Wondering why your network is unstable? Unstable Wi-Fi often starts with wireless congestion, which is common in busy areas.
In essence, having too many competing Wi-Fi signals can negatively impact the connection speed. However, there are ways to fix an unstable Wi-Fi connection and restore normal connection speeds. But keep in mind, that Wi-Fi instability can arise from other causes, such as a Windows update, arcing electricity, weather phenomenon, and more.
Unstable Wi-Fi Is Caused by Wireless Interference
Wireless congestion is caused by issues with two factors: frequency overlap and limited Wi-Fi channels.
1. Wireless Overlap
Imagine an old car radio. Rotating the station dial sometimes plays a muddled combination of two different radio stations. That's because two radio towers can operate on the same frequency channel. The same is true for Wi-Fi routers: when two or more routers transmit on the same channel, they slow each other down and cause unstable connections.
The problem is worst in dense living spaces. For example, in an apartment complex, dozens of routers can transmit on the same channel. Even modern Wi-Fi technology, which breaks each band into channels, can't cope with that level of interference.
2. Wi-Fi Channels
Like radio, Wi-Fi is broken up into frequencies on the gigahertz (GHz) spectrum of 2.4GHz and 5GHz for Wi-Fi 5 and 6. If you have Wi-Fi 6E, you'll get access to the newly available 6GHz band. Each frequency is broken up into smaller increments called channels.
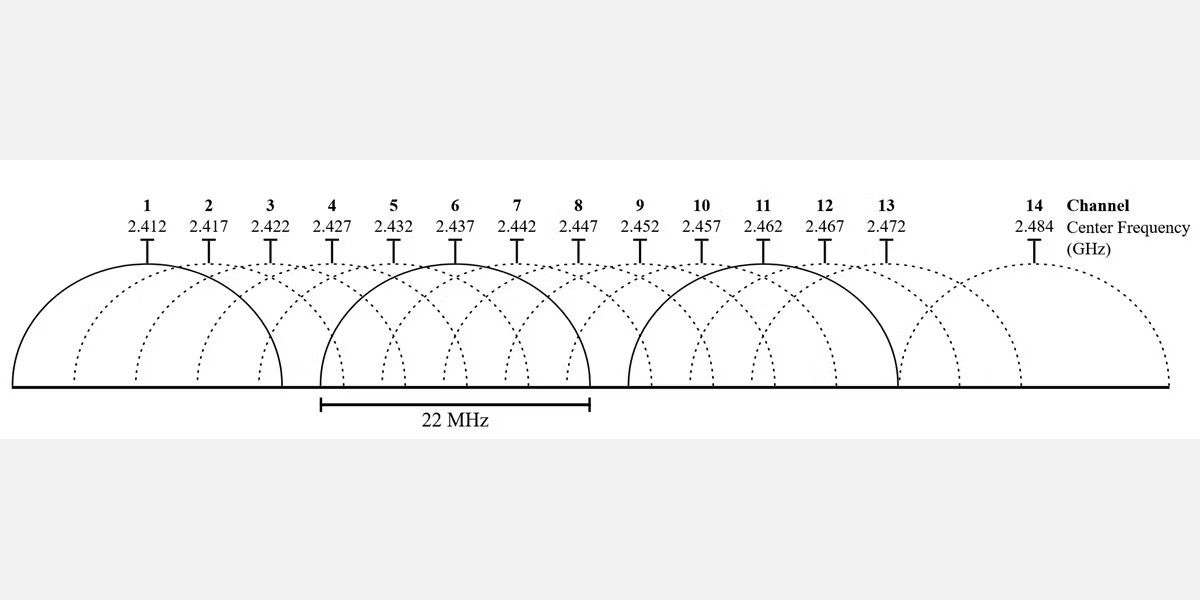
The 2.4GHz frequency suffers from the worst congestion because of its limited number of channels and long range. While 2.4GHz has 11 channels, only three of these are non-overlapping. That means speed and connection quality suffer when there are more routers in the same area.
5GHz, on the other hand, offers 23 non-overlapping channels. It also suffers from a shorter range, meaning fewer overlapping radio signals. It's a lot like AM and FM radio, where the longer-range AM has poorer audio fidelity, and FM sounds great, but it comes at the expense of range.
Fortunately, you can change your router's channel the same way you can change a radio dial. It works like this: identify which channels aren't congested and switch your device over to it. If that doesn't work, consider upgrading your router to a 5GHz or 6GHz model.
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E Routers Offer Excellent Stability
A 6GHz, Wi-Fi 6E model router has distinct advantages over its predecessors. The 6GHz spectrum is new enough that few consumers have access to it. That means it's unlikely to suffer from interference issues. However, if you own a Wi-Fi 6E router, which offers a 6GHz band, it has slightly more channels than Wi-Fi 5. According to the Wi-Fi Alliance's 6E specifications, a 6E router can access 14 "fat" 80Hz channels or seven "super-wide" 160Hz channels. As wider channels are faster, 6E offers both speed and reliability.
3. USB 3.0 Devices and Cables Generate Wireless Interference
Another source of wireless interference is radiation generated by un-shielded USB 3.0 cables and devices. Thanks to a bug in the USB 3.0 standard, which is discussed in an Intel White Paper PDF, some cables emit a very short-range 2.4GHz radiation, trampling over the signals of Bluetooth and 2.4GHz wireless devices. There are several possible fixes:
- Unplug your USB 3.0 devices and check if your wireless signal improves
- Buy shielded cables
- Move your wireless receivers away from USB 3.0 cables and devices using extension cables
- Move USB dongles as far away as possible from antennas or USB transmitters/receivers
Just a note on shielded cables: they have a layer of metal that protects the cable from external wireless interference. But that layer of metal also prevents the cable from functioning as an antenna for 2.4GHz radiation. Aside from cables, a lot of poorly designed dongles and USB devices also emit interference when plugged into a USB 3.0 port. So simply unplugging all your dongles sometimes improves wireless connectivity on the 2.4GHz spectrum.
How to Fix Your Unstable Wi-Fi Connection Using Wi-Fi Analyzer
There are numerous Wi-Fi network analyzers with similar functionality, but we're going to use Wi-Fi Analyzer for this short guide.
1. Download and Install Wi-Fi Analyzer
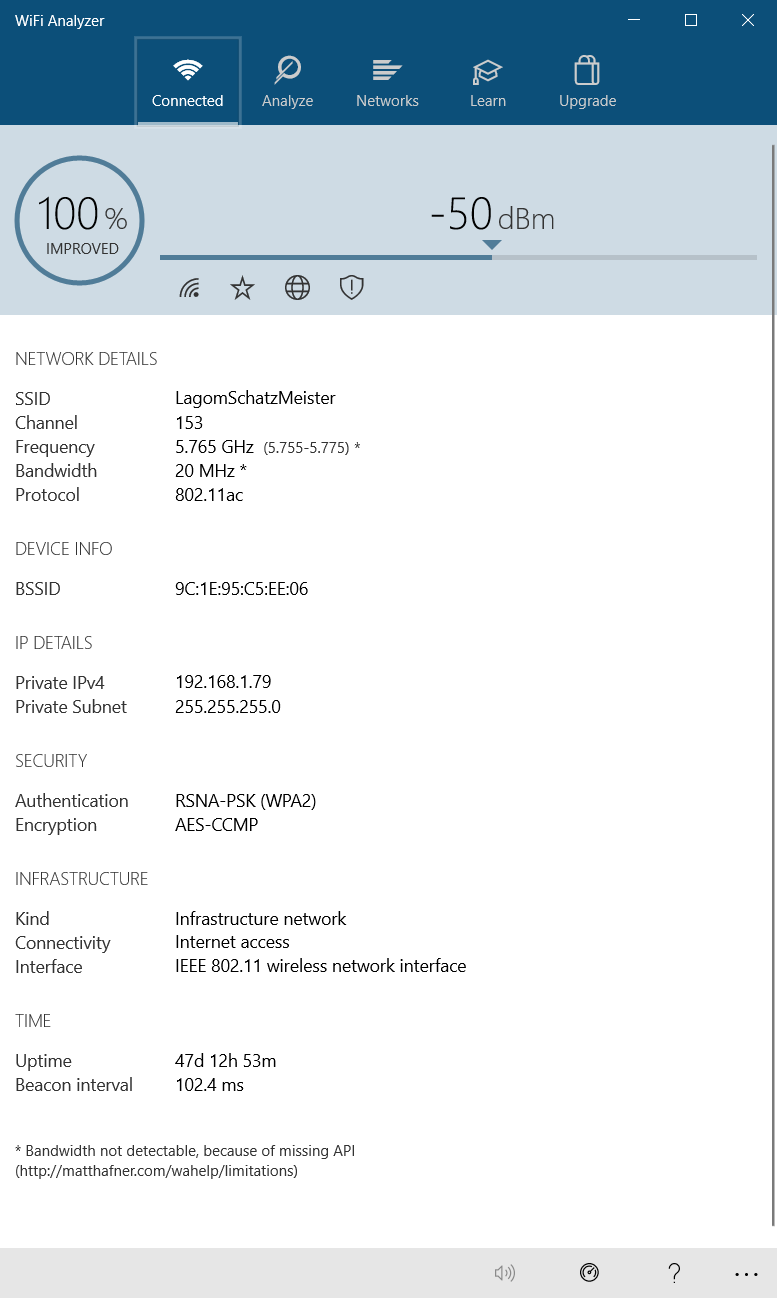
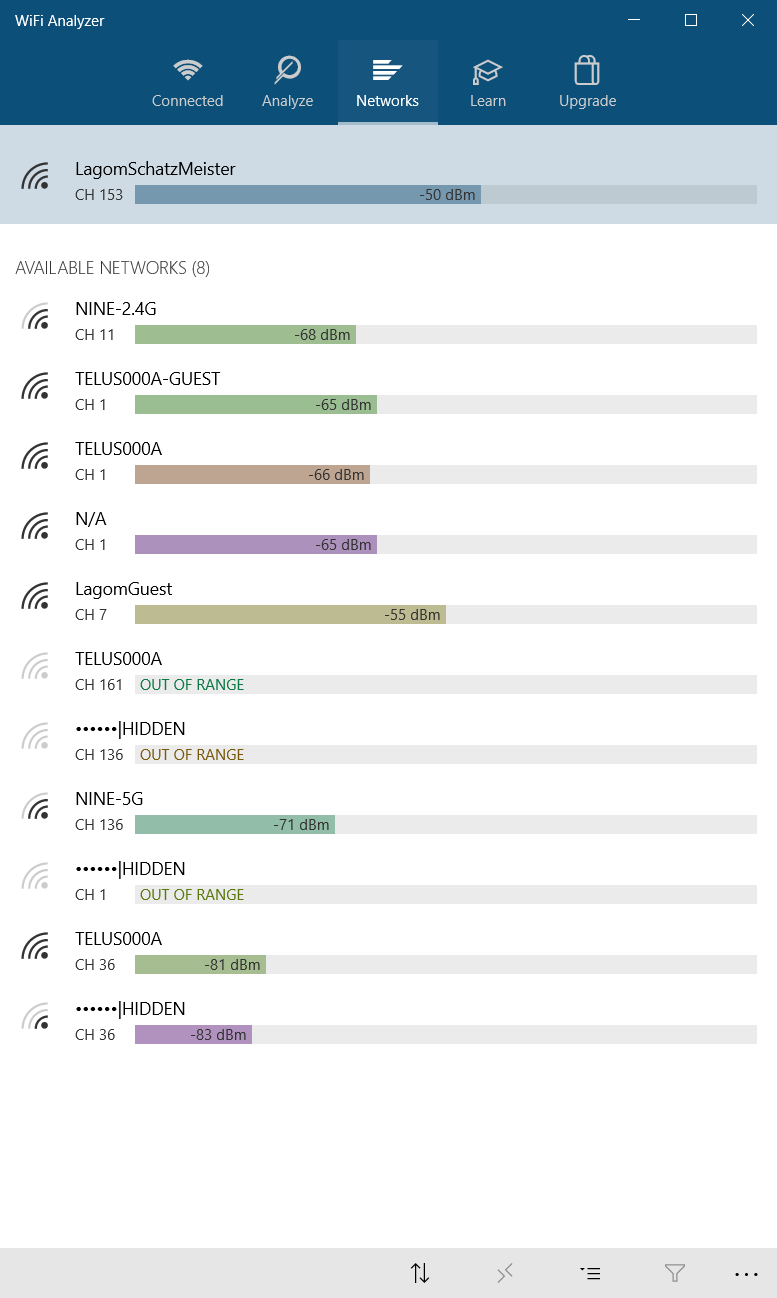
On Windows, many free apps can analyze the quality of wireless channels. One of the best options is Wi-Fi Analyzer, which is available on the Microsoft Store. For those without Windows, search your respective operating system's app store for "Wi-Fi Analyzer," and you'll see dozens of options.
Download: Wi-Fi Analyzer for Windows (Free)
If you have Windows but can't access the Microsoft Store, I recommend NirSoft's WifiInfoView. Both Wi-Fi analysis apps work essentially the same way.
2. Detect Unstable Wi-Fi
Using Wi-Fi Analyzer is dead simple. Just install and run the app. After installation, you can launch it by going to Windows Search (Windows key + S) > Wi-Fi Analyzer.
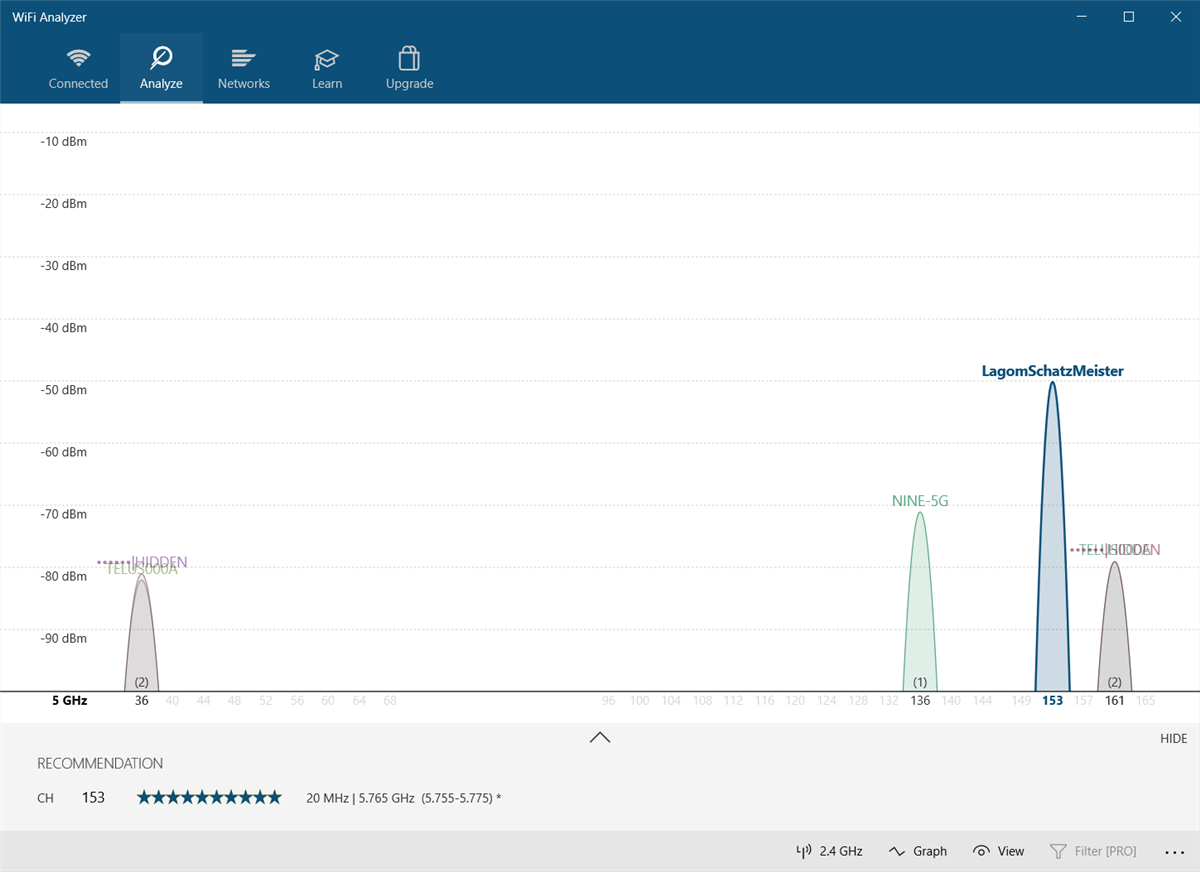
The tool should detect your Wi-Fi signal strength, ranging from zero to -100 decibel milliwatts (dBm). If you have a 5GHz network, a toggle at the bottom of the app interface allows you to switch between detecting 2.4GHz and 5GHz.
To analyze your wireless router's signal quality, take the following actions:
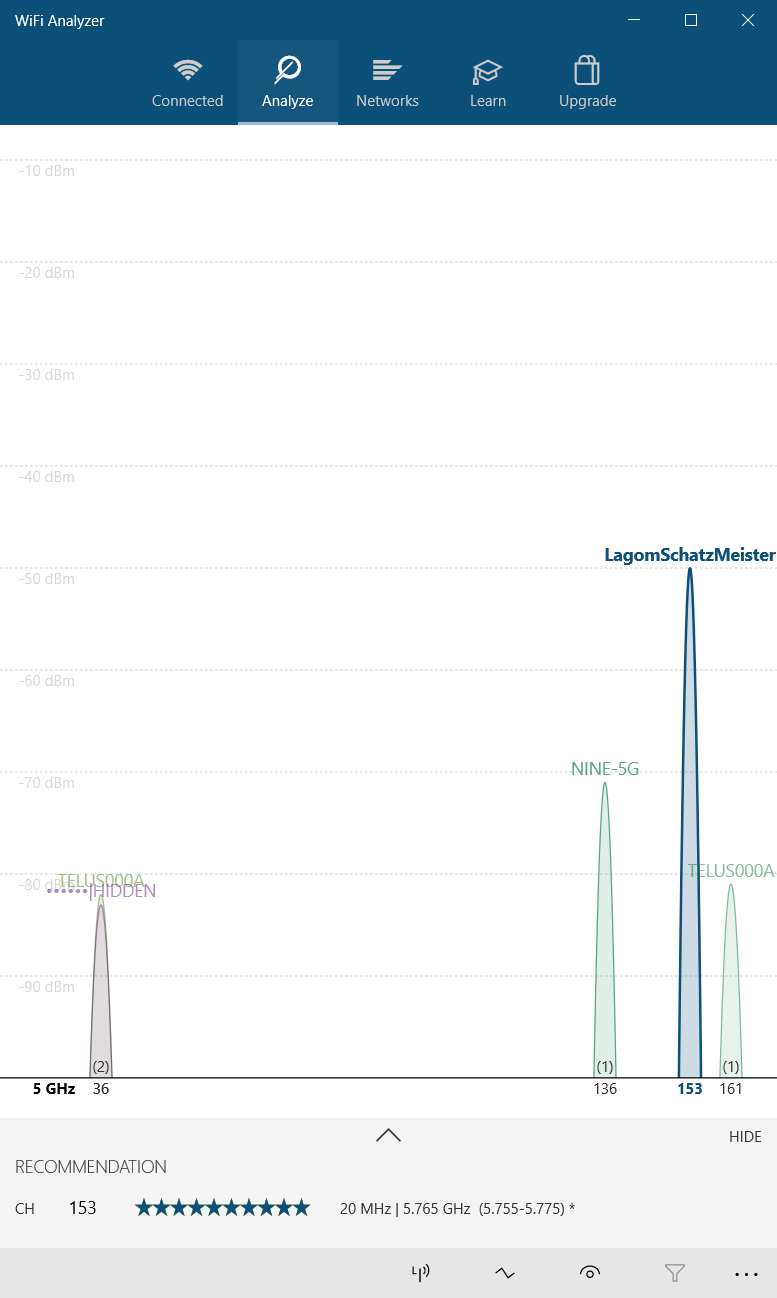
Click on Analyze in the top menu bar.
Wi-Fi Analyzer then displays a visualization of the Wi-Fi networks in your vicinity. If two networks broadcast on the same channel, you'll notice overlap. Each channel has a number between one and 161 on the 5GHz frequency and one through 11 on the 2.4GHz frequency.
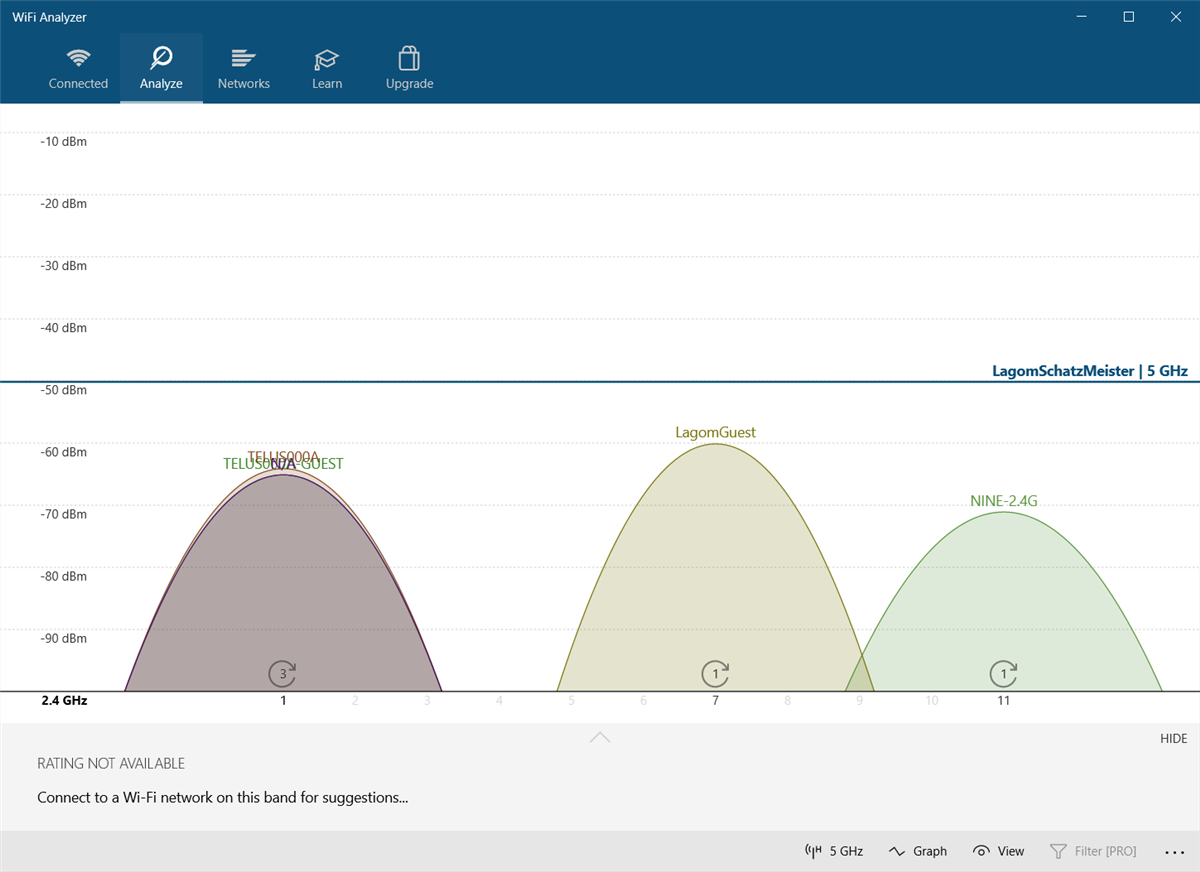
Here's what it looks like when two networks overlap:
The X-axis represents the channels available on the 2.4GHz spectrum. As you can see, channels four to seven are unoccupied. Channels five and six have no competition whatsoever. Given the app's analysis, I should change my router's 2.4GHz channel to either five or six.
But how do you change your router's channel?
3. How to Change Your Router's Channel
Accessing your router's settings requires a browser like Chrome or Microsoft Edge. Accessing its settings, unfortunately, varies between different router models, but some general rules apply.
- Netgear routers: In your browser, navigate to https://routerlogin.net
- TP-Link routers: In your browser, navigate to https://tplinklogin.net
- Linksys routers: In your browser, navigate to 192.168.1.1.
You can complete an internet search to find the login URL for your specific router brand and model.
Most routers use "admin" as the login and "password" as the password. The login details may also be printed on the back of the router or in the instruction manual that came with it. If you cannot access your router, try searching the internet for your individual router's access method.
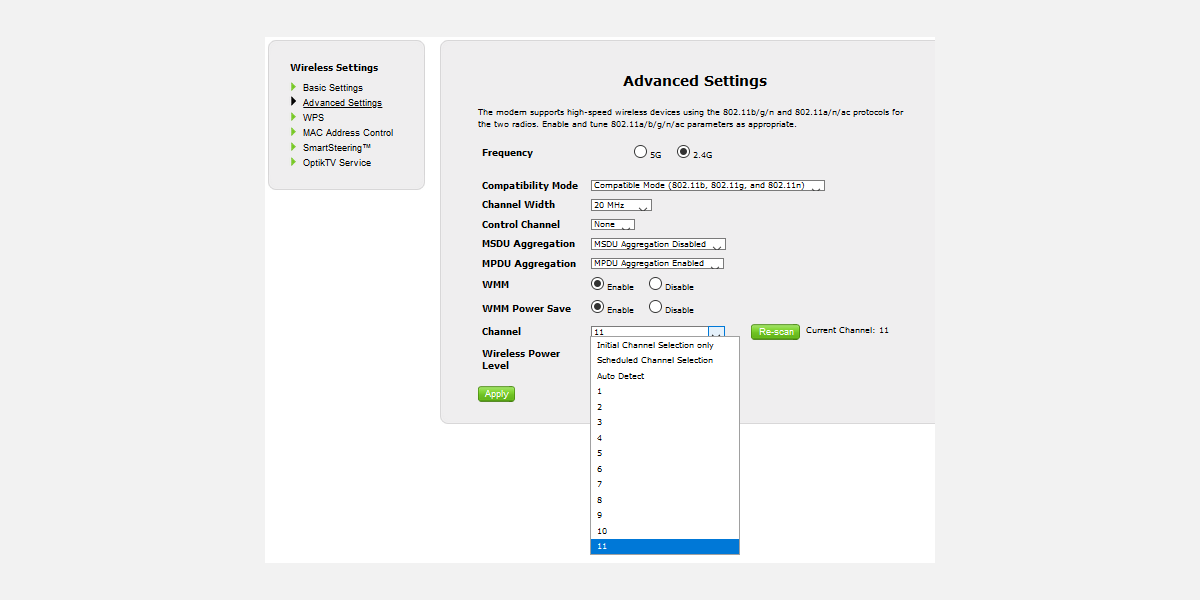
For my own Telus router, changing the Wi-Fi channel is easy. First, I navigate to the router login address and enter my login and password. Changing the channel is usually located under Wireless Settings > Advanced Settings.
I then change the network channel to the option which offers a good connection, save the settings, and restart the router by power cycling it (turning it off and on again). Afterward, it stopped randomly disconnecting.
One thing to mention is that most modern routers include a dual-band feature that combines 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies onto a single network name or SSID. This feature is notoriously unreliable, and if you're having network problems, I suggest disabling it if nothing else works. On a Telus router, it's referred to as SmartSteering. Other brands have completely different names.
Once disabled, you'll see your 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands as separate networks.
Why Is My Network Unstable? How to Fix Unstable Wi-Fi
If your Wi-Fi sucks, a Wi-Fi analysis app is the best way to find out your router's ideal network channel settings. If you're still getting unreliable internet after changing your router's channel, consider looking into the USB 3.0 bug. But if all your attempts to fix the issue fail, the best solution is to upgrade your router to Wi-Fi 6 or 6E model, but only if your devices support it.
It's worth noting that Wi-Fi 6 routers sometimes offer a wider range of channels, compared to older Wi-Fi 5 routers. As such, an upgrade of your network hardware can clean up a lot of problems that channel tweaks cannot.