We’ve seen on repeated occasions over the past few years that Android is vulnerable to a host of hacking techniques that would previously only have been possible on desktop PCs running Windows.
Most of these vulnerabilities come via the app store, Google Play, and with the news in August 2016 that over 100 apps are carrying the same Trojan horse payload, it’s time to take a look at how you can avoid accidentally downloading such malware to your own device.
The Trojan That Spies
Trojan horse malware, by definition, offers a hidden and inconspicuous avenue for hackers to gain access to your data, system, or both. Typically they offer some kind of backdoor to everything.
In the case of the Android.Spy.277.origin Trojan, installation of an infected app results in the Trojan stealing "...confidential information and delivers advertisements. It is distributed via bogus versions of popular Android applications on the Google Play store."
Not something you would want to happen to you.
A grand total of 104 apps were affected, and the Trojan is believed to have been downloaded by at least 3.2 million users. Once installed, 30 unique pieces of identifiable data are collected by the Trojan -- including your device IMEI -- which are then forwarded to a server that's under the control of the attacker.
If you were victim to such an attack, it wouldn't take long for that information to be used against you, resulting in empty bank accounts, maxed out credit cards, or worse.
Burn Down the Trojans
In the past we’ve had Trojans for Android that were linked to the online porn industry and other seedy attempts to divert the attention of potential targets. We’re now at a stage where it's clear that security software is a necessity for Android as it is for Windows.
But is there anything else you can do?
In other words, how can you avoid installing Trojans onto your Android device? It’s difficult, but by changing your habits when installing apps on the Android Play Store, you can reduce your likelihood of installing a Trojan, or any other Android malware.
Stick to Well-Known Apps & Respected Developers
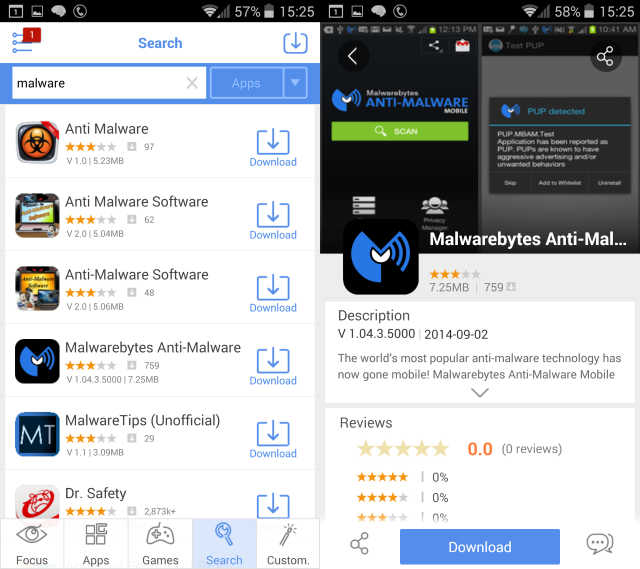
When you're browsing Google Play for apps, you need to take the time to check the name of the developer. You'll find this just below the name of the app, and in many cases you'll find a link to their website. Also, look for other apps from the same developer.
Tens of thousands (if not more) of said developers provide apps for Android devices, but only a very small portion of these are recognizable names. You'll need to spend a bit of time looking at the other apps they've released and even take a few moments Googling for potential horror stories.
If you've failed to turn anything up after five minutes or so of searching, you can be pretty confident that this is a reputable developer (or at the very least isn't a disreputable developer). That doesn't mean you should stop there, however...
Read the App Reviews
Every app and game on Google Play has reviews. So if you read the reviews, you'll get an idea as to whether the software -- and by extension, the developer -- is trustworthy or not.
Look for bad comments, and also replies to see how the developer responds to complaints. Do they do so in a competent, friendly manner? Do comments suggest that something is amiss, that the app or game is behaving in a way that suggests suspicious activity?
Spending a few moments to find out more about who you're doing business with is always wise.
Check and Understand the Permissions
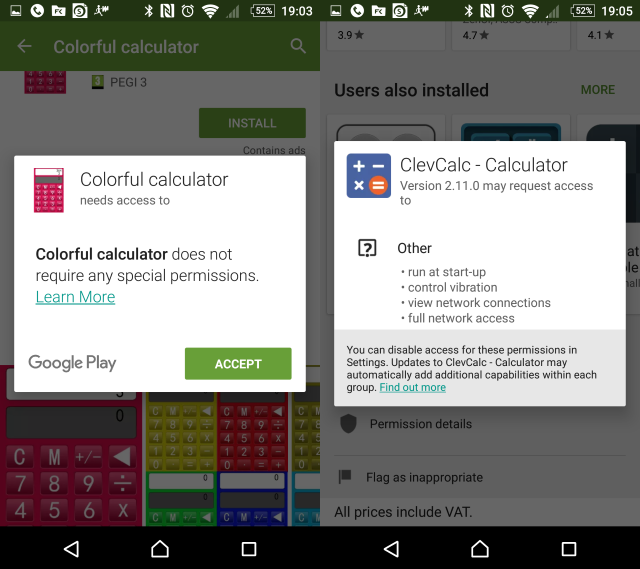
When you install software on your Android phone or tablet, you're always advised of the permissions that the app or game will require. When these don't square with the purpose of the app, you've possibly hit upon a potential for misuse.
If you've already read the reviews and checked out the developer's reputation and found something amiss, then you shouldn't have reached this stage. But if you suddenly find that a calculator app requests network access, then that should be a red flag.
So check the permissions, understand what is being requested, and if it doesn't meet with your expectations for the app, don't install. You'll find a list of Permission Details via a link at the bottom of the app's Google Play listing.
Avoid Third-Party App Stores
If you're using a Kindle Fire tablet, you use the Amazon App Store. If you're using an iPhone or iPad, you get your apps and games from the App Store. Similarly, with standard Android devices, you should use Google Play.
Official app stores like these are relatively safe because they have systems for weeding out the malware-ridden apps, but it can take time.
While it is possible to install apps from third-party app stores (using the Unknown Sources security setting), it's rarely a good idea. First of all, everything you need is available in Google Play. If you're looking for an app that is not available from Play, then there's likely a very good reason for that.
So the rule here is to only install apps from the app store that comes with your mobile OS. Used in conjunction with the above concepts, you should find it easy to avoid Trojans and other malware on your Android device.
Block Malware with Security Software
Even if you're up to speed with the risks from malicious software on Android, there is another thing that you can do, and that is install security software on your device. Antivirus and firewall tools are available Android phones and tablets (and other devices, like set-top boxes) and are well worth your time.
Our guide to Android security apps provides you with a good choice, and these will block malware, scan apps, and more.
The mobile app market is now wholly confirmed as a target for hackers and online scammers. There’s no reason why you shouldn’t already be running security software, but this should be used in conjunction with the other suggestions, not as a single alternative.
Have you been struck by Android malware? Tell us about what happened to you in the comments below.
Image Credit: Giovanni Domenico Tiepolo via Wikimedia Commons