Overclocking your graphics card to squeeze out extra performance is an exhilarating experience. However, running your hardware harder and hotter is a risky proposition given the ongoing shortages and exorbitant prices.
Chances are, you probably want to prolong your graphics card’s life by running it cooler. What if there’s a way to do that without losing much (or any) of the stock performance? This is entirely possible through GPU undervolting, and it’s a surprisingly easy process.
Here’s how you can run your graphics card cooler and prolong its life through GPU undervolting.
What Is GPU Undervolting?
At the heart of your graphics card lies at least one GPU, which renders images by rapidly switching billions of transistors on and off. Each operation consumes some amount of power, and most of it is dissipated as heat. Therefore, the performance of a GPU is limited by the maximum power and heat it can handle without damaging itself.
Give your GPU a light task, and it will sip a small amount of power. But running a ray-traced game at “Ultra” settings will cause it to guzzle power to the tune of hundreds of watts. Most of this electrical energy is then dissipated as heat. However, pumping more than 200 watts during a typical gaming session taxes the graphics card’s power delivery subsystem.
The resulting heat dissipation also takes the GPU silicon substrate beyond 87°C (or 189°F). A typical graphics card has inbuilt protections to prevent electrical and thermal overload, but running it at the limit day in and day out takes a toll on its lifespan.
This might even send your graphics card to an early grave.
GPU undervolting, however, reduces the total power drawn and heat generated during high load applications such as gaming. This is especially important for small form factor (SFF) computers, where the lack of space and ventilation results in sub-optimal cooling. Gaming laptops and SFF PCs are particularly susceptible to damage occurring from sustained overheating.
What Does GPU Undervolting Do?
GPU undervolting primarily reduces the maximum load temperature by cutting back on the total power consumption. GPU power draw can be lowered by reducing either the voltage or current supply. It’s smarter to reduce voltage because every semiconductor device is designed to operate within a maximum and minimum voltage range.
Exceeding this voltage range can permanently damage the component, whereas insufficient voltage leads to temporary issues such as visual artifacts and system instability. As the quality of silicon varies between production batches, manufacturers tend to use a preset voltage that is high enough to account for variance in chip quality.
In theory, carefully reducing supply voltage can reduce GPU power draw and temperature under load without affecting performance. Doing so involves incrementally decreasing the GPU voltage just until the threshold of system instability.
The idea is to find the goldilocks zone where the GPU is supplied with just the right amount of power to perform optimally without generating excessive heat and fan noise.
How to Undervolt a GPU With MSI Afterburner
Unlike CPU overclocking, which involves tinkering with the system BIOS, GPU undervolting is a simple affair that can be done within minutes from the safety of your operating system. This guide will use the MSI Afterburner utility to undervolt the GPU. Be sure to download the latest version.
You will also need a stable benchmarking tool to give you reliable initial GPU parameters to fine-tune the supply voltage. Usually, any GPU benchmark will work, but we recommend UNIGINE’s Heaven Benchmark because it can run in windowed mode without crashing.
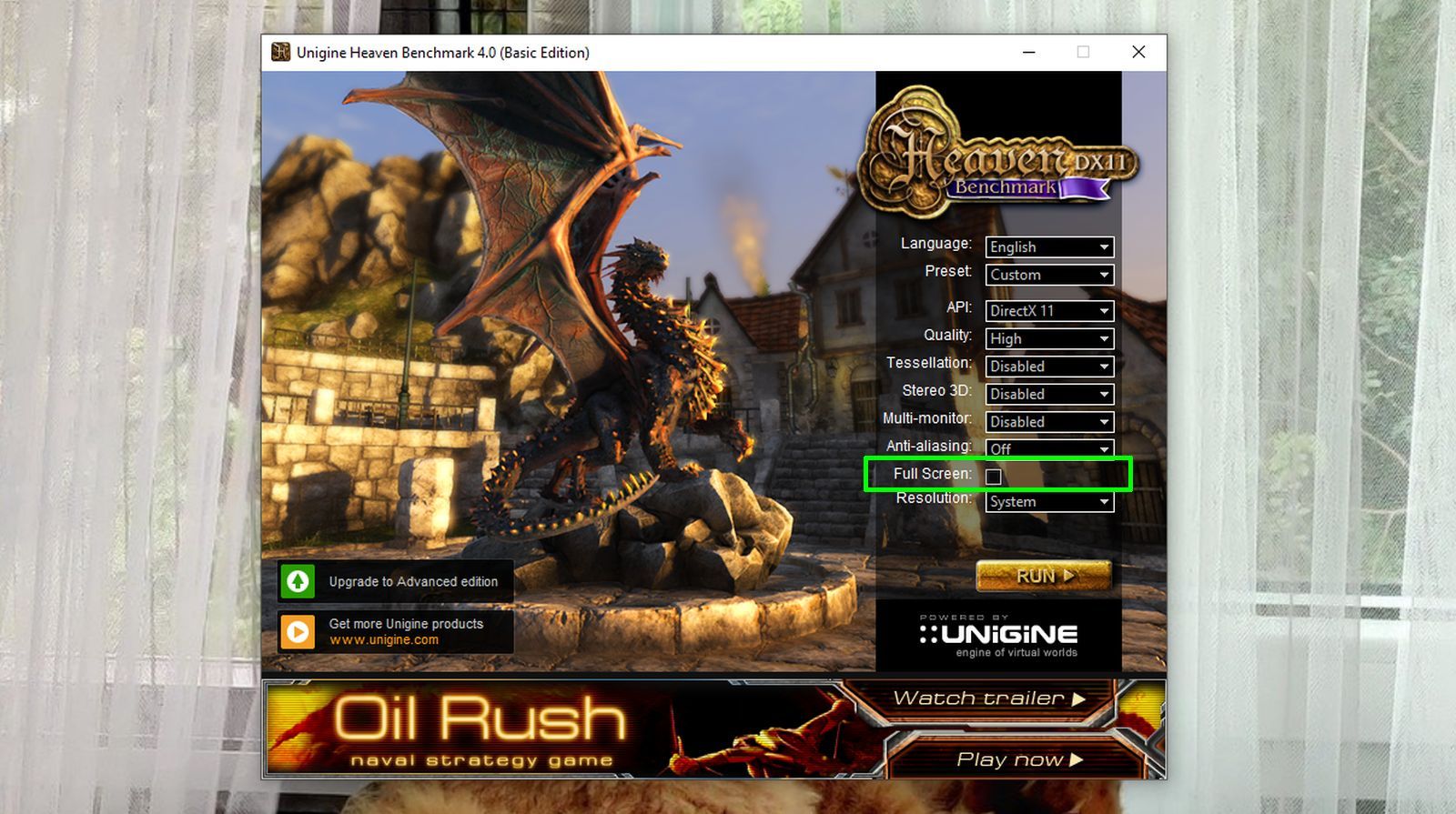
After downloading and installing Heaven Benchmark, it is important to deselect the Fullscreen option from the Settings menu because we will be using the MSI Afterburner utility in conjunction with the benchmark. Running it in the windowed mode makes it easy to tweak GPU settings simultaneously.
Step 1: Fire Up the Heaven Benchmark
Run the benchmark with the default settings in the windowed mode. This allows the GPU to hit its maximum stable core clock speed during graphics-intensive applications such as gaming.
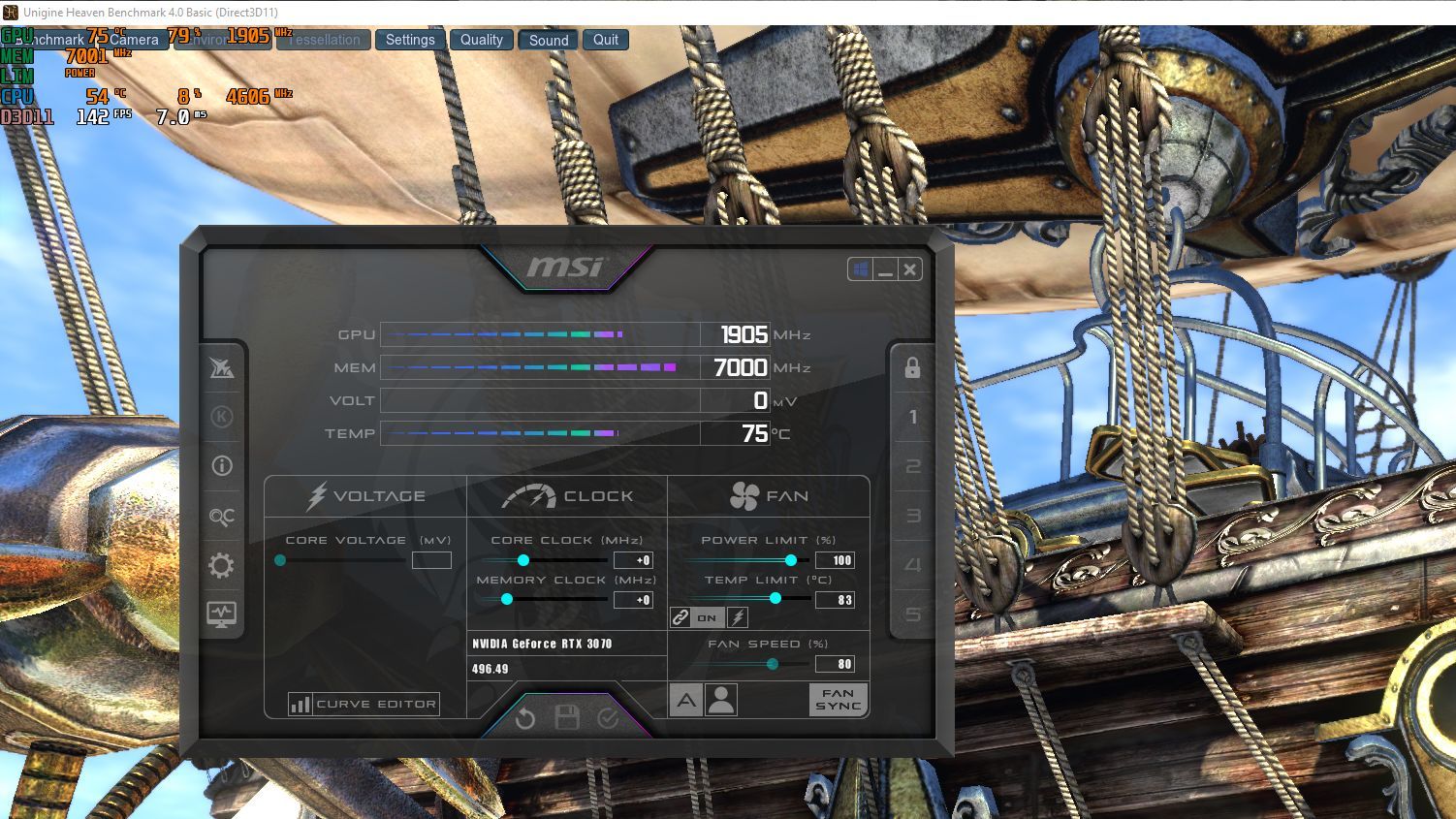
Step 2: Launch MSI Afterburner Utility
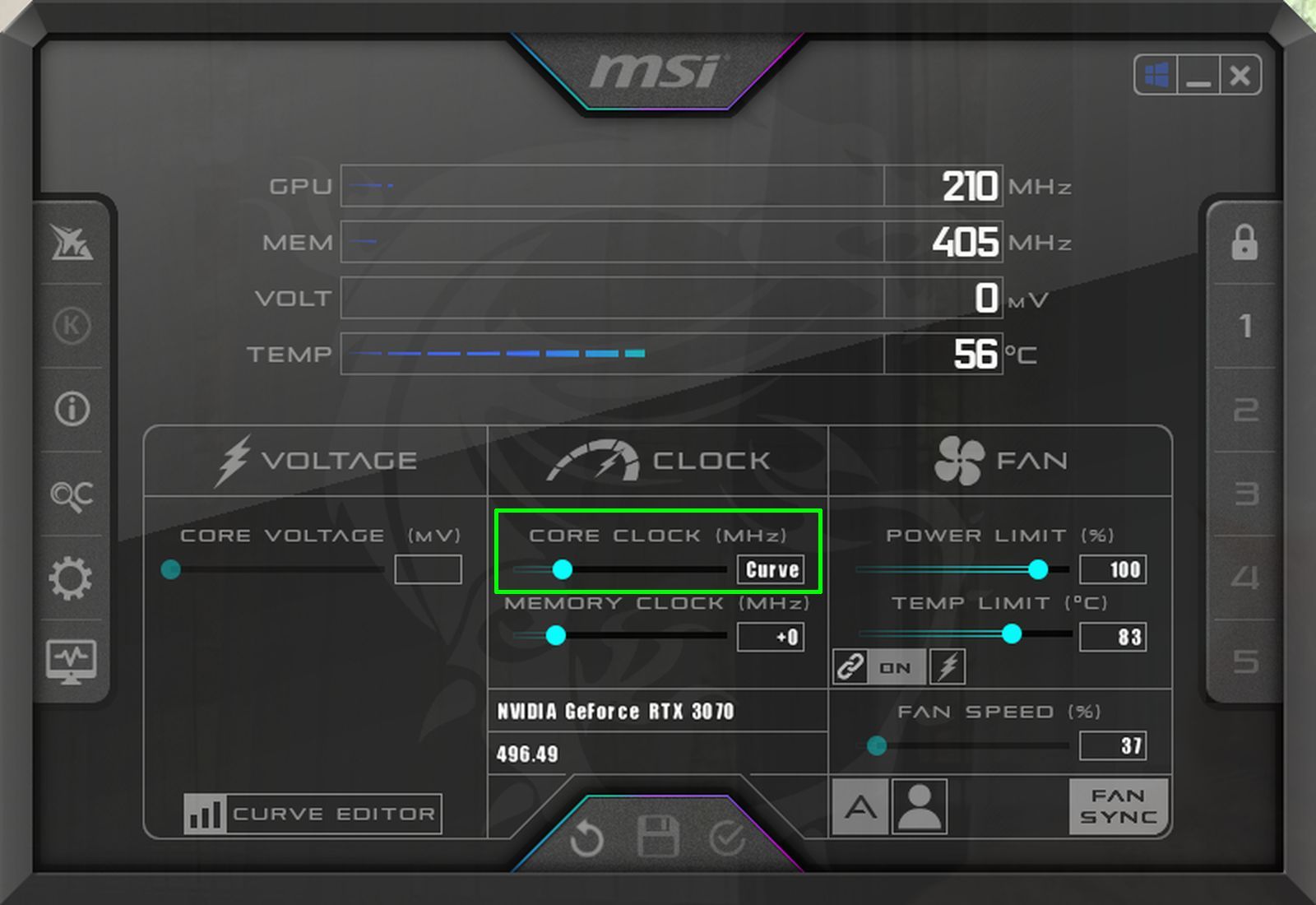
Run the MSI Afterburner GPU overclocking utility and pay attention to the GPU clock speed readout right at the top. In our case, the NVIDIA RTX 3070 settled in at a core clock speed of 1905MHz. Make a note of the clock speed that your GPU settles at after 10 to 15 minutes of operation.
You’ll need this value later.
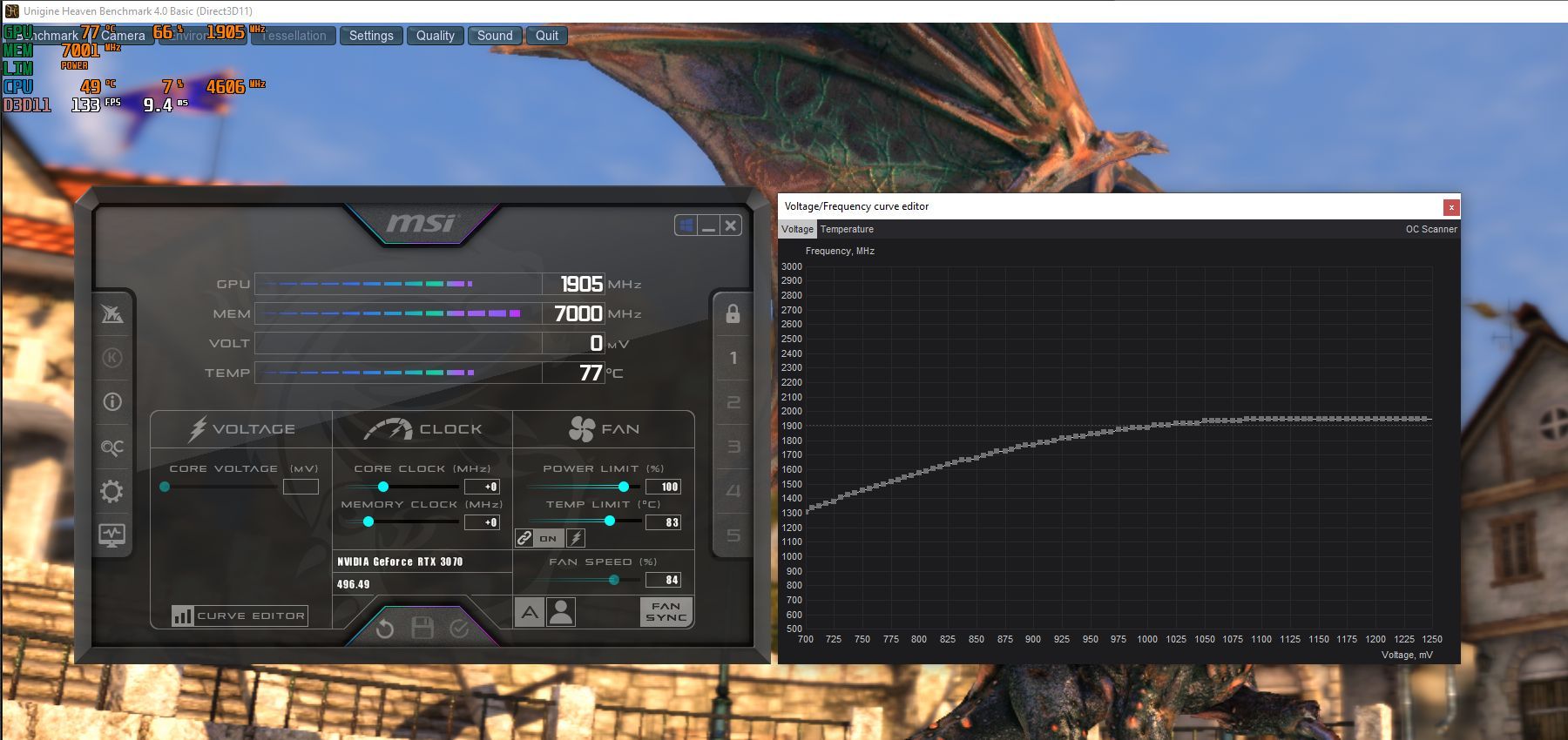
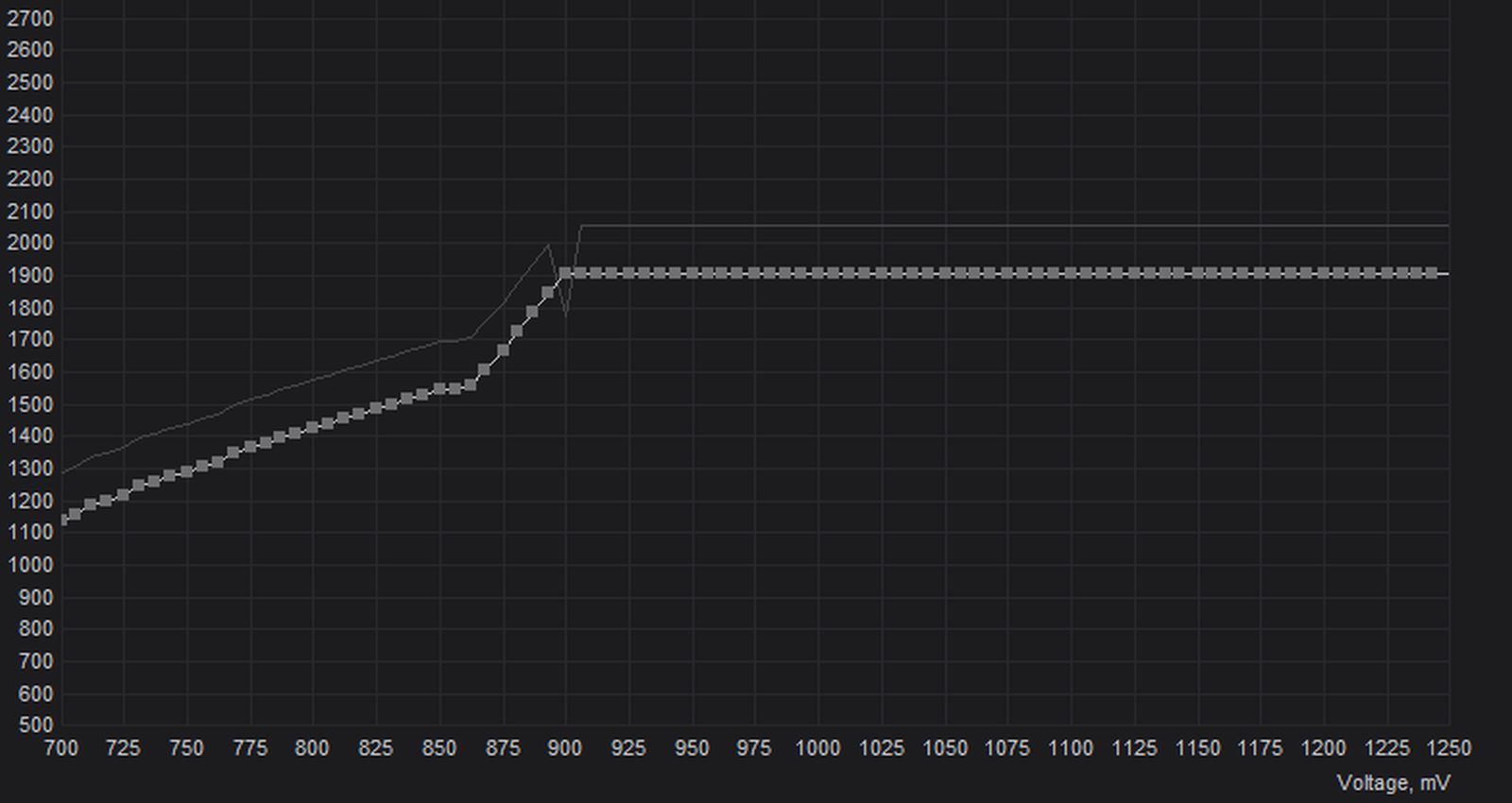
Step 3: Analyze the Voltage/Frequency Curve
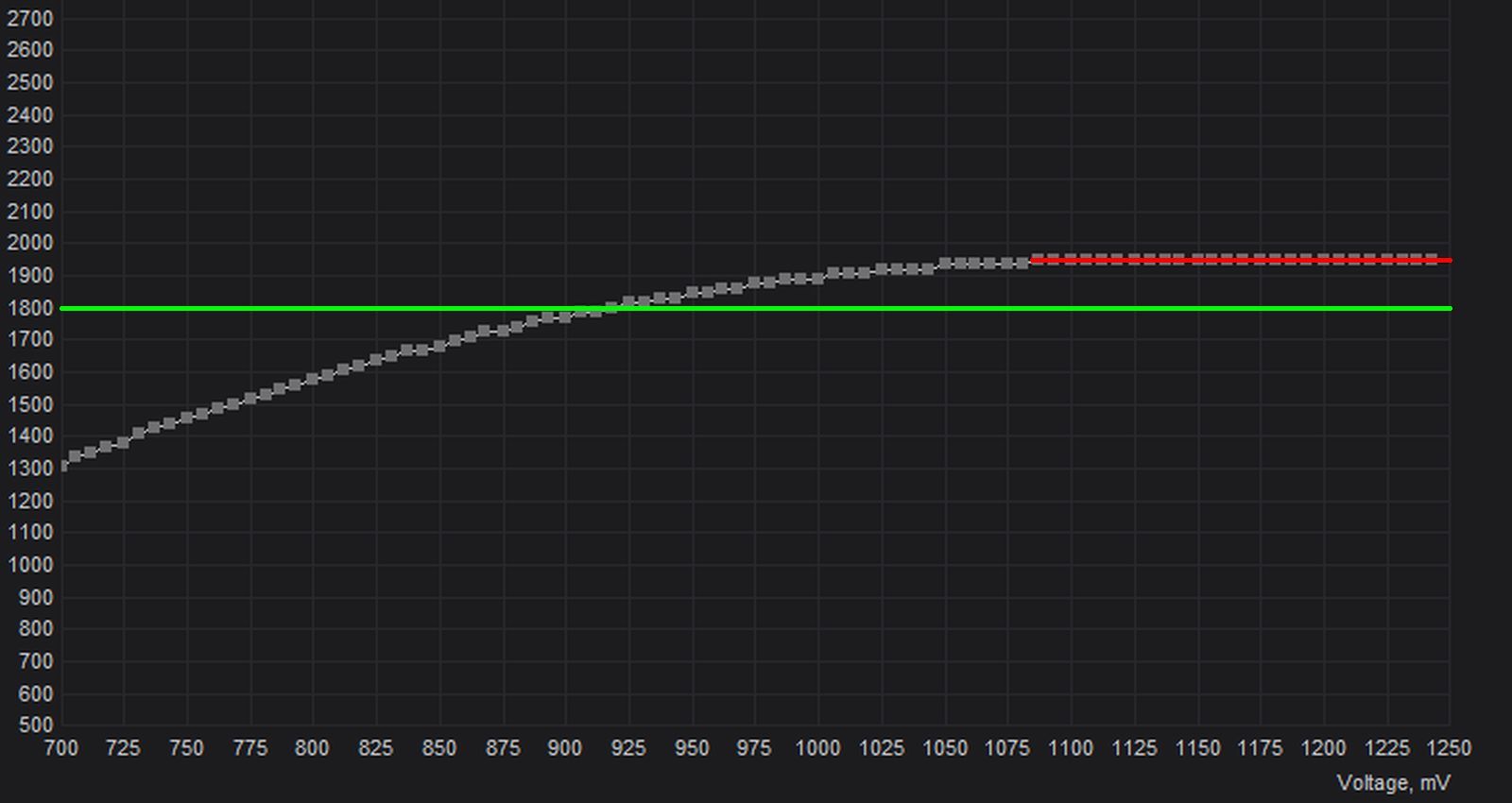
Press CTRL + F to bring up the Curve Editor in the MSI Afterburner utility. Make a note of the GPU core clock frequency (vertical or Y-axis values) where the curve terminates at the right-hand side of the screen. This has been highlighted in red in the adjoining screenshot.
In our case, the curve maxes out at approximately 1950MHz between voltages ranging from 1150mV to 1250mV. The frequency sweet spot for most modern NVIDIA GPUs lies around 1800MHz. Our goal is to modify the frequency/voltage curve to max out at 1800MHz, as represented by the green line.
Simply put, you have to figure out the difference in frequencies represented by the red and green lines. In our case, we must bring the curve down from 1950Mhz to 1800Mhz, a difference of 150MHz. Make a note of this calculated value.
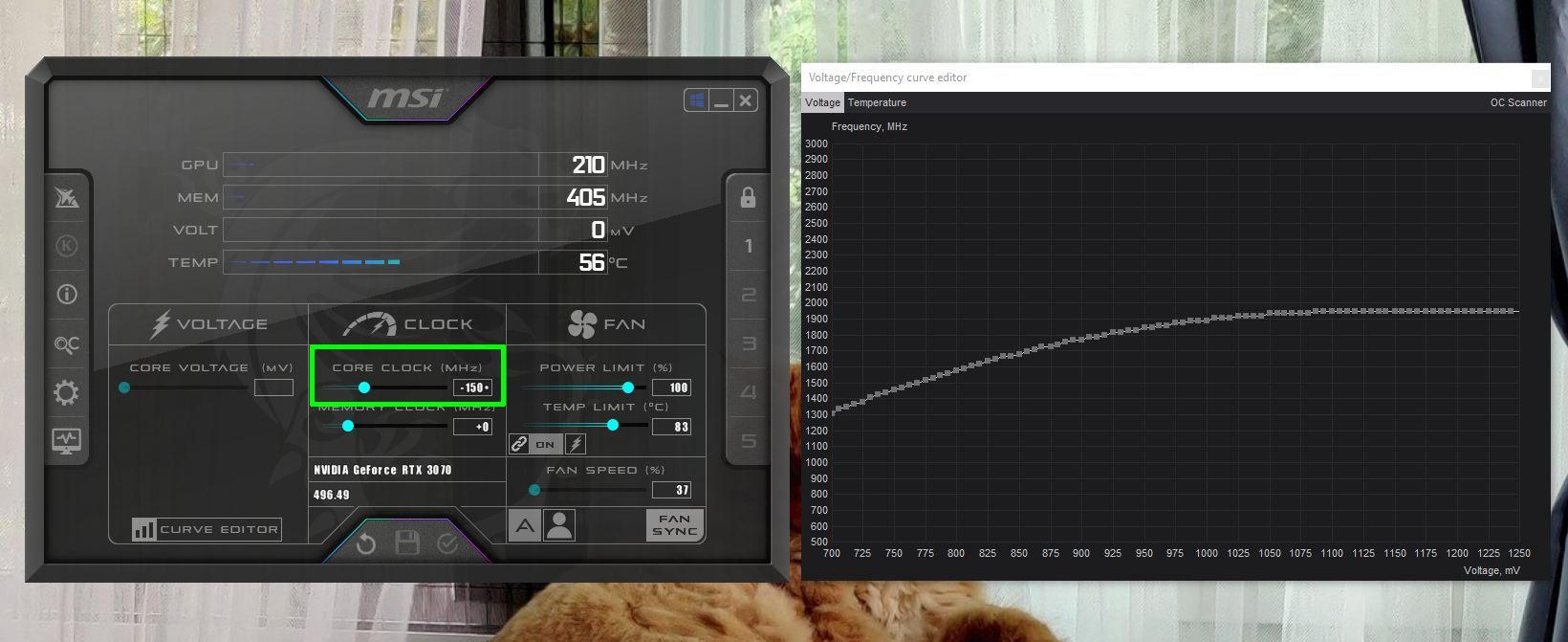
Step 4: Reduce GPU Core Clock Speed by the Calculated Value
Enter this calculated value in the Core Clock section within the main MSI Afterburner utility and hit the Enter key. This should drop the GPU core clock frequency curve to the desired frequency range of 1800MHz.
Step 5: Set Max GPU Voltage Threshold
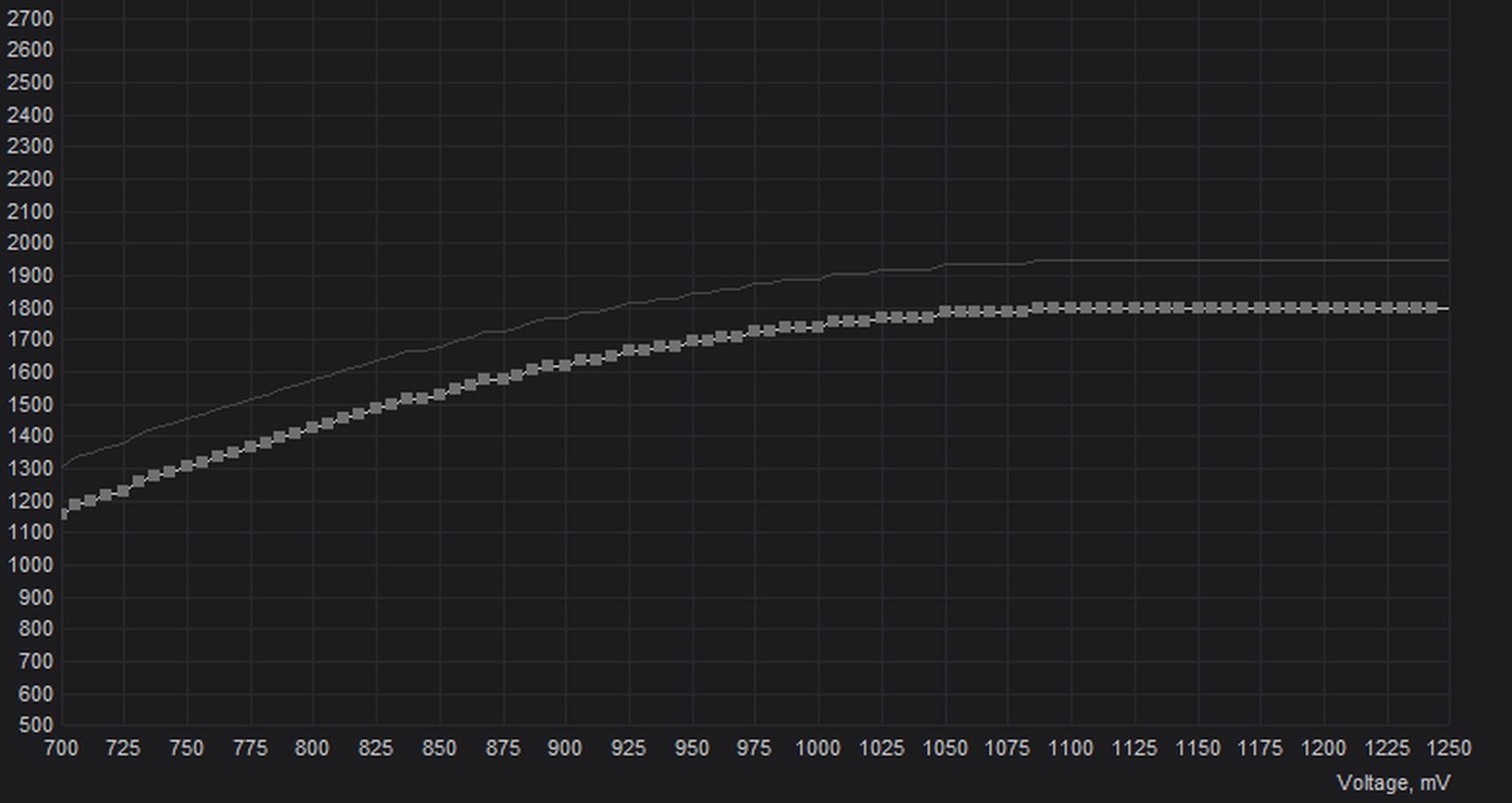
Our goal here is to reduce GPU voltage without compromising on system stability. The adjoining graph shows how our NVIDIA RTX 3070 maxes out at 1085mV. Depending on the quality of the silicon on your graphics card, you should easily be able to run it at a significantly lower voltage without any issues.
It’s smarter to start at a conservative voltage of 950mV for your first attempt and check the system for stability before optimizing the GPU operational voltage further. We chose to set the ball rolling by reducing GPU voltage to 900mV.
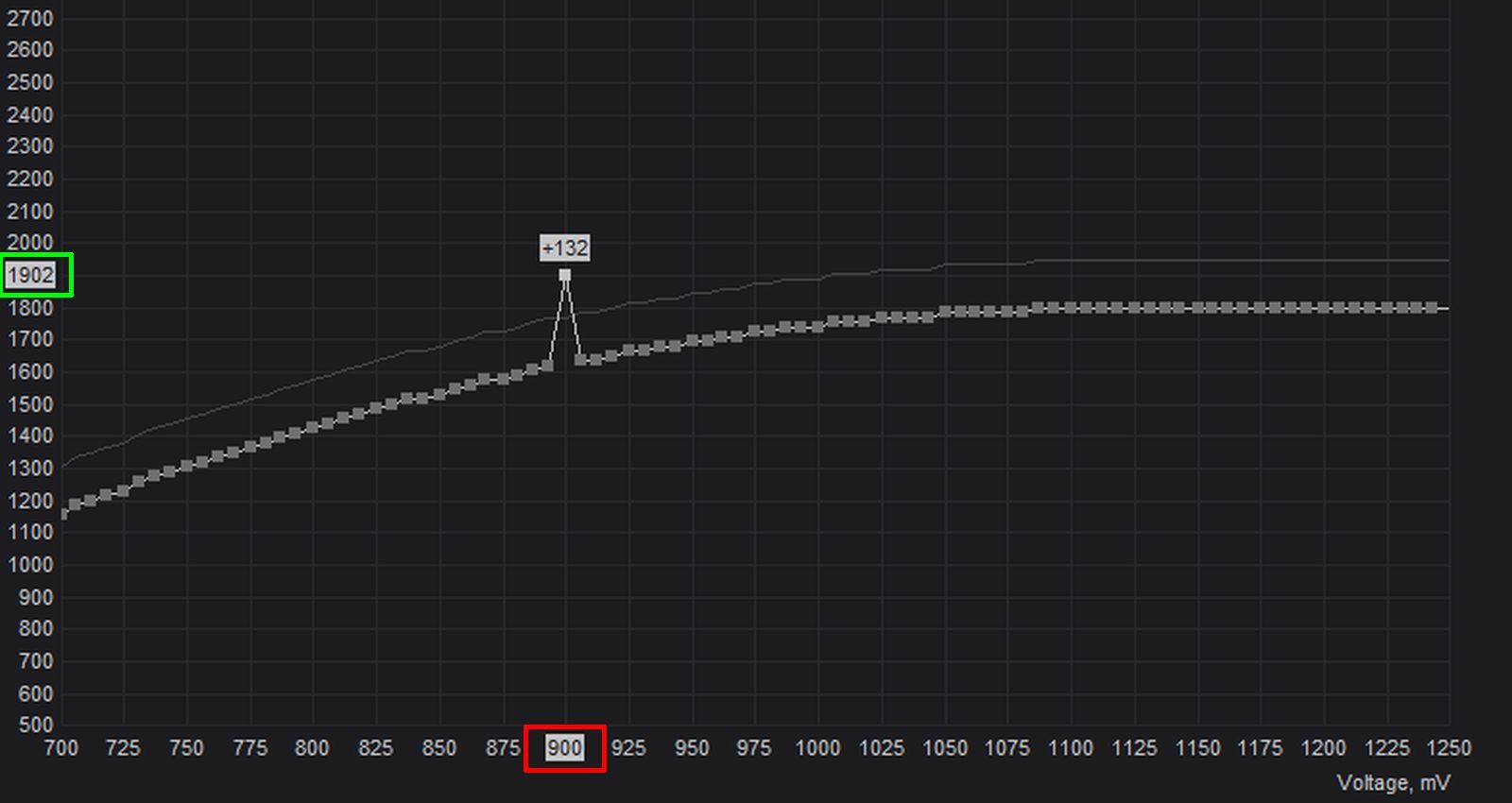
Doing that involves clicking on the square point corresponding to the 900mV reading (marked in red) along the (horizontal) X-axis. Now drag the point upwards along the Y-axis until you are close to the GPU core clock frequency value (marked in green) we had noted in Step 2.
It’s a good idea to go a notch or two below the target frequency to benefit system stability.
Step 6: Apply the New Voltage Curve
Click on the check mark button in the main MSI Afterburner utility window to apply the new voltage curve. This will cause the frequency/voltage curve to go flat beyond the 900mV mark.
You can also verify this by showing the Curve readout instead of the GPU clock frequency offset (highlighted in green).
Step 7: Testing GPU for Stability
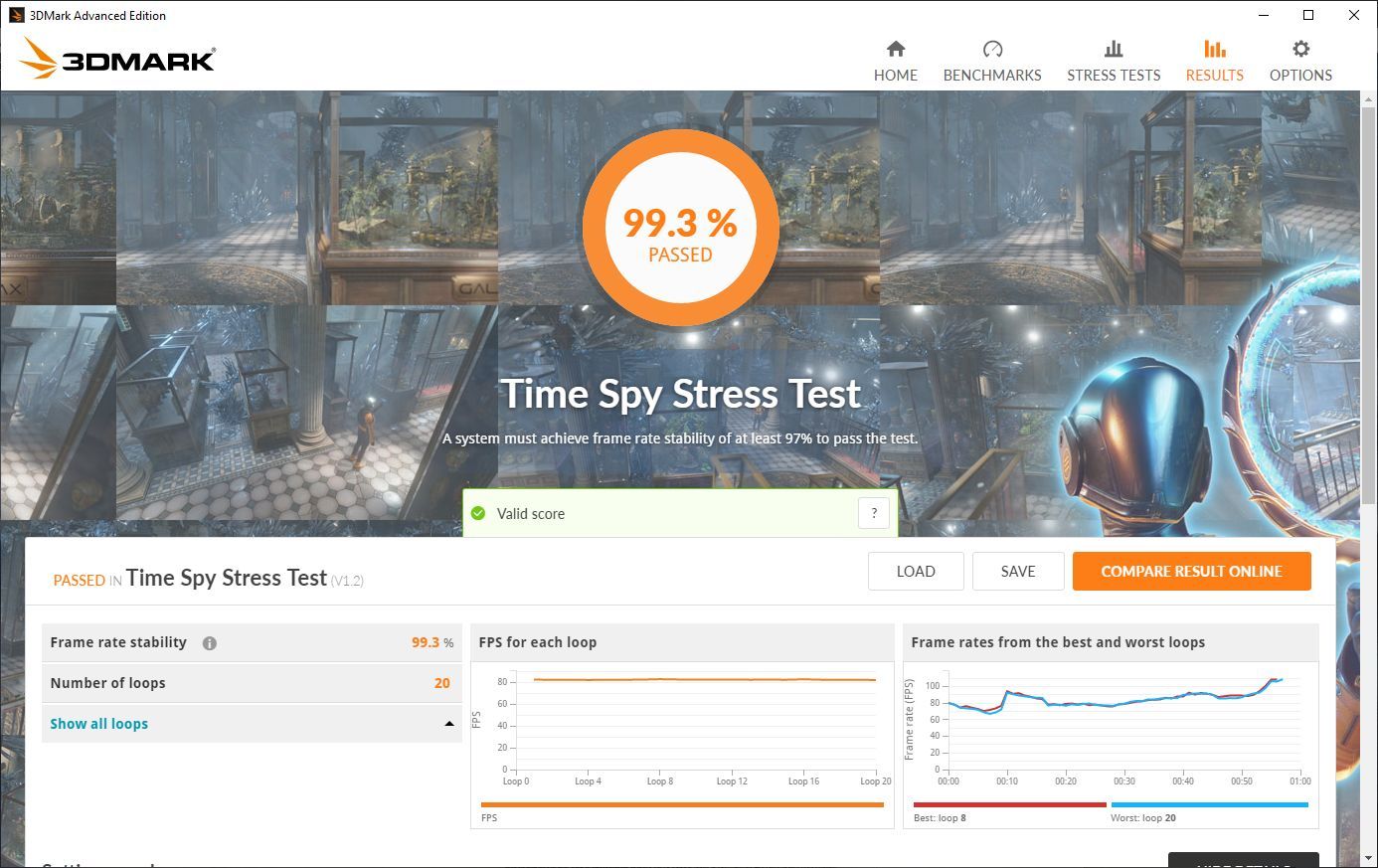
The best way to validate the GPU undervolt is to run a graphics card-specific stress test with a low tolerance for system instability. The 3D Mark Time Spy Extreme benchmark is ideal for this purpose. Choose the Time Spy Extreme Stress Test option and watch out for graphical glitches while it runs.
The Time Spy stress test will also provide a frame rate stability metric at the end. You want to score at least 97 percent.
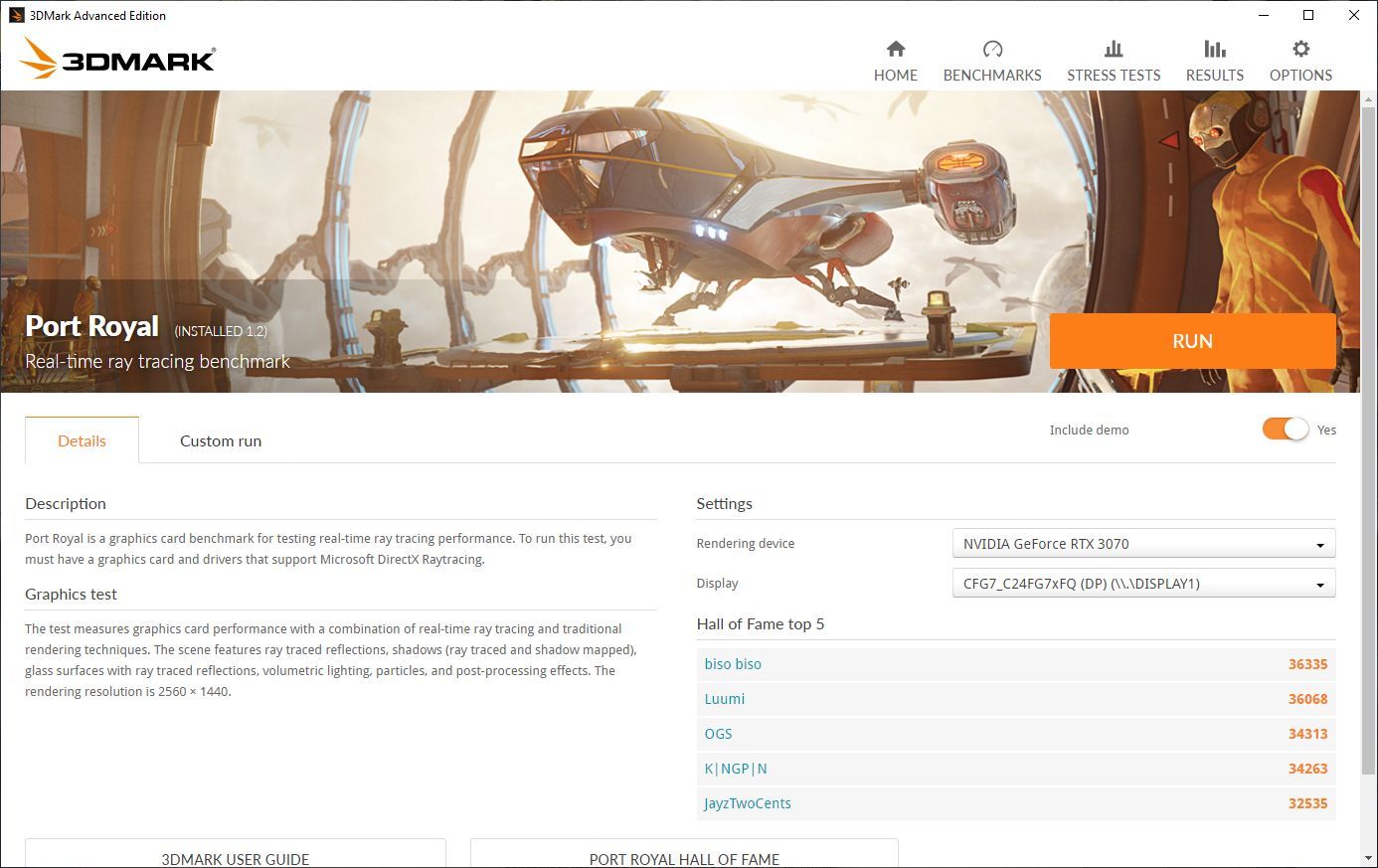
If you own a modern GPU capable of ray tracing, you might additionally want to run the 3D Mark Port Royal stress test. It is optimized to push the ray tracing ASIC cores to their limits and, therefore, an important tool for GPUs outfitted with ray-tracing capabilities.
If your GPU is starved for voltage, this will either manifest as graphical issues or cause the benchmark to error out. Your operating system might crash in the worst-case scenario, but the lack of voltage won’t harm your hardware.
If you experience such issues, repeat Step 5 while increasing the voltage value by 25mV. For example, we would increase our GPU voltage to 925mV if 900mV caused system instability or graphical issues.
Step 7: Reduce GPU Voltage Further
Alternatively, if your GPU can handle 900mV with ease, you might want to repeat Step 5 with the GPU voltage set to 875mV, followed by another round of stress testing. Once you find the point of failure for your GPU, revert to the last stable (or second to last, to be safe) voltage and follow it up with extensive testing with demanding games.
Run your favorite games for a couple of hours, at least before validating these settings.
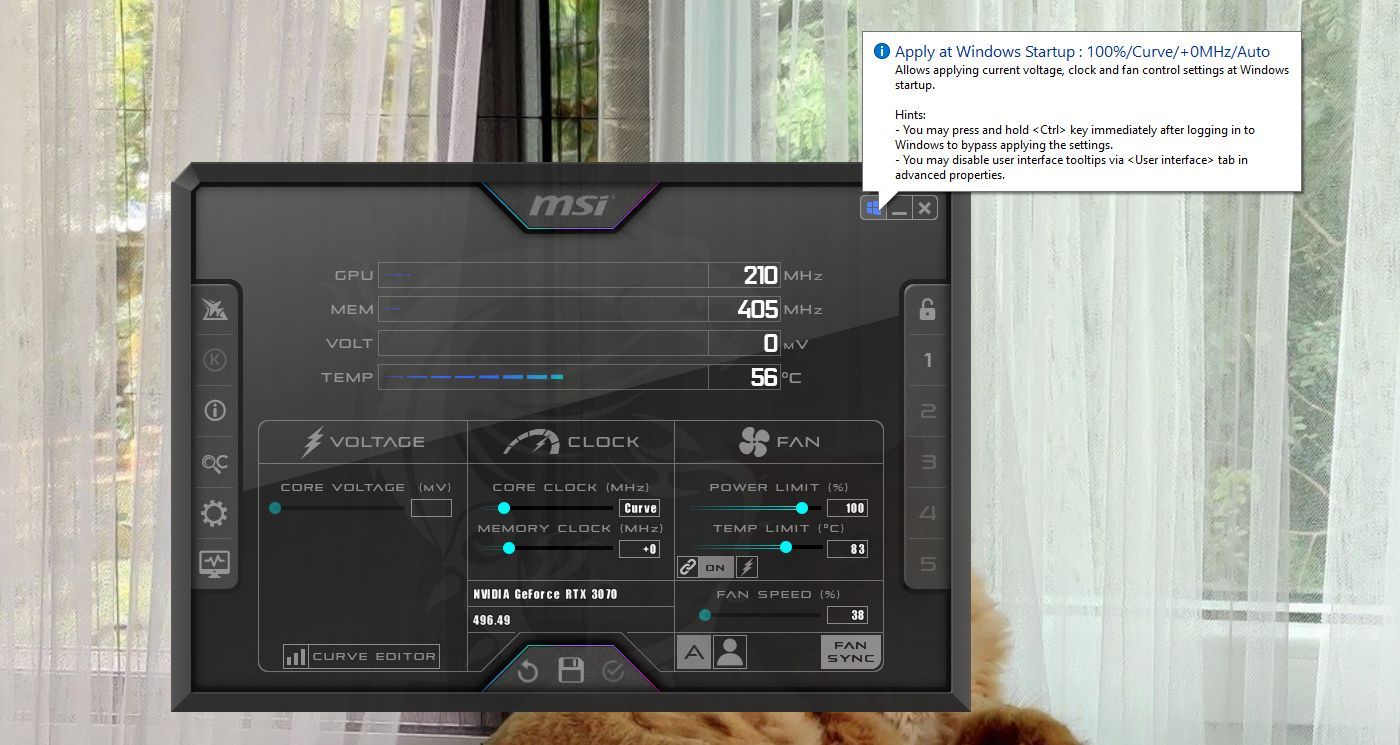
Once you are satisfied, save the underclock to one of the five preset Afterburner profiles. Clicking on the Windows icon (refer to the image above) automatically applies the undervolt at system start-up. This way, you don’t have to keep MSI Afterburner open to reap the benefits of the GPU undervolt.
Enjoy Silent Operation and Longer GPU Life
There isn’t much more to GPU undervolting. This should not only make your graphics card run cooler and quieter but should also prolong its lifespan. Running at a stable, locked frequency also has additional benefits, such as improved and consistent frame-pacing. This eliminates micro-stutters.
What’s more, modern GPUs (those featuring NVIDIA Boost, for example) tend to run at higher clock speeds when the GPU runs cooler. In some cases, this might even result in better than stock performance.