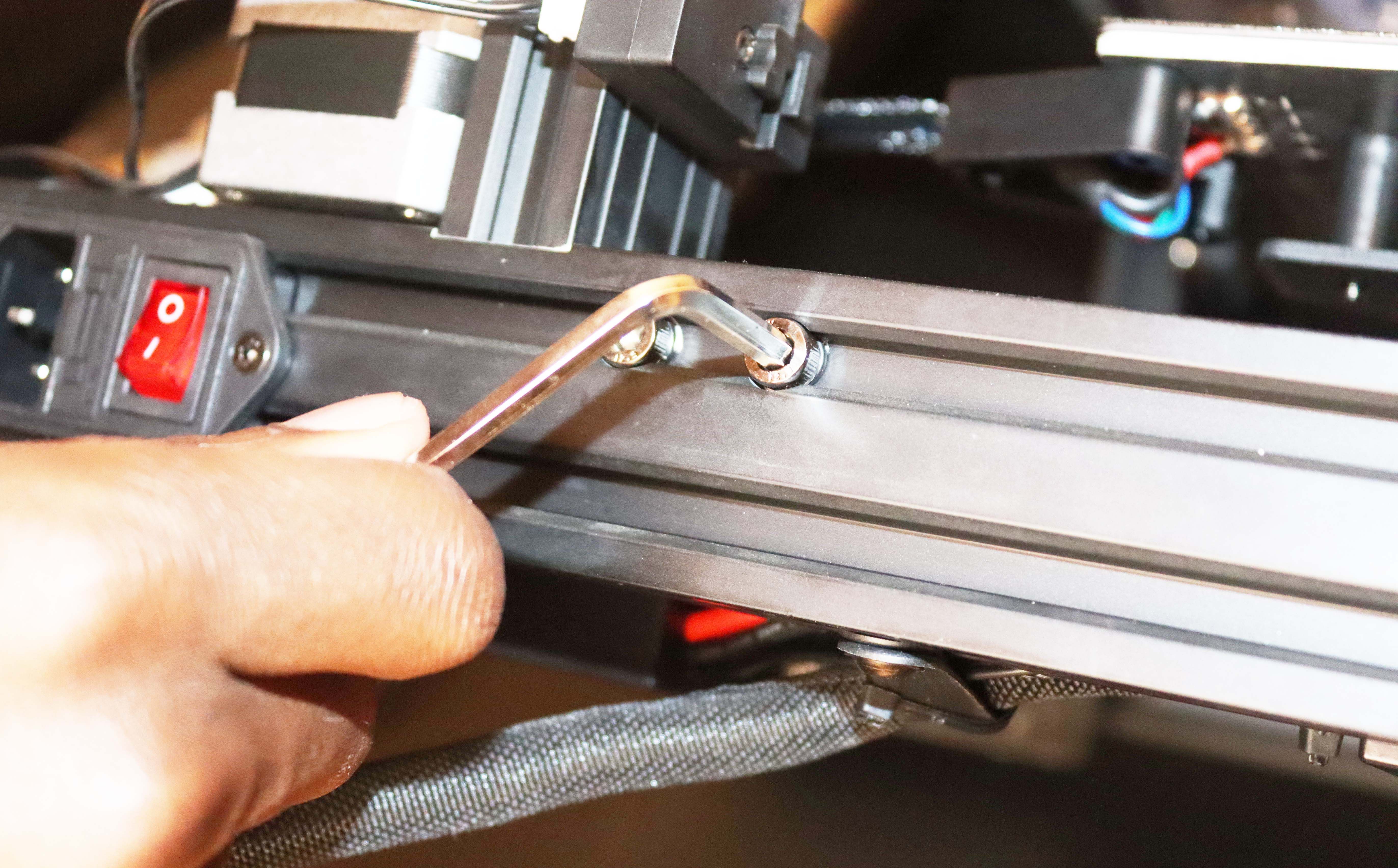
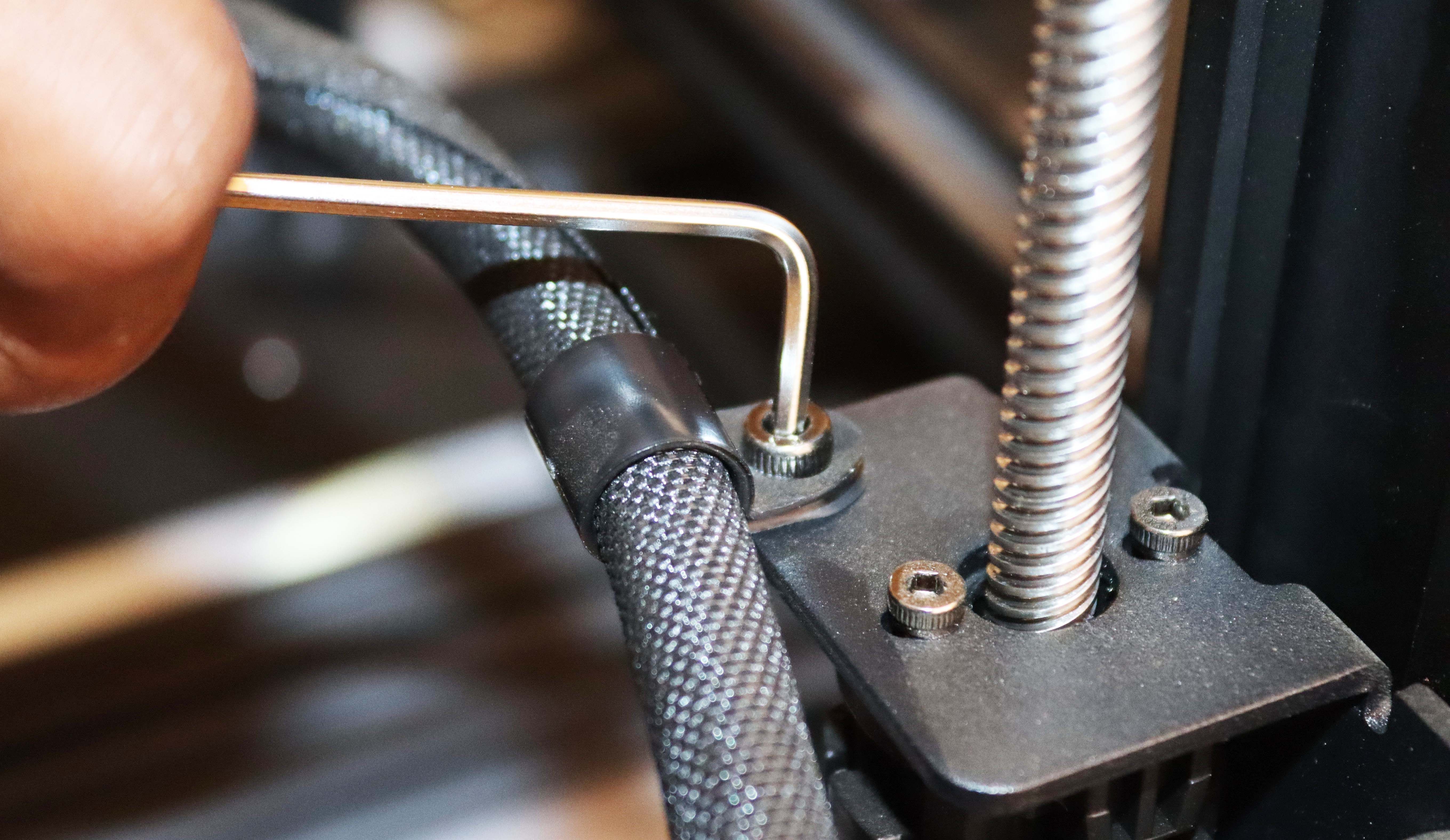
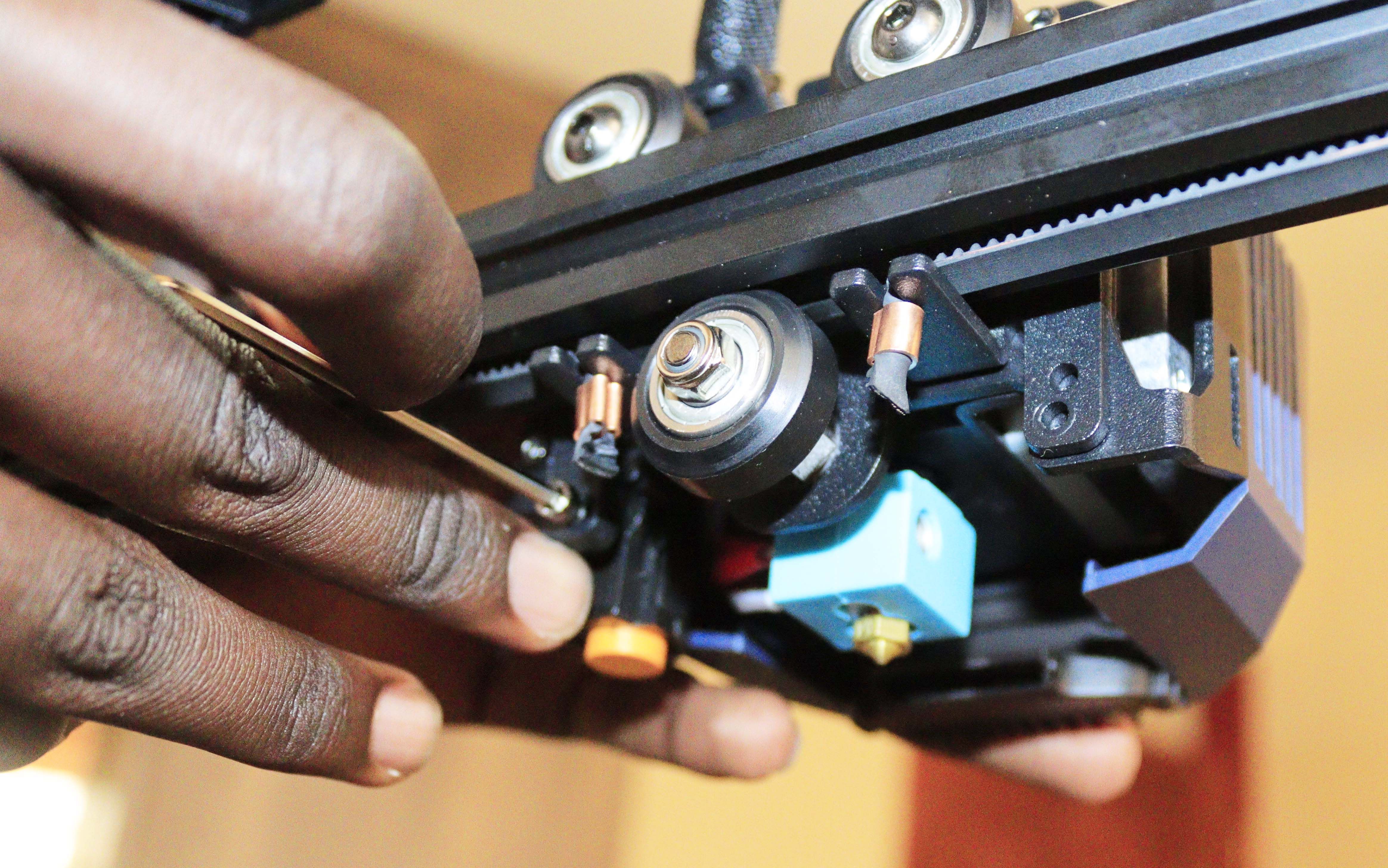
Step 7: Secure the Print Head Harness
As shown below, use one M4 screw and the R-type cable clamp to secure the print head harness in the bracket.
Ensure the length between the R-type cable clamp and the print head wiring position is around 26cm (10.25in). You can measure using a tape measure, as shown below.
Continued usage can damage the harness if the length is less than 26cm.
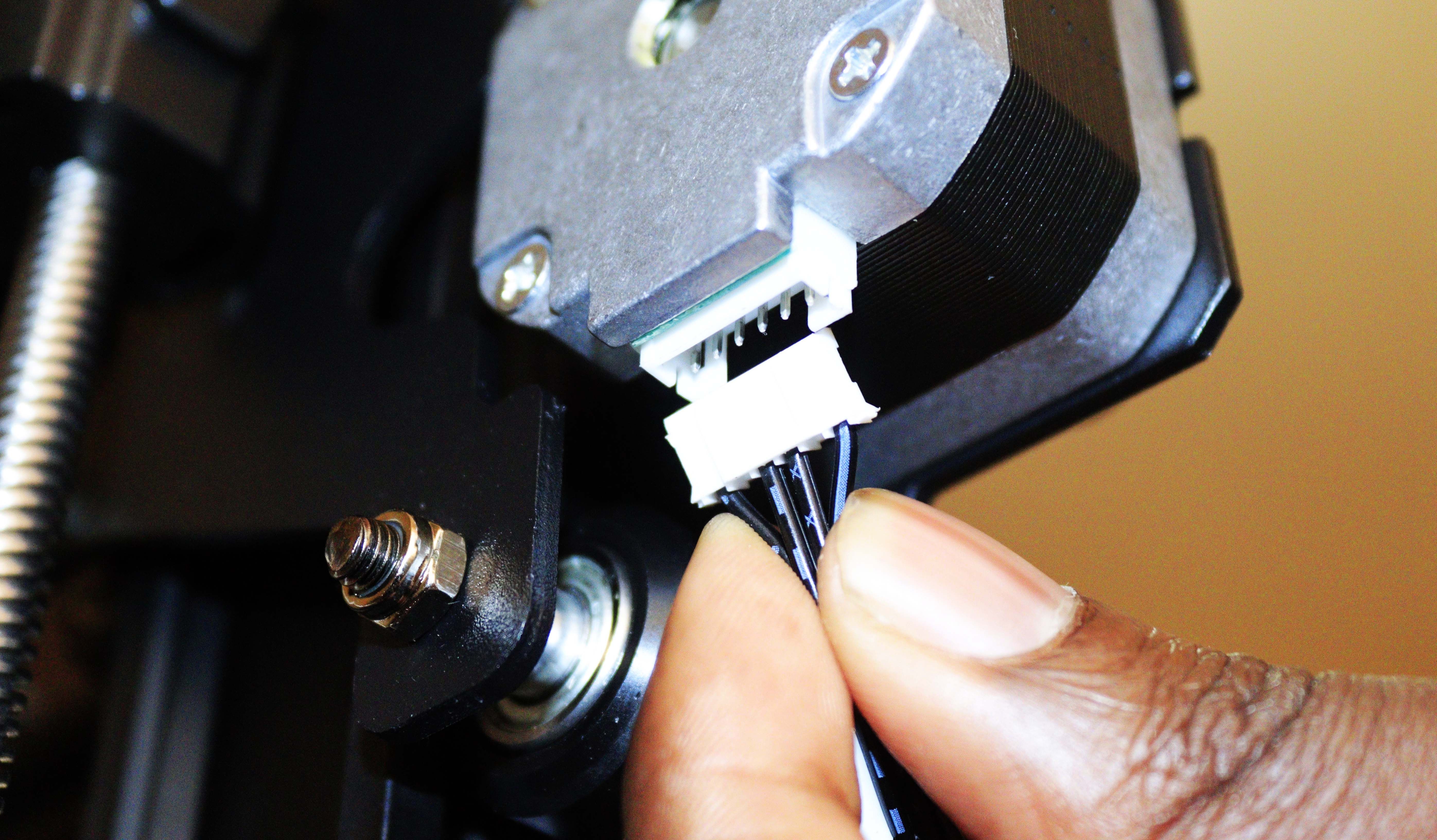
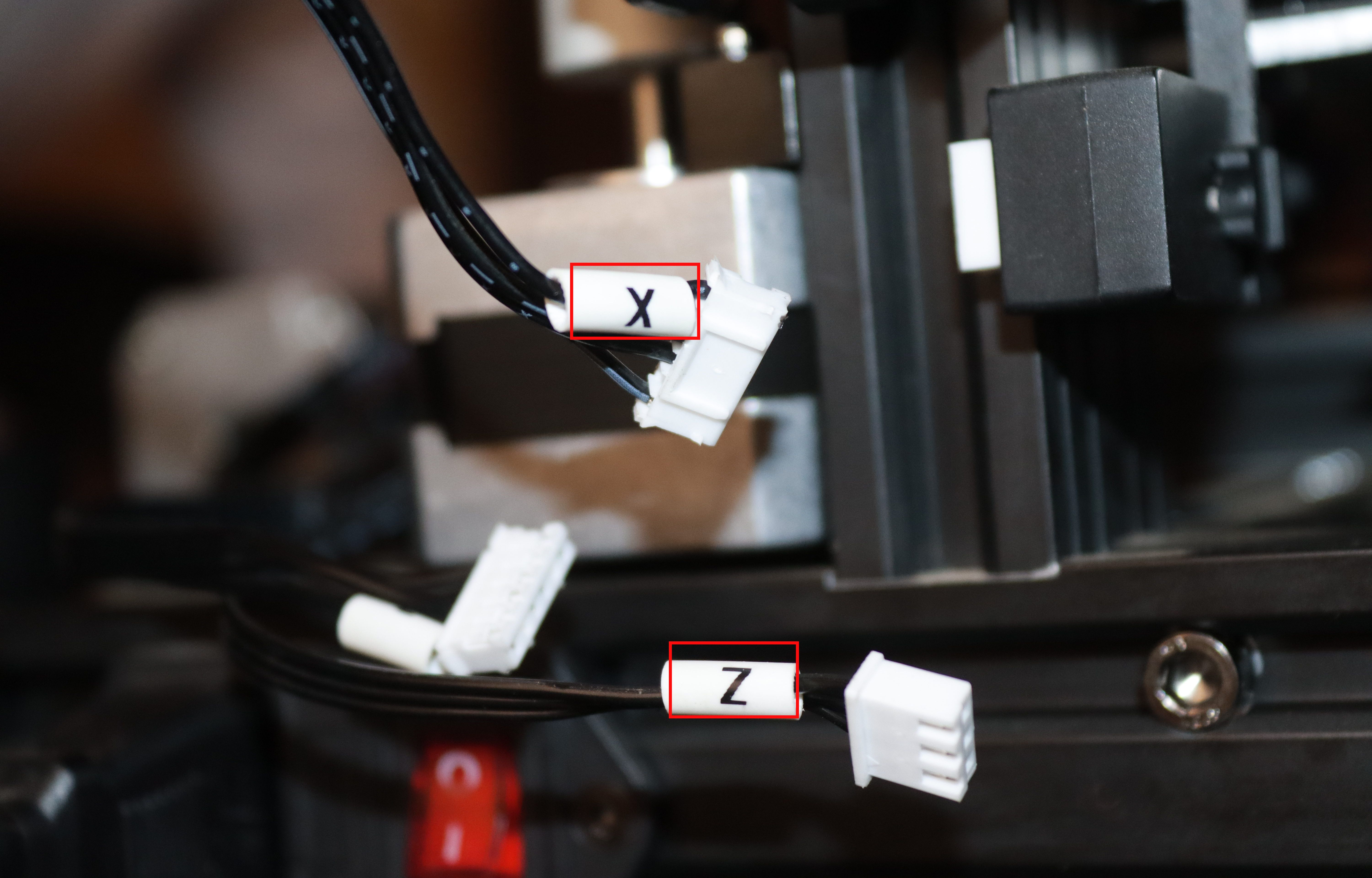
Step 8: Connect the Wires
There are six connections that you need to make to their respective positions:
- X motor
- X-axis limit switch
- Y-axis limit switch
- Y motor
- Z motor
- Z-axis limit switch
The wires are marked with their specific names, as shown below.
So you can simply plug them into their corresponding positions. As you insert the wires, ensure you don’t use much force to avoid damaging the sockets.
Step 9: Inspect Before You Start 3D Printing
After installation and wiring, it’s time to inspect everything to ensure everything is in place. You can begin by shaking the y-axis; if it wobbles, you can rotate the eccentric nuts to tighten them. Next, try shaking the print head to see if it is loose. If it is, tighten the nuts until it is a bit tight. It should now be moving smoothly along the x-axis.
You can also check the z-axis wheels and see if they are moving smoothly without applying force. If it’s not moving freely, you can adjust the tension on the wheels. If the belts are too loose, you can also tighten them.
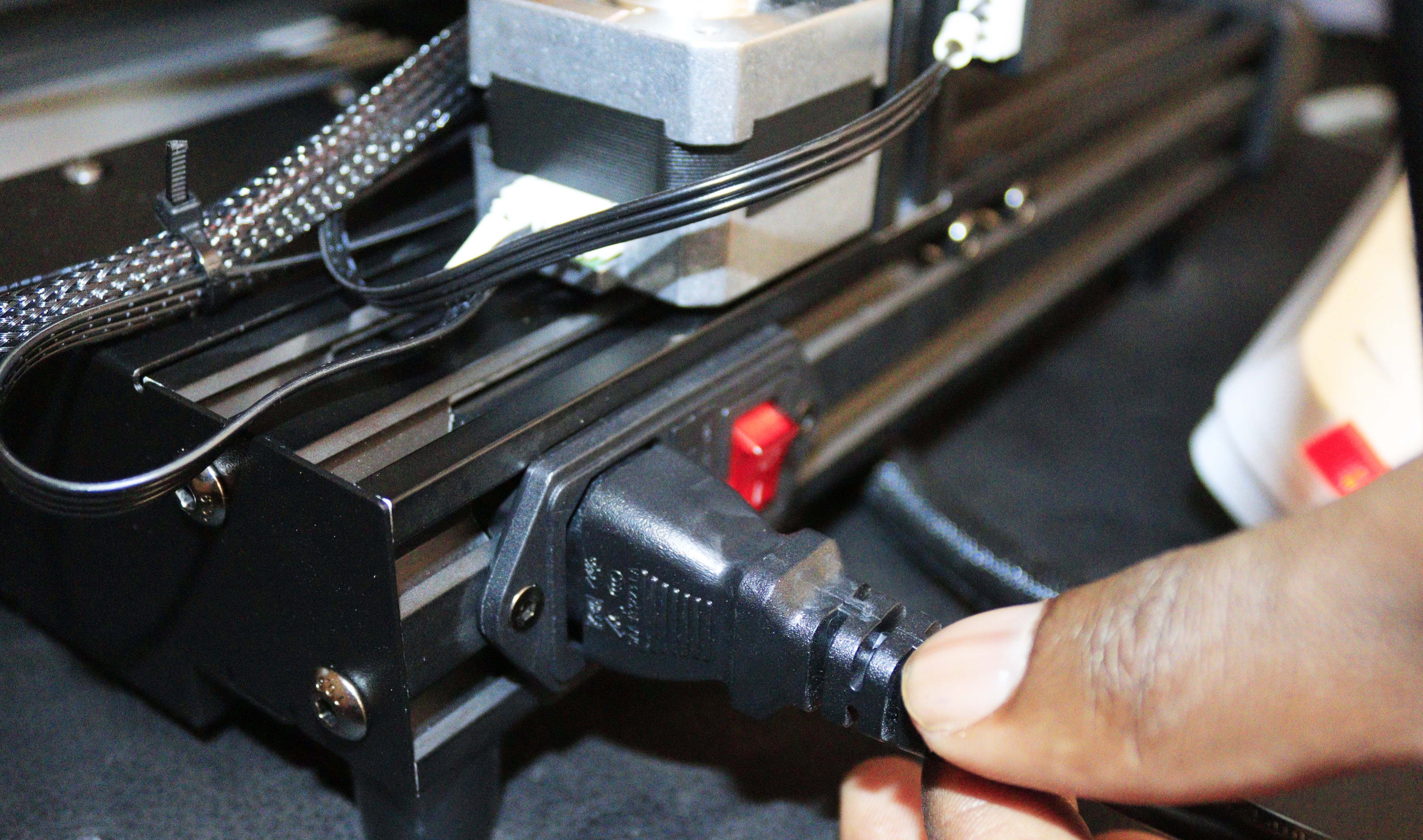
Step 10: Plug the 3D Printer Into the Power Source
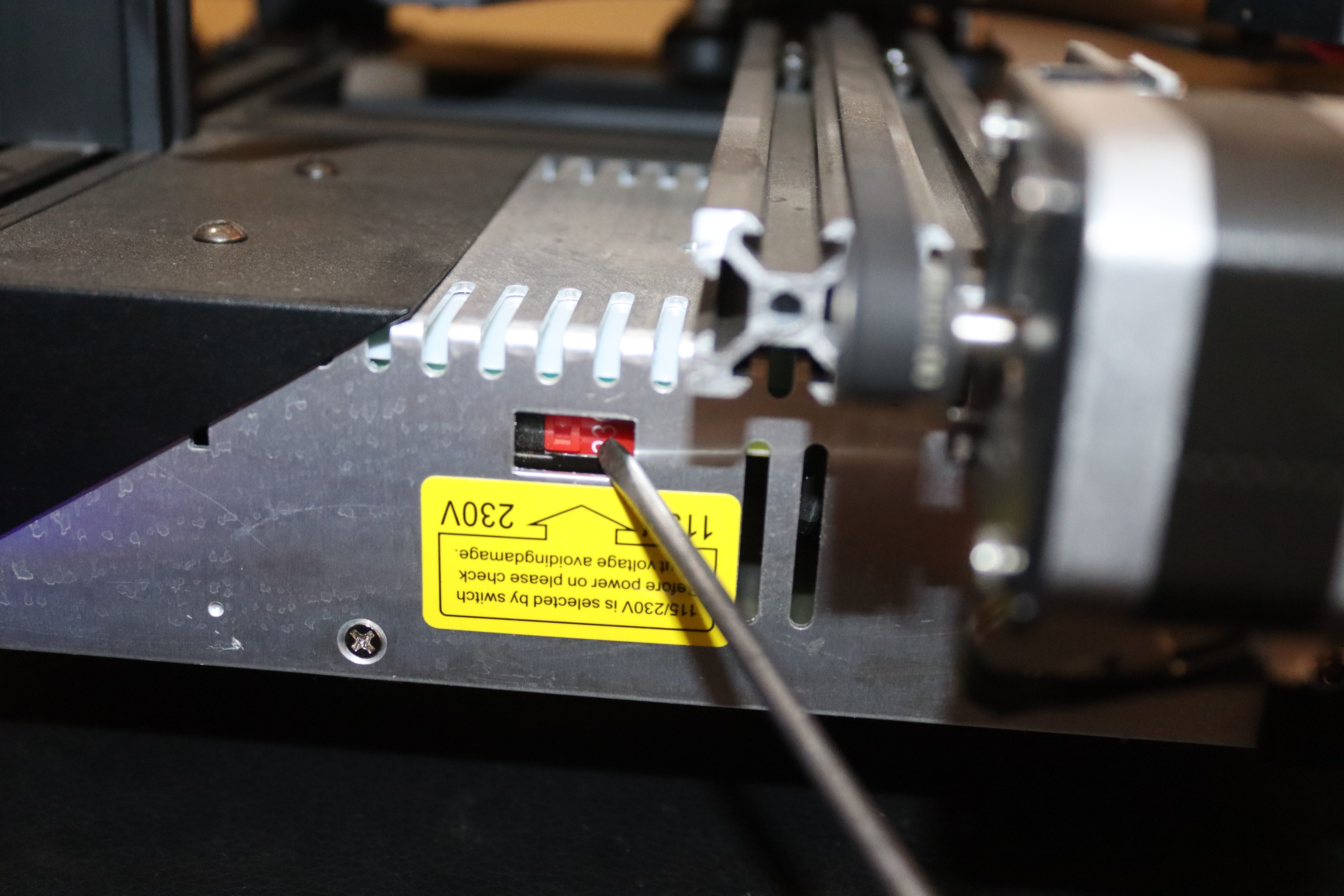
Start by putting the power cord to the power source, connecting it to the 3D printer, and turn it on. Remember to check the voltage setting and ensure it corresponds with your local mains voltage (~115V or ~230V) before you turn it on; otherwise, you will need to replace the power supply as the difference in voltage will damage it.
You can use the red switch inside to change the voltage, as shown below.
In most cases, 230V is the default setting. Once you set it correclty and turn on the power, you should see the screen lighting up.
Step 11: Leveling the 3D Printer Bed
To level the 3D printer bed, on the screen, go to Menu > Leveling > Auto Leveling. Press the knob to select the Auto Leveling option.
You should be able to see the printer leveling itself. Wait for a few minutes until it finishes leveling.
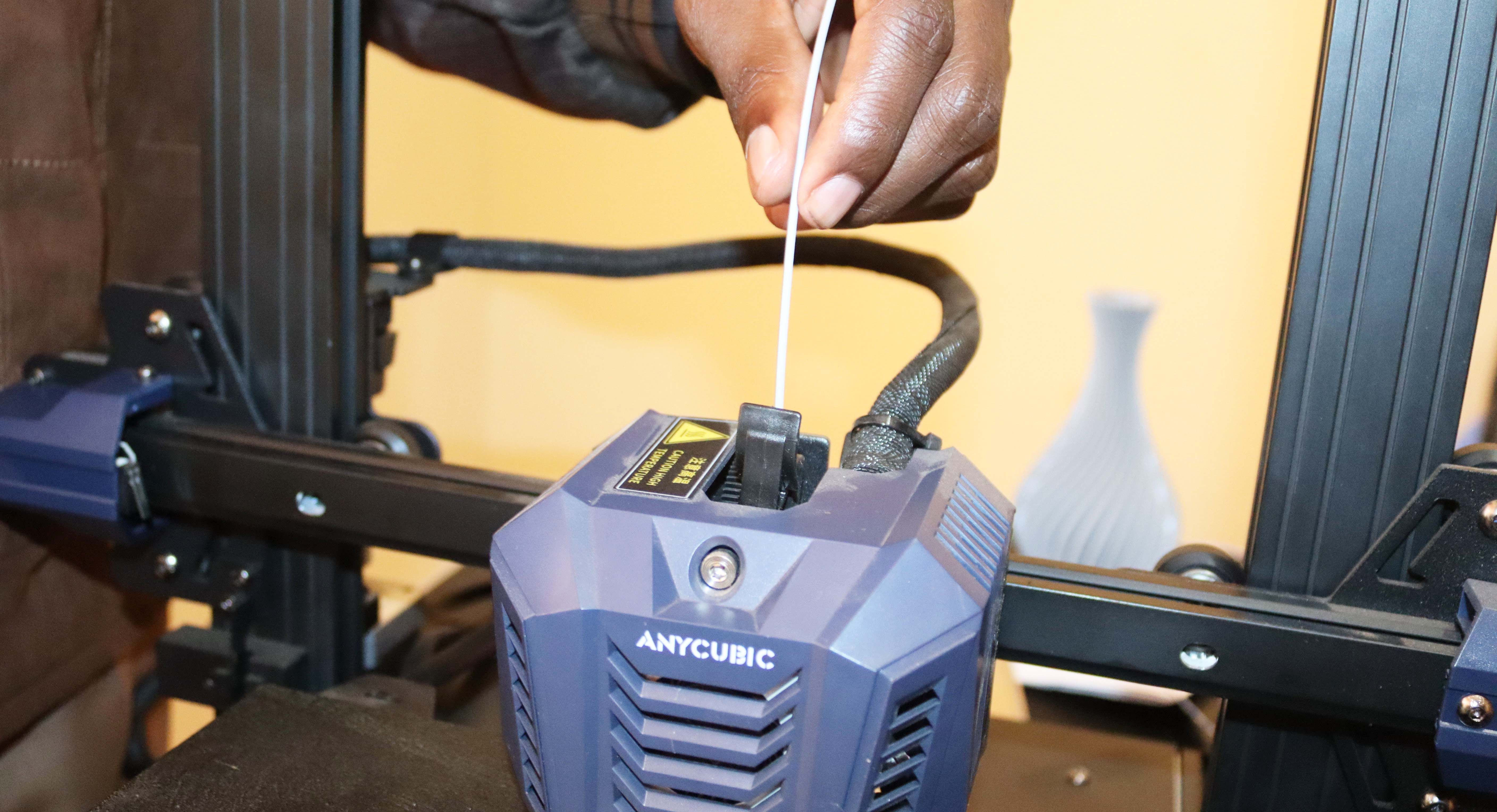
Step 12: Load and Preheat the Filament
First, you’ll need to prepare the filament spool. Make sure to choose the right filament for the 3D printer, as they come in different sizes and types. The Anycubic Kobra Neo usually supports 1.75 mm filament by default (that is if you have not changed your nozzle).
Once you’ve ensured the spool is the right size, you can use a sharp knife to slash the tip of the filament so that it can quickly enter the print head. Next, you will insert it from the top, as in the image below.
Go to the Menu > Prepare > Load Filament and press it, and the print head will start loading the filament.
After loading, go to Menu > Prepare > Preheat PLA if you are using PLA.
If you are using ABS filament, you can select Preheat ABS instead. Once selected, you will see a thin filament extruding from the nozzle.
Step 13: Adjust the Z Offset Height
The Z offset height is the distance between the build plate and the nozzle tip of the 3D printer. This distance is crucial because it determines the quality of the printed object, as it affects the adhesion of the 3D filament to the build plate, the layer height, and the overall printing quality.
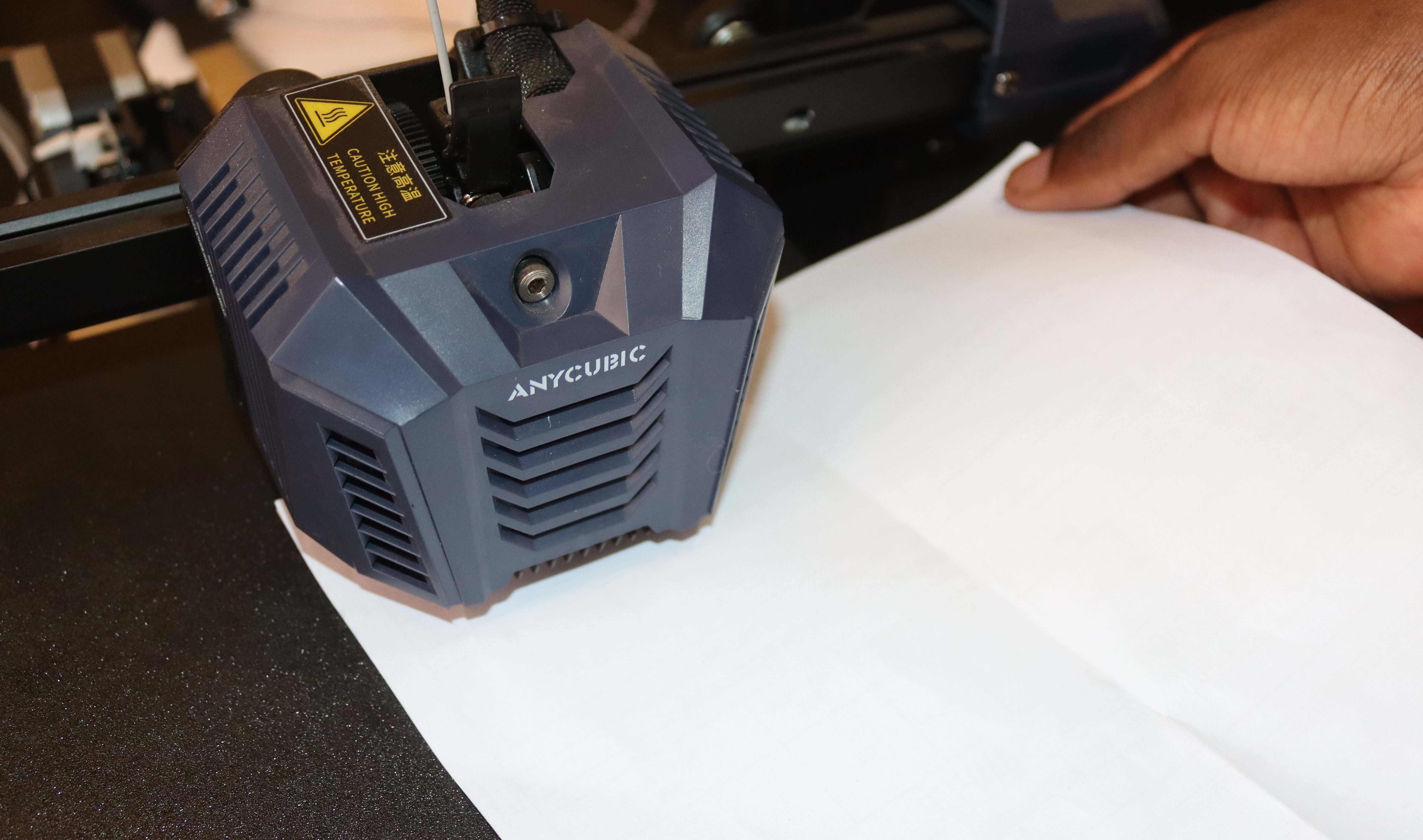
To adjust it, put a piece of paper on the build plate.
Then go to Menu > Leveling > Z Offset, and turn the knob to move the print head downwards until it touches the paper.
Continue until the point at which it’s difficult for you to move the paper by hand. That particular position is the Z offset. You can then press the knob to save.
Step 14: 3D Printing Process
Insert the memory card in the slot at the base. To select the design to print, go to Menu > Print from SD Card.
Choose the 3D model you want to print and press the knob. The printer will start heating, and when the temperature of the bed and the nozzle reaches the maximum, you will see it starting to print. Observe how the first print turns out and see if there are first-layer woes.
If there are any, you can try adjusting the Z offset again to ensure that the distance between the nozzle and the 3D printer bed is appropriate.
Assembling Anycubic Kobra Neo Is Easy
Unlike most DIY 3D printers that take a lot of time to assemble and figure out where each component should be placed, setting up the Anycubic Kobra Neo is easy. Even if you have never built a 3D printer, you should be able to do it without any issues.
The manual that comes with it is handy, too, as it helps you through the assembly process. If the manual isn’t enough, there are many YouTube videos available that you can follow too.