You've switched on your computer, preparing to do some work, edit a document, mix a composition, or just play a game... but something goes wrong. Ubuntu won't boot.
Sadly, as reliable as Linux is in general and as popular as Ubuntu is, sometimes it runs into problems, just like Windows 11 or macOS. In most cases, you'll be able to work around this.
Whether you're using Ubuntu Desktop or Ubuntu Server, here's what to do if Ubuntu doesn't boot.
Ubuntu Not Booting? Try These 5 Tips
Ubuntu typically works out of the box. You can spot most booting issues either by a very slow boot or by Ubuntu not starting at all.
If Ubuntu is not booting, work through these five steps:
- Check for bootable devices
- Is the GRUB bootloader working?
- Repair the bootloader menu
- Reinstall Ubuntu
- Replace faulty hardware
While these steps are primarily for Ubuntu users, you can apply them to other Linux operating systems. Note, however, that if you're using disk encryption, some of these fixes will not work.
If your Ubuntu system isn't booting, it's time to work through these five steps. You can use these steps at any time, whether you've been running Ubuntu for a while or if Ubuntu is not booting right after you install it.
1. Is an Attached Device Causing Ubuntu Boot Problems?
If Ubuntu doesn't start, it could be because there is a bootable disk attached.
You're not alone. This is one of the most common problems with Ubuntu not booting, usually occurring right after installation. This is because the Ubuntu boot disk (USB device or a DVD) is set as the boot device. It's such a problem that the installer instructs you to eject your installation media before the first boot.
To check the current boot device, boot into the system UEFI/BIOS or boot order menu. Both can be accessed from the POST screen, which appears when your PC powers up. If you run into trouble finding the boot order menu, check the computer's (or motherboard's) documentation.
2. Ubuntu Doesn't Boot Because the GRUB Bootloader Is Not Working
GRUB is the bootloader that ensures the selected operating system boots. On a dual booting machine, it will list and boot all installed operating systems, including Windows.
However, installing Windows alongside Ubuntu can lead to the bootloader being overwritten, leading to problems booting Ubuntu.
Other issues can corrupt the bootloader, such as a failed upgrade or power failure. Whatever the situation, you might see an error on Ubuntu, such as "grub failed boot detection."
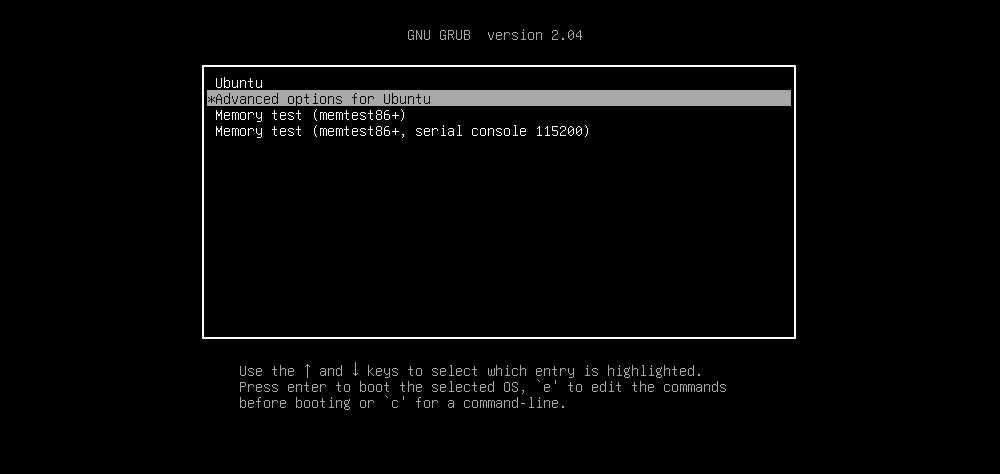
To check the GRUB bootloader, restart your PC while holding Shift. You should now see a list of the installed operating systems; navigate the menu using the arrow keys.
If not, then the problem is that the GRUB bootloader is broken or overwritten. Repairing the bootloader is the only solution. (If you're dual booting, you'll still be able to access Windows).
If you see the GRUB Bootloader, skip down to the next section.
Repair the GRUB Bootloader to Boot Ubuntu
If GRUB is not loading, then Ubuntu won't boot. Fortunately, you can repair GRUB using the Ubuntu installation media. Restart the computer with the disc inserted and wait for it to load up.
Again, you may need to change the boot order, as described above. Make a note of the boot order before you change it!
With the installation media booted into the Live environment, confirm you have a network connection and then open a Terminal. Enter:
sudo grub-install /dev/sda
You can also update GRUB with:
sudo update-grub
You should now be able to restart your PC and boot into Ubuntu. Alternatively, it will be listed as an option in the GRUB bootloader menu.
3. Ubuntu Still Won't Boot, but GRUB Is Loading? Fix the Bootloader Menu
If you can see the bootloader, then you don't have to do any of the above. There is a built-in recovery tool to help when Ubuntu doesn't boot.
In the bootloader menu:
- Select Advanced options for Ubuntu
-
Use the arrow keys to select the entry appended with (recovery mode)
- Tap Enter to continue
Wait as Ubuntu boots into a slimmed-down version of the operating system. If you've ever booted Windows Safe Mode, you'll notice this is similar.
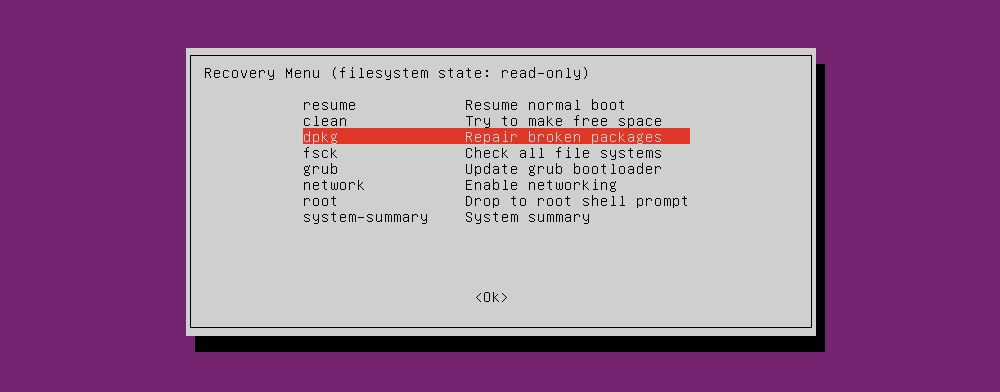
Several repair options can solve situations when Ubuntu won't boot. The three you should try, in order, are:
- fsck: This is the file system check tool, which scans the hard disk drive and repairs any errors it finds.
- clean: Use this to make free space; useful if the reason for Ubuntu not booting is a lack of HDD space.
- dpkg: With this, you can repair broken software packages. Failed software installations or updates can cause problems with Ubuntu not starting. Repairing them should solve this.
If you have just installed Ubuntu, and it won't boot, you should also try the failsafeX tool. Graphics drivers or a problem with the Xorg graphical server might be the fault in this scenario. Use failsafeX to overcome this Ubuntu booting error.
The root menu item is for advanced users who have the skills to fix the problem manually.
4. Ubuntu Boot Failed to Start? It's Time to Reinstall
Of course, if Ubuntu doesn't work due to a failure that could prove time-consuming to resolve, you might prefer to simply reinstall Ubuntu. You can do this without overwriting your existing files and folders. In fact, it's one of the easiest fixes if Ubuntu won't boot.
- First, boot into the Live environment on your Ubuntu installation media as explained above.
- Next, commence installation of Ubuntu.
- When the installer detects Ubuntu is already installed, select Reinstall Ubuntu.
- Select the option with the note "Documents, music, and other personal files will be kept."
- Proceed with reinstallation.
Of course, as a precaution, you should already have a backup of all your Ubuntu data. This might have been made manually with a backup utility or using a disk cloning tool like dd.
Once the reinstallation is complete, Ubuntu should be back up and running.
The Erase Ubuntu and Install option is not advised unless other options fail. Again, you should back up your data first.
5. Ubuntu Linux Not Booting? Check for Faulty Hardware
Another cause of Ubuntu being unable to boot comes in the shape of faulty hardware. Boot problems can be caused by the following:
- A hard disk drive (HDD) or cabling fault
- Motherboard issues
- A processor (CPU) problem
- Power Supply Unit (PSU) issues
Try our guide for repairing a hard disk drive. You might also read up on focusing your efforts on diagnosing hardware issues that prevent a computer from booting.
Once a faulty HDD is replaced, you'll typically need to reinstall Ubuntu from scratch unless you have a backup. While it's a "scorched earth" approach, this will solve problems with Ubuntu not starting.
Say Goodbye to Ubuntu Booting Problems!
Whether your newly installed Ubuntu's boot failed or your old Ubuntu installation is not working, it isn't necessarily an easy fix.
If you fail to repair the GRUB bootloader, it could be a long time before you have a usable computer again. Yet another argument in favor of maintaining regular backups or at least syncing your valuable data with the cloud!
Remember, this can happen with any operating system, not just Ubuntu. If nothing works, in the end, you should perform a clean install of the latest Ubuntu version.