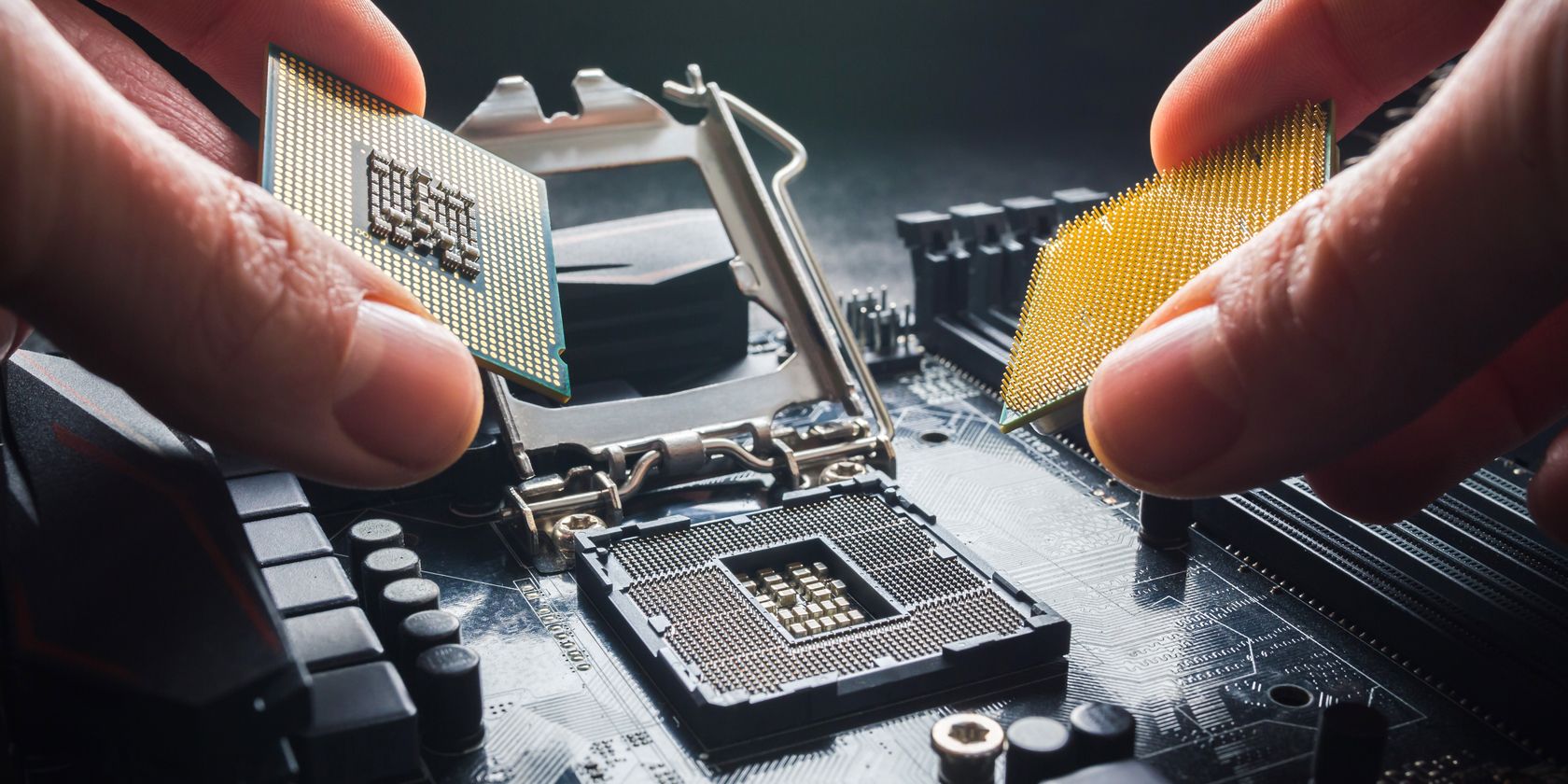
The CPU and motherboard are the main components of your computer. Without them, other crucial components like your RAM and GPU wouldn't work.
However, you can't simply put any CPU with any motherboard; both have to be compatible with one another. If you pair a chipset with an incompatible motherboard, you'll have potentially wasted a lot of money.
The two main competitors in the market are Intel and AMD. You cannot install an AMD CPU on an Intel motherboard, and vice versa, for a number of reasons.
The Main Differences Between Intel and AMD Motherboards
If you take a look at the underside of an Intel or AMD CPU, you'll notice lots of pins or contact points. These pins must match the socket on your motherboard in order to be compatible. It's a bit like trying to plug a US plug into a UK socket; it won't fit, and thus, it won't work.
Below is an overview of Intel and AMD CPUs since 2015 and their subsequent pin counts.
|
Socket |
CPU |
Pin Count |
|
LGA 1151 |
|
1,151 |
|
LGA 2066 |
|
2,066 |
|
LGA 1200 |
|
1,200 |
|
LGA 1700 |
Intel Alder Lake (12th gen) |
1,700 |
|
LGA 1700 |
Intel Raptor Lake (13th gen) |
1,700 |
|
Socket |
CPU |
Pin Count |
|
AM4 |
|
1,331 |
|
TR4 |
AMD Ryzen Threadripper |
4,094 |
|
sTRX4 |
AMD Ryzen Threadripper (3000 series) |
4,094 |
|
AM5 |
AMD Ryzen 7000 series |
1,718 |
You can see from a quick glance at the numbers on this list that slotting an AMD CPU into an Intel socket won't work, and vice versa.
When purchasing a motherboard, you'll need to decide what CPU you want beforehand. For example, if you opt for the Intel 12th or 13th Gen processors, you'll need a compatible LGA 1700 motherboard like the ASUS TUF Gaming B660M-PLUS WiFi D4.
On the other hand, if you're swaying toward AMD, any of the Ryzen series CPUs up to Ryzen 9 will be compatible with an AM4 motherboard like the ASUS ROG Strix B550-F Gaming. But, if you go for a Ryzen 7000-Series CPU, you'll need an AM5 motherboard that supports DDR5. Unlike Intel, AMD stuck to the same AM4 motherboard socket for years.
Intel and AMD Motherboard Sockets Aren't the Only Difference
However, sockets aren't the only difference between Intel and AMD motherboards. Not all chipsets work with the same processors. Though, again, Intel is more complicated than AMD.
A chipset determines what features the motherboard has, like connectivity compatibility, ports, and so on. Intel's Z590 chipset is compatible with 10th-Gen Comet Lake and 11th-Gen Rocket Lake processors but not 12th-Gen Alder Lake processors. AMD's AM4 chipsets work with most Ryzen, Athlon, and 7th-Gen A-Series CPUs. Some CPUs won't be supported, but in many cases, a BIOS upgrade can result in compatibility.
To add even more ingredients to the mix, the naming conventions of each Intel and AMD motherboard can also provide clues as to what's compatible and what's not. Intel's 12th and 13th-Gen CPUs support both DDR4 and DDR5, but since DDR5 isn't backward compatible, you'll need to find a motherboard that supports either DDR4 or DDR5 (not both).
Similarly, Ryzen 7000 Series CPUs support DDR5, whereas Ryzen 9 and below will only support DDR4.
Z-Series Intel motherboards tend to offer the best features and are considered high-end. B-Series Intel motherboards are considered mid-range, generally for casual gamers who don't need to prioritize overclocking. H-Series motherboards are at the budget end of the scale, with limited ports and lesser features.
On the AMD side, there are generally X-Series and B-Series motherboards. AMD X motherboards often provide more PCIe slots, NVMe slots, and more I/O ports, whereas B motherboards vary between mid-range and budget.
AMD or Intel, Not Both
While there are several factors that determine which CPUs are compatible with which motherboards, the underlying fact is that Intel is not compatible with AMD and vice versa. It really comes down to personal preference as to whether you choose AMD or Intel since both are constantly competing with each other to offer the best and next-gen technology.
Whichever you decide to go with, just remember to ensure your CPU socket is compatible with your motherboard and that your motherboard chipset offers the features you're looking for.